Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [1]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunocytochemistry [1]
- Other assay [2]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- PA5-65609 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- C11orf84 Polyclonal Antibody
- Antibody type
- Polyclonal
- Antigen
- Recombinant protein fragment
- Description
- Immunogen sequence: PGNKKPRGQRW KEPPGEEPVR KKRGRPMTKN LDPDPEPPSP DSPTETFAAP AEVRHFTDGS FPAGFVLQLF SHTQLRGPDS KDSPKDREVA EG Highest antigen sequence identity to the following orthologs - mouse 81%, rat 80%.
- Reactivity
- Human
- Host
- Rabbit
- Isotype
- IgG
- Vial size
- 100 μL
- Concentration
- 0.05 mg/mL
- Storage
- Store at 4°C short term. For long term storage, store at -20°C, avoiding freeze/thaw cycles.
Submitted references The Spin1 interactor, Spindoc, is dispensable for meiotic division, but essential for haploid spermatid development in mice.
Jiang X, Zhu X, Cheng Y, Azhar M, Xing X, Li W, Cao Y, Shi Q, Bao J
Reproductive biology and endocrinology : RB&E 2021 Sep 15;19(1):144
Reproductive biology and endocrinology : RB&E 2021 Sep 15;19(1):144
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
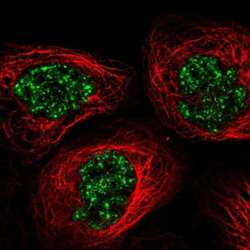
- Immunofluorescent staining of C11orf84 in human cell line A-431 shows localization to nuclear speckles. Samples were probed using a C11orf84 Polyclonal Antibody (Product # PA5-65609).
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
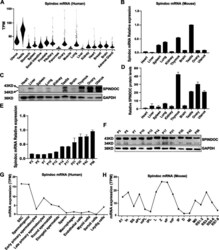
- Fig. 1 Spindoc is predominantly expressed in testis. (A) Violin plots showing the mRNA expression pattern of Spindoc in multiple human organs in the GTEx database (TPM, Transcripts Per Million). (B) RT-qPCR analyses of Spindoc mRNA levels across ten organs from adult wild-type (WT) mice. Data are presented as mean +- SEM, n = 3. ( C ) Western blot showing the expression levels of Spindoc protein among ten organs of WT adult mice. GAPDH served as a loading control. ( D ) Densitometric quantification of Spindoc protein levels as in ( C ). Data are presented as mean +- SEM, n = 3. ( E ) RT-qPCR analyses of Spindoc mRNA levels in developing testes. Testes at postnatal Day 3 (P3), P5, P7, P10, P12, P14, P17, P21, P35, P42 and P56 were analyzed. Data are presented as mean +- SEM, n = 3. ( F ) Western blot illustrating the Spindoc protein levels in developing testes. Testes at postnatal Day 3 (P3), P5, P7, P10, P12, P14, P17, P21, P35, P42 and P56 were analyzed. GAPDH served as a loading control. ( G ) Dynamic expression pattern of Spindoc mRNA from single cell RNA-seq analyses in adult human testes []. SSC, Spermatogonial Stem cells. ( H ) Dynamic expression levels of Spindoc mRNA from single cell RNA-seq analyses in RA-synchronized testicular cells []. A1, type A1 spermatogonia; In, intermediate spermatogonia; BS, S phase type B spermatogonia; ePL, early preleptotene; mPL, middle preleptotene; lPL, Late preleptotene; L, leptotene; Z, zygotene; eP, early pachytene; mP, middle pachy
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
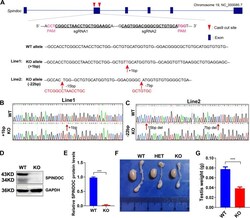
- Fig. 2 Generation of Spindoc knockout mouse models. ( A ) Schematic diagram shows the targeting strategy for generating Spindoc knockout (KO) mice using the CRISPR/Cas9 system. Blue boxes represent exons of the Spindoc gene on mouse chromosome 19. The genomic sequence targeted by a pair of sgRNAs are underlined with PAM sequences being highlighted in purple color. The red arrowheads point to the cut sites around exon 2 of Spindoc gene. Two F0 founder lines were generated - Line 1 carried 1 nt (T) insertion, while Line 2 carried a combination of 22 bp deletions as indicated; ( B, C ) Sanger sequencing of genomic DNA from mouse tail clips showing the frameshift variant (+ 1 nt) of KO mice (Line 1) (B), and the other frameshift variant (- 22 nt) (Line 2) (C); ( D ) Representative western blot analyses validated the Spindoc protein levels in WT and KO adult testes. GAPDH was used as a loading control. ( E ) Quantitative analysis of Spindoc protein levels in WT and KO adult testes. Data are presented as mean +- SEM, n = 3. P < 0.001 by student t-test . ( F ) Representative morphology of testes and epididymis from WT, Heterozygote (HET) and KO mice. The testis of KO was smaller than that of the WT; the epididymis of KO was more transparent than that of the WT. ( G ) Histogram showing the testis weights in WT and KO adult mice. Data are presented as mean +- SEM, n = 3. p < 0.001 by student t-test
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry