Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [13]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunohistochemistry [1]
- Other assay [10]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- 36-6800 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- CKS1 Polyclonal Antibody
- Antibody type
- Polyclonal
- Antigen
- Synthetic peptide
- Reactivity
- Human
- Host
- Rabbit
- Isotype
- IgG
- Vial size
- 100 μg
- Concentration
- 0.25 mg/mL
- Storage
- -20°C
Submitted references Repurposing a psychoactive drug for children with cancer: p27(Kip1)-dependent inhibition of metastatic neuroblastomas by Prozac.
PADI3 plays an antitumor role via the Hsp90/CKS1 pathway in colon cancer.
Hormonal and Growth Regulation of Epithelial and Stromal Cells From the Normal and Malignant Endometrium by Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor.
TGF-β activates APC through Cdh1 binding for Cks1 and Skp2 proteasomal destruction stabilizing p27kip1 for normal endometrial growth.
Upregulation of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors CDKN1B and CDKN1C in hepatocellular carcinoma-derived cells via goniothalamin-mediated protein stabilization and epigenetic modifications.
Identification and pharmacological inactivation of the MYCN gene network as a therapeutic strategy for neuroblastic tumor cells.
Tampering with cell division by using small-molecule inhibitors of CDK-CKS protein interactions.
Overexpression of CDC28 protein kinase regulatory subunit 1B confers an independent prognostic factor in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Epidermal growth factor upregulates Skp2/Cks1 and p27(kip1) in human extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cells.
In CD28-costimulated human naïve CD4+ T cells, I-κB kinase controls the expression of cell cycle regulatory proteins via interleukin-2-independent mechanisms.
TGFbeta prevents proteasomal degradation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27kip1 for cell cycle arrest.
Forkhead box M1 regulates the transcriptional network of genes essential for mitotic progression and genes encoding the SCF (Skp2-Cks1) ubiquitin ligase.
Control of the SCF(Skp2-Cks1) ubiquitin ligase by the APC/C(Cdh1) ubiquitin ligase.
Bibbo' S, Lamolinara A, Capone E, Purgato S, Tsakaneli A, Panella V, Sallese M, Rossi C, Ciufici P, Nieddu V, De Laurenzi V, Iezzi M, Perini G, Sala G, Sala A
Oncogenesis 2020 Jan 2;9(1):3
Oncogenesis 2020 Jan 2;9(1):3
PADI3 plays an antitumor role via the Hsp90/CKS1 pathway in colon cancer.
Chai Z, Wang L, Zheng Y, Liang N, Wang X, Zheng Y, Zhang Z, Zhao C, Zhu T, Liu C
Cancer cell international 2019;19:277
Cancer cell international 2019;19:277
Hormonal and Growth Regulation of Epithelial and Stromal Cells From the Normal and Malignant Endometrium by Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor.
Daubriac J, Pandya UM, Huang KT, Pavlides SC, Gama P, Blank SV, Shukla P, Crawford SE, Gold LI
Endocrinology 2017 Sep 1;158(9):2754-2773
Endocrinology 2017 Sep 1;158(9):2754-2773
TGF-β activates APC through Cdh1 binding for Cks1 and Skp2 proteasomal destruction stabilizing p27kip1 for normal endometrial growth.
Pavlides SC, Lecanda J, Daubriac J, Pandya UM, Gama P, Blank S, Mittal K, Shukla P, Gold LI
Cell cycle (Georgetown, Tex.) 2016;15(7):931-47
Cell cycle (Georgetown, Tex.) 2016;15(7):931-47
Upregulation of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors CDKN1B and CDKN1C in hepatocellular carcinoma-derived cells via goniothalamin-mediated protein stabilization and epigenetic modifications.
Peng YT, Wu WR, Chen LR, Kuo KK, Tsai CH, Huang YT, Lan YH, Chang FR, Wu YC, Shiue YL
Toxicology reports 2015;2:322-332
Toxicology reports 2015;2:322-332
Identification and pharmacological inactivation of the MYCN gene network as a therapeutic strategy for neuroblastic tumor cells.
Chayka O, D'Acunto CW, Middleton O, Arab M, Sala A
The Journal of biological chemistry 2015 Jan 23;290(4):2198-212
The Journal of biological chemistry 2015 Jan 23;290(4):2198-212
Tampering with cell division by using small-molecule inhibitors of CDK-CKS protein interactions.
Hamdi A, Lesnard A, Suzanne P, Robert T, Miteva MA, Pellerano M, Didier B, Ficko-Blean E, Lobstein A, Hibert M, Rault S, Morris MC, Colas P
Chembiochem : a European journal of chemical biology 2015 Feb 9;16(3):432-9
Chembiochem : a European journal of chemical biology 2015 Feb 9;16(3):432-9
Overexpression of CDC28 protein kinase regulatory subunit 1B confers an independent prognostic factor in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Lee SW, Lin CY, Tian YF, Sun DP, Lin LC, Chen LT, Hsing CH, Huang CT, Hsu HP, Huang HY, Wu LC, Li CF, Shiue YL
APMIS : acta pathologica, microbiologica, et immunologica Scandinavica 2014 Mar;122(3):206-14
APMIS : acta pathologica, microbiologica, et immunologica Scandinavica 2014 Mar;122(3):206-14
Epidermal growth factor upregulates Skp2/Cks1 and p27(kip1) in human extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cells.
Kim JY, Kim HJ, Park JH, Park DI, Cho YK, Sohn CI, Jeon WK, Kim BI, Kim DH, Chae SW, Sohn JH
World journal of gastroenterology 2014 Jan 21;20(3):755-73
World journal of gastroenterology 2014 Jan 21;20(3):755-73
In CD28-costimulated human naïve CD4+ T cells, I-κB kinase controls the expression of cell cycle regulatory proteins via interleukin-2-independent mechanisms.
Lupino E, Buccinnà B, Ramondetti C, Lomartire A, De Marco G, Ricotti E, Tovo PA, Rinaudo MT, Piccinini M
Immunology 2010 Oct;131(2):231-41
Immunology 2010 Oct;131(2):231-41
TGFbeta prevents proteasomal degradation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27kip1 for cell cycle arrest.
Lecanda J, Ganapathy V, D'Aquino-Ardalan C, Evans B, Cadacio C, Ayala A, Gold LI
Cell cycle (Georgetown, Tex.) 2009 Mar 1;8(5):742-56
Cell cycle (Georgetown, Tex.) 2009 Mar 1;8(5):742-56
Forkhead box M1 regulates the transcriptional network of genes essential for mitotic progression and genes encoding the SCF (Skp2-Cks1) ubiquitin ligase.
Wang IC, Chen YJ, Hughes D, Petrovic V, Major ML, Park HJ, Tan Y, Ackerson T, Costa RH
Molecular and cellular biology 2005 Dec;25(24):10875-94
Molecular and cellular biology 2005 Dec;25(24):10875-94
Control of the SCF(Skp2-Cks1) ubiquitin ligase by the APC/C(Cdh1) ubiquitin ligase.
Bashir T, Dorrello NV, Amador V, Guardavaccaro D, Pagano M
Nature 2004 Mar 11;428(6979):190-3
Nature 2004 Mar 11;428(6979):190-3
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
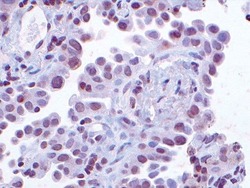
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemical staining of human non-small cell lung carcinoma tissue using Rb anti-Cks1 (Product # 36-6800). Image courtesy of Dr. Michele Pagano, New York University, NY.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
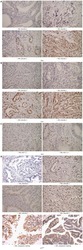
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
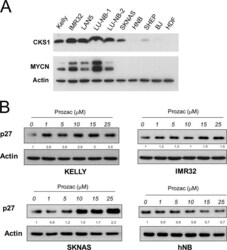
- FIGURE 7. SAHH, BLM, CKS1B, and PKMYT1 are highly expressed in naturally MYCN-amplified neuroblastoma cell lines. A , Western blot showing SAHH, BLM, PKMYT1, and CKS1B protein expression in a panel of MYCN -amplified and nonamplified Neuroblastoma cell lines. Actin was used as a loading control. B , Q-PCR demonstrating relative gene expression levels in the MYCN positive or negative Neuroblastoma cell lines. Gene expression levels in the non-MYCN-amplified cell line GIMEN was arbitrarily set to 1, and GAPDH expression was used for normalization. The error bars indicate standard deviation. *, p < 0.005; **, p < 0.001 (Student's t test n = 3).
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
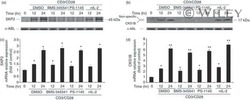
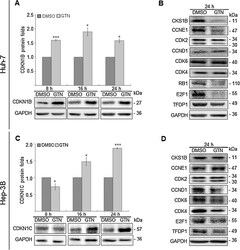
- Fig. 2 While Goniothalamin (GTN) increased the protein abundance of CDKN1B and CDKN1C, positive regulator proteins of G 1 to S phase were downregulated in Huh-7 and Hep-3B cells. Immunoblotting analysis demonstrated that (A, C) CDKN1B and CDKN1C protein levels were significantly upregulated after GTN treatments for 8, 16 and 24 h in Huh-7 cells; for 16 and 24 h in Hep-3B cells, respectively. (B, D) Of several CDKN1B and CKDN1C upstream and downstream G 1 and S regulators, GTN notably suppressed CKS1B, CCNE1, CDK2, RB1, E2F1 and TFDP1 protein levels in Huh-7; CDK2, CCND1, CDK6, CDK4, E2F1 and TFDP1 protein abundance in Hep-3B cells.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
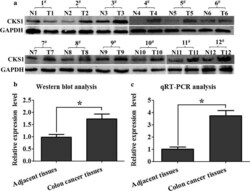
- Fig. 1 Expression profile of CKS1 in colon cancer and their corresponding adjacent tissues determined using qRT-PCR and Western blot analysis. a Western blot analysis was used to measure the expression level of CKS1 in colon cancer tissues and their corresponding adjacent tissues at the translational level. These paired tissue samples were obtained from 12 different patients; GAPDH was used to normalize the relative expression level of CKS1; b statistical analysis of Western blot; c qRT-PCR was used to measure the expression level of CKS1 in the colon cancer tissues and corresponding adjacent tissues at the transcriptional level. N: corresponding adjacent tissues, T: tumor tissues. *Indicates p < 0.05 for three independent experiments analyzed by Student's t test
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
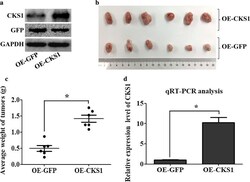
- Fig. 3 Function study of CKS1 in vivo. CKS1-expressing HCT116 cells were injected into the BALB/c nude mice to study the function of CKS1 in tumorigenesis, GFP-expressing HCT116 cells were injected into the BALB/c nude mice as the control group; a western blot analysis was used to confirm CKS1 expression level both in CKS1-expressing HCT116 cells and in GFP-expressing HCT116 cells; b tumors were dissected 42 days after cell injection, the upper group of tumors was developed from CKS1-expressing HCT116 cells, and the lower group of tumors was developed from GFP-expressing HCT116 cells; c tumors weight were measured and statistically analyzed; d qRT-PCR was used to measure the expression level of CKS1 in the tumor tissues dissected after 42 days injection. *Indicates p < 0.05 for three independent experiments analyzed by Student's t test
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
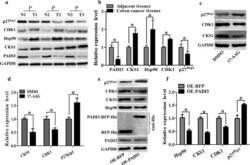
- Fig. 4 Both 17-AAG and PADI3 can suppress CKS1 expression in HCT116 cells. a Expression profile of PADI3, CKS1, Hsp90, CDK1 and p27 kip1 were detected using western blot in colon cancer tissues and their corresponding adjacent tissues at the translational level, GAPDH was used to normalize the relative expression of them; b statistical analysis of western blot results in A; c 5 muM 17-AAG was used to treat HCT116 cells for 24 h, and western blot was used to measure the expression level of CKS1, CDK1 and p27 kip1 ; d Statistic analysis of c ; e Overexpression of PADI3 was performed in HCT116 cells, and western blot was used to detect the expression level of Hsp90, CKS1, CDK1 and p27 kip1 , overexpression of RFP as the control group; f statistical analysis of western blot results in e . GAPDH was selected as the internal control, *indicates p < 0.05 for three independent experiments analyzed by Student's t test
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
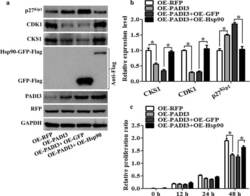
- Fig. 6 Function of Hsp90 on PADI3 regulated CKS1 expression. RFP stable expressing HCT116 cells as the negative control, PADI3 stable expressing HCT116 cells as the positive control, Hsp90 overexpression plasmid was transfected into the PADI3 stable expressing HCT116 cells to study the function of Hsp90 on PADI3 regulated CKS1 expression, GFP overexpression plasmid was transfected into the PADI3 stable expressing HCT116 cells as the negative control group. a Western blot was used to measure the expression level of CKS1, CDK1 and p27kip1 after Hsp90 transfected into PADI3 stable expressing HCT116 cells; b qRT-PCR was used to verify the results of a . c CCK8 analysis was used to study the function of Hsp90 in the regulating of cell proliferation in PADI3 stable expressing HCT116 cells. GAPDH was selected as the internal control, *indicates p < 0.05 for three independent experiments analyzed by Student's t test
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
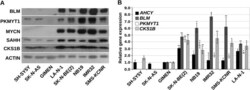
- Fig. 1 CKS1 and p27 expression in neuroblastoma cell lines. a Protein extracts from neuroblastoma cell lines (MYCN amplified = Kelly, IMR32, LAN5, LU-NB-1, LU-NB-2; non-MYCN amplified = SKNAS, SHEP, hNB), normal human dermal fibroblasts (hDF) or immortalised, non-tumourigenic, human fibroblasts (BJ) were subjected to western blot analysis with the indicated antibodies. b The selected neuroblastoma cell lines were cultured in the presence of increasing concentrations of Prozac and subjected to western blot analysis with a p27 antibody. Folds of p27 inductions relative to actin are indicated between the blots. Cells were lysed in RIPA Buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, 1% NP40, 0.1% SDS, 150 mM NaCl) supplemented with protease inhibitor cocktail (Sigma-Aldrich) and phosphatase inhibitor cocktail (Roche) for 30 min in ice. Insoluble material was removed by centrifugation (13,000 rpm for 20 min at 4 degC) and protein concentration was assessed by the method of Bradford. Equal amounts of protein were separated by SDS/PAGE on 15% polyacrylamide gel and transferred into nitrocellulose membrane. Membranes were blocked with 5% non-fat dry milk in PBS 0.1% Tween 20 for 1 h at room temperature and incubated with primary antibodies. The antibodies used were: N-Myc (sc-53993, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, 1:500 dilution), CKS1 (36-6800, Invitrogen 1:400 dilution), beta-Actin (A5441, Sigma-Aldrich 1:40000 dilution), p27 Kip1 (sc-1641, Santa Cruz Biotechnology 1:200 dilution). After washes, membranes were
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot ELISA
ELISA Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry