Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [70]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunocytochemistry [10]
- Immunoprecipitation [1]
- Immunohistochemistry [2]
- Flow cytometry [5]
- Other assay [9]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- MA5-13070 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- EGFR Monoclonal Antibody (H11)
- Antibody type
- Monoclonal
- Antigen
- Other
- Description
- MA5-13070 targets Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in FACS, ICC/IF, IHC (P), IP, and WB applications and shows reactivity with Human and Mouse samples. This antibody is not recommended for mouse lymph node tissue or human breast carcinoma in IHC applications. The MA5-13070 immunogen is hC2 20 d2 cells.
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse
- Host
- Mouse
- Isotype
- IgG
- Antibody clone number
- H11
- Vial size
- 500 μL
- Concentration
- 0.2 mg/mL
- Storage
- 4°C
Submitted references Epigenetic silencing and tumor suppressor gene of HAND2 by targeting ERK signaling in colorectal cancer.
CMTM5 inhibits the development of prostate cancer via the EGFR/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.
EGFR-Targeted Photodynamic Therapy.
Analysis of Increased EGFR and IGF-1R Signaling and Its Correlation with Socio-Epidemiological Features and Biological Profile in Breast Cancer Patients: A Study in Northern Brazil.
Growth and site-specific organization of micron-scale biomolecular devices on living mammalian cells.
The prognostic and predictive significance of cytokeratin 5/6 and epidermal growth factor receptor in metastatic triple-negative breast cancer treated with maintenance capecitabine.
Proteomics identifies EGF-like domain multiple 7 as a potential therapeutic target for epidermal growth factor receptor-positive glioma.
Mammalian Expression and In Situ Biotinylation of Extracellular Protein Targets for Directed Evolution.
Sortilin limits EGFR signaling by promoting its internalization in lung cancer.
MUC1 stimulates EGFR expression and function in endometrial cancer.
Multilayered, Hyaluronic Acid-Based Hydrogel Formulations Suitable for Automated 3D High Throughput Drug Screening of Cancer-Stromal Cell Cocultures.
Cross-talk between EGFR and T-cadherin: EGFR activation promotes T-cadherin localization to intercellular contacts.
Efficacy and mechanism of action of Proellex, an antiprogestin in aromatase overexpressing and Letrozole resistant T47D breast cancer cells.
Triepitopic antibody fusions inhibit cetuximab-resistant BRAF and KRAS mutant tumors via EGFR signal repression.
Trastuzumab induces antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) in HER-2-non-amplified breast cancer cell lines.
Coexpression of SGLT1 and EGFR is associated with tumor differentiation in oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Enrichment of circulating tumor cells from a large blood volume using leukapheresis and elutriation: proof of concept.
Glioblastoma-derived epidermal growth factor receptor carboxyl-terminal deletion mutants are transforming and are sensitive to EGFR-directed therapies.
(-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate down-regulates EGFR, MMP-2, MMP-9 and EMMPRIN and inhibits the invasion of MCF-7 tamoxifen-resistant cells.
Quantitative assays for the measurement of HER1-HER2 heterodimerization and phosphorylation in cell lines and breast tumors: applications for diagnostics and targeted drug mechanism of action.
Evaluation of PTEN and Mcl-1 expressions in NSCLC expressing wild-type or mutated EGFR.
Determination of the minimal melatonin exposure required to induce osteoblast differentiation from human mesenchymal stem cells and these effects on downstream signaling pathways.
Concurrent inhibition of NF-kappaB, cyclooxygenase-2, and epidermal growth factor receptor leads to greater anti-tumor activity in pancreatic cancer.
Design of surfaces for liquid crystal-based bioanalytical assays.
Activity and cellular localization of an oncogenic glioblastoma multiforme-associated EGF receptor mutant possessing a duplicated kinase domain.
Overexpression of cortactin increases invasion potential in oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Proteomic and immunologic analyses of brain tumor exosomes.
Epidermal growth factor receptor as a potential therapeutic target in triple-negative breast cancer.
Erlotinib and bevacizumab have synergistic activity against melanoma.
Endothelial expression of autocrine VEGF upon the uptake of tumor-derived microvesicles containing oncogenic EGFR.
Sennoside B inhibits PDGF receptor signaling and cell proliferation induced by PDGF-BB in human osteosarcoma cells.
miR-200 expression regulates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in bladder cancer cells and reverses resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor therapy.
Sensitivity to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor requires E-cadherin expression in urothelial carcinoma cells.
Overexpression of JKTBP1 induces androgen-independent LNCaP cell proliferation through activation of epidermal growth factor-receptor (EGF-R).
Acquired resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in cancer cells is mediated by loss of IGF-binding proteins.
Engineering of PDMS surfaces for use in microsystems for capture and isolation of complex and biomedically important proteins: epidermal growth factor receptor as a model system.
Activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase by 12-hydroxyheptadecatrienoic acid in prostate cancer PC3 cells.
EGF-independent activation of cell-surface EGF receptors harboring mutations found in gefitinib-sensitive lung cancer.
Type II combi-molecules: design and binary targeting properties of the novel triazolinium-containing molecules JDD36 and JDE05.
Truncation of annexin A1 is a regulatory lever for linking epidermal growth factor signaling with cytosolic phospholipase A2 in normal and malignant squamous epithelial cells.
Structure-guided development of affinity probes for tyrosine kinases using chemical genetics.
Radiotherapy response in oral squamous carcinoma cell lines: evaluation of apoptotic proteins as prognostic factors.
Improved transduction of human corneal epithelial progenitor cells with cell-targeting adenoviral vectors.
A dual PI3 kinase/mTOR inhibitor reveals emergent efficacy in glioma.
Novel toll-like receptor 9 agonist induces epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibition and synergistic antitumor activity with EGFR inhibitors.
Estrogen receptors in membrane lipid rafts and signal transduction in breast cancer.
Multiple acquired renal carcinoma tumor capabilities abolished upon silencing of ADAM17.
Herpes simplex virus 1 amplicon vector-mediated siRNA targeting epidermal growth factor receptor inhibits growth of human glioma cells in vivo.
Uncoupling between epidermal growth factor receptor and downstream signals defines resistance to the antiproliferative effect of Gefitinib in bladder cancer cells.
Inhibition of the type III epidermal growth factor receptor variant mutant receptor by dominant-negative EGFR-CD533 enhances malignant glioma cell radiosensitivity.
HER-2/neu overexpression increases the viable hypoxic cell population within solid tumors without causing changes in tumor vascularization.
In vivo antitumor activity of NVP-AEW541-A novel, potent, and selective inhibitor of the IGF-IR kinase.
In vivo antitumor activity of NVP-AEW541-A novel, potent, and selective inhibitor of the IGF-IR kinase.
AEE788: a dual family epidermal growth factor receptor/ErbB2 and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor with antitumor and antiangiogenic activity.
Expression of a naturally occurring constitutively active variant of the epidermal growth factor receptor in mouse fibroblasts increases motility.
The combi-targeting concept: dissection of the binary mechanism of action of the combi-triazene SMA41 in vitro and antitumor activity in vivo.
Domain-level antibody epitope mapping through yeast surface display of epidermal growth factor receptor fragments.
Broadly distributed chemical reactivity of natural antibodies expressed in coordination with specific antigen binding activity.
Combinatorial efficacy achieved through two-point blockade within a signaling pathway-a chemical genetic approach.
Inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor-mediated signaling by "Combi-triazene" BJ2000, a new probe for Combi-Targeting postulates.
Epidermal growth factor receptor mutation type III transfected into a small cell lung cancer cell line is predominantly localized at the cell surface and enhances the malignant phenotype.
Epidermal growth factor receptor mutation type III transfected into a small cell lung cancer cell line is predominantly localized at the cell surface and enhances the malignant phenotype.
Neuregulin expression, function, and signaling in human ovarian cancer cells.
Adenovirus-mediated overexpression of dominant negative epidermal growth factor receptor-CD533 as a gene therapeutic approach radiosensitizes human carcinoma and malignant glioma cells.
Adenovirus-mediated overexpression of dominant negative epidermal growth factor receptor-CD533 as a gene therapeutic approach radiosensitizes human carcinoma and malignant glioma cells.
Physical interaction between epidermal growth factor receptor and DNA-dependent protein kinase in mammalian cells.
Physical interaction between epidermal growth factor receptor and DNA-dependent protein kinase in mammalian cells.
Cell migration and MMP-9 secretion are increased by epidermal growth factor in HaCaT-ras transfected cells.
Cell migration and MMP-9 secretion are increased by epidermal growth factor in HaCaT-ras transfected cells.
Monoclonal antibodies against EGFRvIII are tumor specific and react with breast and lung carcinomas and malignant gliomas.
Yuan Z, Yu X, Chen W, Chen D, Cai J, Jiang Y, Liu X, Wu Z, Wang L, Grady WM, Wang H
Cell communication and signaling : CCS 2022 Jul 23;20(1):111
Cell communication and signaling : CCS 2022 Jul 23;20(1):111
CMTM5 inhibits the development of prostate cancer via the EGFR/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.
Li L, Hu Y, Chen D, Zhu J, Bao W, Xu X, Chen H, Chen W, Feng R
Molecular medicine reports 2022 Jan;25(1)
Molecular medicine reports 2022 Jan;25(1)
EGFR-Targeted Photodynamic Therapy.
Ulfo L, Costantini PE, Di Giosia M, Danielli A, Calvaresi M
Pharmaceutics 2022 Jan 20;14(2)
Pharmaceutics 2022 Jan 20;14(2)
Analysis of Increased EGFR and IGF-1R Signaling and Its Correlation with Socio-Epidemiological Features and Biological Profile in Breast Cancer Patients: A Study in Northern Brazil.
Silva Rocha F, da Silva Maués JH, Brito Lins Pereira CM, Moreira-Nunes CA, Rodriguez Burbano RM
Breast cancer (Dove Medical Press) 2021;13:325-339
Breast cancer (Dove Medical Press) 2021;13:325-339
Growth and site-specific organization of micron-scale biomolecular devices on living mammalian cells.
Jia S, Phua SC, Nihongaki Y, Li Y, Pacella M, Li Y, Mohammed AM, Sun S, Inoue T, Schulman R
Nature communications 2021 Sep 30;12(1):5729
Nature communications 2021 Sep 30;12(1):5729
The prognostic and predictive significance of cytokeratin 5/6 and epidermal growth factor receptor in metastatic triple-negative breast cancer treated with maintenance capecitabine.
Zhu Y, Li K, Zhang J, Wang L, Sheng L, Yan L
Translational cancer research 2021 Mar;10(3):1193-1203
Translational cancer research 2021 Mar;10(3):1193-1203
Proteomics identifies EGF-like domain multiple 7 as a potential therapeutic target for epidermal growth factor receptor-positive glioma.
Wang FY, Wang-Gou SY, Cao H, Jiang N, Yang Q, Huang Q, Huang CH, Li XJ
Cancer communications (London, England) 2020 Oct;40(10):518-530
Cancer communications (London, England) 2020 Oct;40(10):518-530
Mammalian Expression and In Situ Biotinylation of Extracellular Protein Targets for Directed Evolution.
Grindel BJ, Engel BJ, Hall CG, Kelderhouse LE, Lucci A, Zacharias NM, Takahashi TT, Millward SW
ACS omega 2020 Oct 6;5(39):25440-25455
ACS omega 2020 Oct 6;5(39):25440-25455
Sortilin limits EGFR signaling by promoting its internalization in lung cancer.
Al-Akhrass H, Naves T, Vincent F, Magnaudeix A, Durand K, Bertin F, Melloni B, Jauberteau MO, Lalloué F
Nature communications 2017 Oct 30;8(1):1182
Nature communications 2017 Oct 30;8(1):1182
MUC1 stimulates EGFR expression and function in endometrial cancer.
Engel BJ, Bowser JL, Broaddus RR, Carson DD
Oncotarget 2016 May 31;7(22):32796-809
Oncotarget 2016 May 31;7(22):32796-809
Multilayered, Hyaluronic Acid-Based Hydrogel Formulations Suitable for Automated 3D High Throughput Drug Screening of Cancer-Stromal Cell Cocultures.
Engel BJ, Constantinou PE, Sablatura LK, Doty NJ, Carson DD, Farach-Carson MC, Harrington DA, Zarembinski TI
Advanced healthcare materials 2015 Aug 5;4(11):1664-74
Advanced healthcare materials 2015 Aug 5;4(11):1664-74
Cross-talk between EGFR and T-cadherin: EGFR activation promotes T-cadherin localization to intercellular contacts.
Kyriakakis E, Maslova K, Frachet A, Ferri N, Contini A, Pfaff D, Erne P, Resink TJ, Philippova M
Cellular signalling 2013 May;25(5):1044-53
Cellular signalling 2013 May;25(5):1044-53
Efficacy and mechanism of action of Proellex, an antiprogestin in aromatase overexpressing and Letrozole resistant T47D breast cancer cells.
Gupta A, Mehta R, Alimirah F, Peng X, Murillo G, Wiehle R, Mehta RG
The Journal of steroid biochemistry and molecular biology 2013 Jan;133:30-42
The Journal of steroid biochemistry and molecular biology 2013 Jan;133:30-42
Triepitopic antibody fusions inhibit cetuximab-resistant BRAF and KRAS mutant tumors via EGFR signal repression.
Spangler JB, Manzari MT, Rosalia EK, Chen TF, Wittrup KD
Journal of molecular biology 2012 Sep 28;422(4):532-44
Journal of molecular biology 2012 Sep 28;422(4):532-44
Trastuzumab induces antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) in HER-2-non-amplified breast cancer cell lines.
Collins DM, O'Donovan N, McGowan PM, O'Sullivan F, Duffy MJ, Crown J
Annals of oncology : official journal of the European Society for Medical Oncology 2012 Jul;23(7):1788-95
Annals of oncology : official journal of the European Society for Medical Oncology 2012 Jul;23(7):1788-95
Coexpression of SGLT1 and EGFR is associated with tumor differentiation in oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Hanabata Y, Nakajima Y, Morita K, Kayamori K, Omura K
Odontology 2012 Jul;100(2):156-63
Odontology 2012 Jul;100(2):156-63
Enrichment of circulating tumor cells from a large blood volume using leukapheresis and elutriation: proof of concept.
Eifler RL, Lind J, Falkenhagen D, Weber V, Fischer MB, Zeillinger R
Cytometry. Part B, Clinical cytometry 2011 Mar;80(2):100-11
Cytometry. Part B, Clinical cytometry 2011 Mar;80(2):100-11
Glioblastoma-derived epidermal growth factor receptor carboxyl-terminal deletion mutants are transforming and are sensitive to EGFR-directed therapies.
Cho J, Pastorino S, Zeng Q, Xu X, Johnson W, Vandenberg S, Verhaak R, Cherniack AD, Watanabe H, Dutt A, Kwon J, Chao YS, Onofrio RC, Chiang D, Yuza Y, Kesari S, Meyerson M
Cancer research 2011 Dec 15;71(24):7587-96
Cancer research 2011 Dec 15;71(24):7587-96
(-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate down-regulates EGFR, MMP-2, MMP-9 and EMMPRIN and inhibits the invasion of MCF-7 tamoxifen-resistant cells.
Farabegoli F, Papi A, Orlandi M
Bioscience reports 2011 Apr;31(2):99-108
Bioscience reports 2011 Apr;31(2):99-108
Quantitative assays for the measurement of HER1-HER2 heterodimerization and phosphorylation in cell lines and breast tumors: applications for diagnostics and targeted drug mechanism of action.
DeFazio-Eli L, Strommen K, Dao-Pick T, Parry G, Goodman L, Winslow J
Breast cancer research : BCR 2011 Apr 15;13(2):R44
Breast cancer research : BCR 2011 Apr 15;13(2):R44
Evaluation of PTEN and Mcl-1 expressions in NSCLC expressing wild-type or mutated EGFR.
Cetin Z, Ozbilim G, Erdogan A, Luleci G, Karauzum SB
Medical oncology (Northwood, London, England) 2010 Sep;27(3):853-60
Medical oncology (Northwood, London, England) 2010 Sep;27(3):853-60
Determination of the minimal melatonin exposure required to induce osteoblast differentiation from human mesenchymal stem cells and these effects on downstream signaling pathways.
Sethi S, Radio NM, Kotlarczyk MP, Chen CT, Wei YH, Jockers R, Witt-Enderby PA
Journal of pineal research 2010 Oct;49(3):222-38
Journal of pineal research 2010 Oct;49(3):222-38
Concurrent inhibition of NF-kappaB, cyclooxygenase-2, and epidermal growth factor receptor leads to greater anti-tumor activity in pancreatic cancer.
Ali S, Banerjee S, Schaffert JM, El-Rayes BF, Philip PA, Sarkar FH
Journal of cellular biochemistry 2010 May;110(1):171-81
Journal of cellular biochemistry 2010 May;110(1):171-81
Design of surfaces for liquid crystal-based bioanalytical assays.
Lowe AM, Ozer BH, Bai Y, Bertics PJ, Abbott NL
ACS applied materials & interfaces 2010 Mar;2(3):722-31
ACS applied materials & interfaces 2010 Mar;2(3):722-31
Activity and cellular localization of an oncogenic glioblastoma multiforme-associated EGF receptor mutant possessing a duplicated kinase domain.
Ozer BH, Wiepz GJ, Bertics PJ
Oncogene 2010 Feb 11;29(6):855-64
Oncogene 2010 Feb 11;29(6):855-64
Overexpression of cortactin increases invasion potential in oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Yamada S, Yanamoto S, Kawasaki G, Mizuno A, Nemoto TK
Pathology oncology research : POR 2010 Dec;16(4):523-31
Pathology oncology research : POR 2010 Dec;16(4):523-31
Proteomic and immunologic analyses of brain tumor exosomes.
Graner MW, Alzate O, Dechkovskaia AM, Keene JD, Sampson JH, Mitchell DA, Bigner DD
FASEB journal : official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology 2009 May;23(5):1541-57
FASEB journal : official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology 2009 May;23(5):1541-57
Epidermal growth factor receptor as a potential therapeutic target in triple-negative breast cancer.
Corkery B, Crown J, Clynes M, O'Donovan N
Annals of oncology : official journal of the European Society for Medical Oncology 2009 May;20(5):862-7
Annals of oncology : official journal of the European Society for Medical Oncology 2009 May;20(5):862-7
Erlotinib and bevacizumab have synergistic activity against melanoma.
Schicher N, Paulitschke V, Swoboda A, Kunstfeld R, Loewe R, Pilarski P, Pehamberger H, Hoeller C
Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2009 May 15;15(10):3495-502
Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2009 May 15;15(10):3495-502
Endothelial expression of autocrine VEGF upon the uptake of tumor-derived microvesicles containing oncogenic EGFR.
Al-Nedawi K, Meehan B, Kerbel RS, Allison AC, Rak J
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2009 Mar 10;106(10):3794-9
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2009 Mar 10;106(10):3794-9
Sennoside B inhibits PDGF receptor signaling and cell proliferation induced by PDGF-BB in human osteosarcoma cells.
Chen YC, Chang CN, Hsu HC, Chiou SJ, Lee LT, Hseu TH
Life sciences 2009 Jun 19;84(25-26):915-22
Life sciences 2009 Jun 19;84(25-26):915-22
miR-200 expression regulates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in bladder cancer cells and reverses resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor therapy.
Adam L, Zhong M, Choi W, Qi W, Nicoloso M, Arora A, Calin G, Wang H, Siefker-Radtke A, McConkey D, Bar-Eli M, Dinney C
Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2009 Aug 15;15(16):5060-72
Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2009 Aug 15;15(16):5060-72
Sensitivity to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor requires E-cadherin expression in urothelial carcinoma cells.
Black PC, Brown GA, Inamoto T, Shrader M, Arora A, Siefker-Radtke AO, Adam L, Theodorescu D, Wu X, Munsell MF, Bar-Eli M, McConkey DJ, Dinney CP
Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2008 Mar 1;14(5):1478-86
Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2008 Mar 1;14(5):1478-86
Overexpression of JKTBP1 induces androgen-independent LNCaP cell proliferation through activation of epidermal growth factor-receptor (EGF-R).
Wu YY, Li H, Lv XY, Wei Q, Li X, Liu XY, Zhou Q, Wei YQ
Cell biochemistry and function 2008 Jun;26(4):467-77
Cell biochemistry and function 2008 Jun;26(4):467-77
Acquired resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in cancer cells is mediated by loss of IGF-binding proteins.
Guix M, Faber AC, Wang SE, Olivares MG, Song Y, Qu S, Rinehart C, Seidel B, Yee D, Arteaga CL, Engelman JA
The Journal of clinical investigation 2008 Jul;118(7):2609-19
The Journal of clinical investigation 2008 Jul;118(7):2609-19
Engineering of PDMS surfaces for use in microsystems for capture and isolation of complex and biomedically important proteins: epidermal growth factor receptor as a model system.
Lowe AM, Ozer BH, Wiepz GJ, Bertics PJ, Abbott NL
Lab on a chip 2008 Aug;8(8):1357-64
Lab on a chip 2008 Aug;8(8):1357-64
Activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase by 12-hydroxyheptadecatrienoic acid in prostate cancer PC3 cells.
Li X, Wei J, Tai HH
Archives of biochemistry and biophysics 2007 Nov 1;467(1):20-30
Archives of biochemistry and biophysics 2007 Nov 1;467(1):20-30
EGF-independent activation of cell-surface EGF receptors harboring mutations found in gefitinib-sensitive lung cancer.
Choi SH, Mendrola JM, Lemmon MA
Oncogene 2007 Mar 8;26(11):1567-76
Oncogene 2007 Mar 8;26(11):1567-76
Type II combi-molecules: design and binary targeting properties of the novel triazolinium-containing molecules JDD36 and JDE05.
Qiu Q, Domarkas J, Banerjee R, Katsoulas A, McNamee JP, Jean-Claude BJ
Anti-cancer drugs 2007 Feb;18(2):171-7
Anti-cancer drugs 2007 Feb;18(2):171-7
Truncation of annexin A1 is a regulatory lever for linking epidermal growth factor signaling with cytosolic phospholipase A2 in normal and malignant squamous epithelial cells.
Sakaguchi M, Murata H, Sonegawa H, Sakaguchi Y, Futami J, Kitazoe M, Yamada H, Huh NH
The Journal of biological chemistry 2007 Dec 7;282(49):35679-86
The Journal of biological chemistry 2007 Dec 7;282(49):35679-86
Structure-guided development of affinity probes for tyrosine kinases using chemical genetics.
Blair JA, Rauh D, Kung C, Yun CH, Fan QW, Rode H, Zhang C, Eck MJ, Weiss WA, Shokat KM
Nature chemical biology 2007 Apr;3(4):229-38
Nature chemical biology 2007 Apr;3(4):229-38
Radiotherapy response in oral squamous carcinoma cell lines: evaluation of apoptotic proteins as prognostic factors.
Roberg K, Jonsson AC, Grénman R, Norberg-Spaak L
Head & neck 2007 Apr;29(4):325-34
Head & neck 2007 Apr;29(4):325-34
Improved transduction of human corneal epithelial progenitor cells with cell-targeting adenoviral vectors.
Chen Z, Mok H, Pflugfelder SC, Li DQ, Barry MA
Experimental eye research 2006 Oct;83(4):798-806
Experimental eye research 2006 Oct;83(4):798-806
A dual PI3 kinase/mTOR inhibitor reveals emergent efficacy in glioma.
Fan QW, Knight ZA, Goldenberg DD, Yu W, Mostov KE, Stokoe D, Shokat KM, Weiss WA
Cancer cell 2006 May;9(5):341-9
Cancer cell 2006 May;9(5):341-9
Novel toll-like receptor 9 agonist induces epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibition and synergistic antitumor activity with EGFR inhibitors.
Damiano V, Caputo R, Bianco R, D'Armiento FP, Leonardi A, De Placido S, Bianco AR, Agrawal S, Ciardiello F, Tortora G
Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2006 Jan 15;12(2):577-83
Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2006 Jan 15;12(2):577-83
Estrogen receptors in membrane lipid rafts and signal transduction in breast cancer.
Márquez DC, Chen HW, Curran EM, Welshons WV, Pietras RJ
Molecular and cellular endocrinology 2006 Feb 26;246(1-2):91-100
Molecular and cellular endocrinology 2006 Feb 26;246(1-2):91-100
Multiple acquired renal carcinoma tumor capabilities abolished upon silencing of ADAM17.
Franovic A, Robert I, Smith K, Kurban G, Pause A, Gunaratnam L, Lee S
Cancer research 2006 Aug 15;66(16):8083-90
Cancer research 2006 Aug 15;66(16):8083-90
Herpes simplex virus 1 amplicon vector-mediated siRNA targeting epidermal growth factor receptor inhibits growth of human glioma cells in vivo.
Saydam O, Glauser DL, Heid I, Turkeri G, Hilbe M, Jacobs AH, Ackermann M, Fraefel C
Molecular therapy : the journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy 2005 Nov;12(5):803-12
Molecular therapy : the journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy 2005 Nov;12(5):803-12
Uncoupling between epidermal growth factor receptor and downstream signals defines resistance to the antiproliferative effect of Gefitinib in bladder cancer cells.
Kassouf W, Dinney CP, Brown G, McConkey DJ, Diehl AJ, Bar-Eli M, Adam L
Cancer research 2005 Nov 15;65(22):10524-35
Cancer research 2005 Nov 15;65(22):10524-35
Inhibition of the type III epidermal growth factor receptor variant mutant receptor by dominant-negative EGFR-CD533 enhances malignant glioma cell radiosensitivity.
Lammering G, Hewit TH, Holmes M, Valerie K, Hawkins W, Lin PS, Mikkelsen RB, Schmidt-Ullrich RK
Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2004 Oct 1;10(19):6732-43
Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2004 Oct 1;10(19):6732-43
HER-2/neu overexpression increases the viable hypoxic cell population within solid tumors without causing changes in tumor vascularization.
Dragowska WH, Warburton C, Yapp DT, Minchinton AI, Hu Y, Waterhouse DN, Gelmon K, Skov K, Woo J, Masin D, Huxham LA, Kyle AH, Bally MB
Molecular cancer research : MCR 2004 Nov;2(11):606-19
Molecular cancer research : MCR 2004 Nov;2(11):606-19
In vivo antitumor activity of NVP-AEW541-A novel, potent, and selective inhibitor of the IGF-IR kinase.
García-Echeverría C, Pearson MA, Marti A, Meyer T, Mestan J, Zimmermann J, Gao J, Brueggen J, Capraro HG, Cozens R, Evans DB, Fabbro D, Furet P, Porta DG, Liebetanz J, Martiny-Baron G, Ruetz S, Hofmann F
Cancer cell 2004 Mar;5(3):231-9
Cancer cell 2004 Mar;5(3):231-9
In vivo antitumor activity of NVP-AEW541-A novel, potent, and selective inhibitor of the IGF-IR kinase.
García-Echeverría C, Pearson MA, Marti A, Meyer T, Mestan J, Zimmermann J, Gao J, Brueggen J, Capraro HG, Cozens R, Evans DB, Fabbro D, Furet P, Porta DG, Liebetanz J, Martiny-Baron G, Ruetz S, Hofmann F
Cancer cell 2004 Mar;5(3):231-9
Cancer cell 2004 Mar;5(3):231-9
AEE788: a dual family epidermal growth factor receptor/ErbB2 and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor with antitumor and antiangiogenic activity.
Traxler P, Allegrini PR, Brandt R, Brueggen J, Cozens R, Fabbro D, Grosios K, Lane HA, McSheehy P, Mestan J, Meyer T, Tang C, Wartmann M, Wood J, Caravatti G
Cancer research 2004 Jul 15;64(14):4931-41
Cancer research 2004 Jul 15;64(14):4931-41
Expression of a naturally occurring constitutively active variant of the epidermal growth factor receptor in mouse fibroblasts increases motility.
Pedersen MW, Tkach V, Pedersen N, Berezin V, Poulsen HS
International journal of cancer 2004 Feb 20;108(5):643-53
International journal of cancer 2004 Feb 20;108(5):643-53
The combi-targeting concept: dissection of the binary mechanism of action of the combi-triazene SMA41 in vitro and antitumor activity in vivo.
Matheson SL, McNamee JP, Wang T, Alaoui-Jamali MA, Tari AM, Jean-Claude BJ
The Journal of pharmacology and experimental therapeutics 2004 Dec;311(3):1163-70
The Journal of pharmacology and experimental therapeutics 2004 Dec;311(3):1163-70
Domain-level antibody epitope mapping through yeast surface display of epidermal growth factor receptor fragments.
Cochran JR, Kim YS, Olsen MJ, Bhandari R, Wittrup KD
Journal of immunological methods 2004 Apr;287(1-2):147-58
Journal of immunological methods 2004 Apr;287(1-2):147-58
Broadly distributed chemical reactivity of natural antibodies expressed in coordination with specific antigen binding activity.
Planque S, Taguchi H, Burr G, Bhatia G, Karle S, Zhou YX, Nishiyama Y, Paul S
The Journal of biological chemistry 2003 May 30;278(22):20436-43
The Journal of biological chemistry 2003 May 30;278(22):20436-43
Combinatorial efficacy achieved through two-point blockade within a signaling pathway-a chemical genetic approach.
Fan QW, Specht KM, Zhang C, Goldenberg DD, Shokat KM, Weiss WA
Cancer research 2003 Dec 15;63(24):8930-8
Cancer research 2003 Dec 15;63(24):8930-8
Inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor-mediated signaling by "Combi-triazene" BJ2000, a new probe for Combi-Targeting postulates.
Brahimi F, Matheson SL, Dudouit F, McNamee JP, Tari AM, Jean-Claude BJ
The Journal of pharmacology and experimental therapeutics 2002 Oct;303(1):238-46
The Journal of pharmacology and experimental therapeutics 2002 Oct;303(1):238-46
Epidermal growth factor receptor mutation type III transfected into a small cell lung cancer cell line is predominantly localized at the cell surface and enhances the malignant phenotype.
Damstrup L, Wandahl Pedersen M, Bastholm L, Elling F, Skovgaard Poulsen H
International journal of cancer 2002 Jan 1;97(1):7-14
International journal of cancer 2002 Jan 1;97(1):7-14
Epidermal growth factor receptor mutation type III transfected into a small cell lung cancer cell line is predominantly localized at the cell surface and enhances the malignant phenotype.
Damstrup L, Wandahl Pedersen M, Bastholm L, Elling F, Skovgaard Poulsen H
International journal of cancer 2002 Jan 1;97(1):7-14
International journal of cancer 2002 Jan 1;97(1):7-14
Neuregulin expression, function, and signaling in human ovarian cancer cells.
Gilmour LM, Macleod KG, McCaig A, Sewell JM, Gullick WJ, Smyth JF, Langdon SP
Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2002 Dec;8(12):3933-42
Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2002 Dec;8(12):3933-42
Adenovirus-mediated overexpression of dominant negative epidermal growth factor receptor-CD533 as a gene therapeutic approach radiosensitizes human carcinoma and malignant glioma cells.
Lammering G, Lin PS, Contessa JN, Hampton JL, Valerie K, Schmidt-Ullrich RK
International journal of radiation oncology, biology, physics 2001 Nov 1;51(3):775-84
International journal of radiation oncology, biology, physics 2001 Nov 1;51(3):775-84
Adenovirus-mediated overexpression of dominant negative epidermal growth factor receptor-CD533 as a gene therapeutic approach radiosensitizes human carcinoma and malignant glioma cells.
Lammering G, Lin PS, Contessa JN, Hampton JL, Valerie K, Schmidt-Ullrich RK
International journal of radiation oncology, biology, physics 2001 Nov 1;51(3):775-84
International journal of radiation oncology, biology, physics 2001 Nov 1;51(3):775-84
Physical interaction between epidermal growth factor receptor and DNA-dependent protein kinase in mammalian cells.
Bandyopadhyay D, Mandal M, Adam L, Mendelsohn J, Kumar R
The Journal of biological chemistry 1998 Jan 16;273(3):1568-73
The Journal of biological chemistry 1998 Jan 16;273(3):1568-73
Physical interaction between epidermal growth factor receptor and DNA-dependent protein kinase in mammalian cells.
Bandyopadhyay D, Mandal M, Adam L, Mendelsohn J, Kumar R
The Journal of biological chemistry 1998 Jan 16;273(3):1568-73
The Journal of biological chemistry 1998 Jan 16;273(3):1568-73
Cell migration and MMP-9 secretion are increased by epidermal growth factor in HaCaT-ras transfected cells.
Charvat S, Chignol MC, Souchier C, Le Griel C, Schmitt D, Serres M
Experimental dermatology 1998 Aug;7(4):184-90
Experimental dermatology 1998 Aug;7(4):184-90
Cell migration and MMP-9 secretion are increased by epidermal growth factor in HaCaT-ras transfected cells.
Charvat S, Chignol MC, Souchier C, Le Griel C, Schmitt D, Serres M
Experimental dermatology 1998 Aug;7(4):184-90
Experimental dermatology 1998 Aug;7(4):184-90
Monoclonal antibodies against EGFRvIII are tumor specific and react with breast and lung carcinomas and malignant gliomas.
Wikstrand CJ, Hale LP, Batra SK, Hill ML, Humphrey PA, Kurpad SN, McLendon RE, Moscatello D, Pegram CN, Reist CJ
Cancer research 1995 Jul 15;55(14):3140-8
Cancer research 1995 Jul 15;55(14):3140-8
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
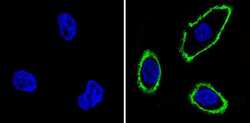
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (green) showing staining in the membrane of A431 cells (right) compared to a negative control without primary antibody (left). Formalin-fixed cells were permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 in TBS for 5-10 minutes and blocked with 3% BSA-PBS for 30 minutes at room temperature. Cells were probed with an Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor monoclonal antibody (Product # MA5-13070) in 3% BSA-PBS at a dilution of 1:100 and incubated overnight at 4 ºC in a humidified chamber. Cells were washed with PBST and incubated with a DyLight-conjugated secondary antibody in PBS at room temperature in the dark. F-actin (red) was stained with a fluorescent red phalloidin and nuclei (blue) were stained with Hoechst or DAPI. Images were taken at a magnification of 60x.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
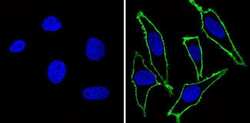
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (green) showing staining in the membrane of Hela cells (right) compared to a negative control without primary antibody (left). Formalin-fixed cells were permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 in TBS for 5-10 minutes and blocked with 3% BSA-PBS for 30 minutes at room temperature. Cells were probed with an Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor monoclonal antibody (Product # MA5-13070) in 3% BSA-PBS at a dilution of 1:100 and incubated overnight at 4 ºC in a humidified chamber. Cells were washed with PBST and incubated with a DyLight-conjugated secondary antibody in PBS at room temperature in the dark. F-actin (red) was stained with a fluorescent red phalloidin and nuclei (blue) were stained with Hoechst or DAPI. Images were taken at a magnification of 60x.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
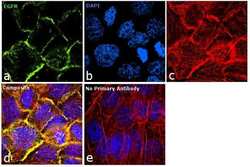
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescence analysis of EGFR was performed using 90% confluent log phase A-431 cells. The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 minutes, permeabilized with 0.1% Triton™ X-100 for 10 minutes, and blocked with 1% BSA for 1 hour at room temperature. The cells were labeled with EGFR Mouse monoclonal antibody (Product # MA5-13070) at 2 µg/mL in 0.1% BSA and incubated for 3 hours at room temperature and then labeled with Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Superclonal™ Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor® 488 conjugate (Product # A28175) at a dilution of 1:2000 for 45 minutes at room temperature (Panel a: green). Nuclei (Panel b: blue) were stained with SlowFade® Gold Antifade Mountant with DAPI (Product # S36938). F-actin (Panel c: red) was stained with Rhodamine Phalloidin (Product # R415, 1:300). Panel d represents the merged image showing membrane localization. Panel e shows the no primary antibody control. The images were captured at 60X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
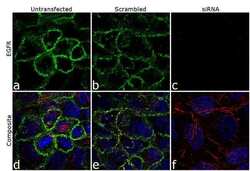
- Experimental details
- Knockdown of EGFR was achieved by transfecting A-431 cells with EGFR specific siRNA (Silencer® select Product # s563, s564 and s565). Immunofluorescence analysis was performed on A431 cells (untransfected, panel a,d), transfected with non-specific scrambled siRNA (panels b,e) and transfected with EGFR specific siRNA (panel c,f) Cells were fixed, permeabilized, and labelled with EGFR Mouse monoclonal Antibody (Product # MA5-13070, 5 µg/mL), followed by Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Superclonal™ Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor® 488 conjugate (Product # A28175, 1:2000). Nuclei (blue) were stained using SlowFade® Gold Antifade Mountant with DAPI (Product # S36938), and Rhodamine Phalloidin (Product # R415, 1:300) was used for cytoskeletal F-actin (red) staining. Loss of signal was observed upon siRNA mediated knockdown (panel c,f) confirming specificity of the antibody to EGFR (green). The images were captured at 60X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
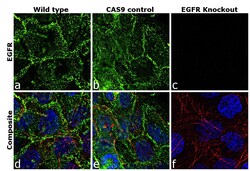
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescence analysis of EGFR was performed using 70% confluent log phase A-431 cells (WIld type, panels a,d), CAS9 control (panels b,e) and EGFR Knockout (panels c,f). The cells were fixed, permeabilized, and labelled with EGFR Mouse Monoclonal Antibody(Product # MA5-13070, 5 µg/mL), followed by Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Superclonal™ Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor® 488 conjugate (Product # A28175, 1:2000). Nuclei (blue) were stained with SlowFade® Gold Antifade Mountant with DAPI (Product # S36938) and Rhodamine Phalloidin (Product # R415, 1:300) was used for cytoskeletal F-actin (red) staining. Loss of signal was observed in EGFR Knockout cells (panel c,f) confirming specificity of the antibody to EGFR(green). The images were captured at 60X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
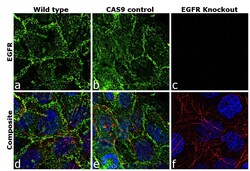
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescence analysis of EGFR was performed using 70% confluent log phase A-431 cells (WIld type, panels a,d), CAS9 control (panels b,e) and EGFR Knockout (panels c,f). The cells were fixed, permeabilized, and labelled with EGFR Mouse Monoclonal Antibody(Product # MA5-13070, 5 µg/mL), followed by Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Superclonal™ Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor® 488 conjugate (Product # A28175, 1:2000). Nuclei (blue) were stained with SlowFade® Gold Antifade Mountant with DAPI (Product # S36938) and Rhodamine Phalloidin (Product # R415, 1:300) was used for cytoskeletal F-actin (red) staining. Loss of signal was observed in EGFR Knockout cells (panel c,f) confirming specificity of the antibody to EGFR(green). The images were captured at 60X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
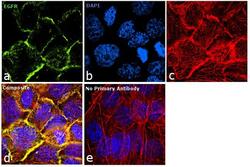
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescence analysis of EGFR was performed using 90% confluent log phase A-431 cells. The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 minutes, permeabilized with 0.1% Triton™ X-100 for 10 minutes, and blocked with 1% BSA for 1 hour at room temperature. The cells were labeled with EGFR Mouse monoclonal antibody (Product # MA5-13070) at 2 µg/mL in 0.1% BSA and incubated for 3 hours at room temperature and then labeled with Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Superclonal™ Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor® 488 conjugate (Product # A28175) at a dilution of 1:2000 for 45 minutes at room temperature (Panel a: green). Nuclei (Panel b: blue) were stained with SlowFade® Gold Antifade Mountant with DAPI (Product # S36938). F-actin (Panel c: red) was stained with Rhodamine Phalloidin (Product # R415, 1:300). Panel d represents the merged image showing membrane localization. Panel e shows the no primary antibody control. The images were captured at 60X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
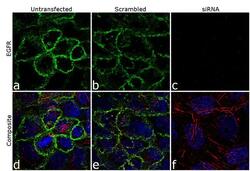
- Experimental details
- Knockdown of EGFR was achieved by transfecting A-431 cells with EGFR specific siRNA (Silencer® select Product # s563, s564 and s565). Immunofluorescence analysis was performed on A431 cells (untransfected, panel a,d), transfected with non-specific scrambled siRNA (panels b,e) and transfected with EGFR specific siRNA (panel c,f) Cells were fixed, permeabilized, and labelled with EGFR Mouse monoclonal Antibody (Product # MA5-13070, 5 µg/mL), followed by Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Superclonal™ Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor® 488 conjugate (Product # A28175, 1:2000). Nuclei (blue) were stained using SlowFade® Gold Antifade Mountant with DAPI (Product # S36938), and Rhodamine Phalloidin (Product # R415, 1:300) was used for cytoskeletal F-actin (red) staining. Loss of signal was observed upon siRNA mediated knockdown (panel c,f) confirming specificity of the antibody to EGFR (green). The images were captured at 60X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
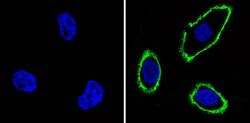
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (green) showing staining in the membrane of Hela cells (right) compared to a negative control without primary antibody (left). Formalin-fixed cells were permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 in TBS for 5-10 minutes and blocked with 3% BSA-PBS for 30 minutes at room temperature. Cells were probed with an Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor monoclonal antibody (Product # MA5-13070) in 3% BSA-PBS at a dilution of 1:100 and incubated overnight at 4 ºC in a humidified chamber. Cells were washed with PBST and incubated with a DyLight-conjugated secondary antibody in PBS at room temperature in the dark. F-actin (red) was stained with a fluorescent red phalloidin and nuclei (blue) were stained with Hoechst or DAPI. Images were taken at a magnification of 60x.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
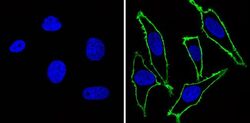
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (green) showing staining in the membrane of A431 cells (right) compared to a negative control without primary antibody (left). Formalin-fixed cells were permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 in TBS for 5-10 minutes and blocked with 3% BSA-PBS for 30 minutes at room temperature. Cells were probed with an Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor monoclonal antibody (Product # MA5-13070) in 3% BSA-PBS at a dilution of 1:100 and incubated overnight at 4 ºC in a humidified chamber. Cells were washed with PBST and incubated with a DyLight-conjugated secondary antibody in PBS at room temperature in the dark. F-actin (red) was stained with a fluorescent red phalloidin and nuclei (blue) were stained with Hoechst or DAPI. Images were taken at a magnification of 60x.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
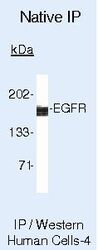
- Experimental details
- Immunoprecipitation of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor using Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (Product # MA5-13070) on Native Human A431 Cells.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
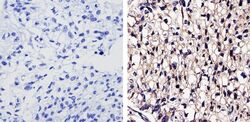
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of EGFR showing staining in the membrane and cytoplasm of paraffin-treated human lung carcinoma (right) compared with a negative control in the absence of primary antibody (left). To expose target proteins, antigen retrieval was performed using 10mM sodium citrate (pH 6.0), microwaved for 8-15 min. Following antigen retrieval, tissues were blocked in 3% H2O2-methanol for 15 min at room temperature, washed with ddH2O and PBS, and then probed with a Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor monoclonal antibody (Product # MA5-13070) diluted by 3% BSA-PBS at a dilution of 1:50 overnight at 4°C in a humidified chamber. Tissues were washed extensively in PBST and detection was performed using an HRP-conjugated secondary antibody followed by colorimetric detection using a DAB kit. Tissues were counterstained with hematoxylin and dehydrated with ethanol and xylene to prep for mounting.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
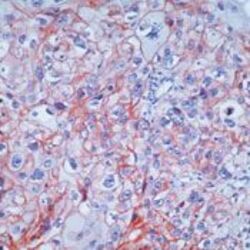
- Experimental details
- Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human squamous cell carcinoma of lung stained with EGFR antibody using peroxidase-conjugate and AEC chromogen. Note cell membrane staining of tumor cells.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
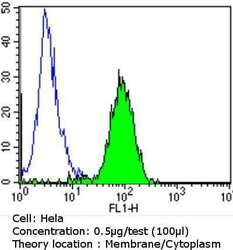
- Experimental details
- Flow cytometry analysis of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Hela cells compared to an isotype control (blue). Cells were harvested, adjusted to a concentration of 1-5x10^6 cells/mL, fixed with 2% paraformaldehyde and washed with PBS. Cells were blocked with a 2% solution of BSA-PBS for 30 min at room temperature and incubated with a Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor monoclonal antibody (Product # MA5-13070) at a dilution of 0.5 µg/test for 60 min at room temperature. Cells were then incubated for 40 min at room temperature in the dark using a Dylight 488-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L) secondary antibody and re-suspended in PBS for FACS analysis.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
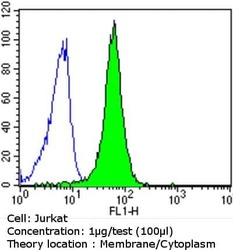
- Experimental details
- Flow cytometry analysis of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Jurkat cells compared to an isotype control (blue). Cells were harvested, adjusted to a concentration of 1-5x10^6 cells/mL, fixed with 2% paraformaldehyde and washed with PBS. Cells were blocked with a 2% solution of BSA-PBS for 30 min at room temperature and incubated with a Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor monoclonal antibody (Product # MA5-13070) at a dilution of 1 µg/test for 60 min at room temperature. Cells were then incubated for 40 min at room temperature in the dark using a Dylight 488-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L) secondary antibody and re-suspended in PBS for FACS analysis.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
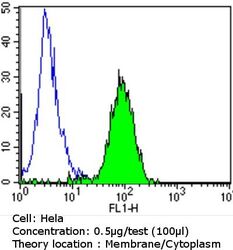
- Experimental details
- Flow cytometry analysis of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Hela cells compared to an isotype control (blue). Cells were harvested, adjusted to a concentration of 1-5x10^6 cells/mL, fixed with 2% paraformaldehyde and washed with PBS. Cells were blocked with a 2% solution of BSA-PBS for 30 min at room temperature and incubated with a Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor monoclonal antibody (Product # MA5-13070) at a dilution of 0.5 µg/test for 60 min at room temperature. Cells were then incubated for 40 min at room temperature in the dark using a Dylight 488-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L) secondary antibody and re-suspended in PBS for FACS analysis.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
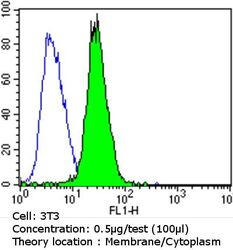
- Experimental details
- Flow cytometry analysis of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in NIH/3T3 cells compared to an isotype control (blue). Cells were harvested, adjusted to a concentration of 1-5x10^6 cells/mL, fixed with 2% paraformaldehyde and washed with PBS. Cells were blocked with a 2% solution of BSA-PBS for 30 min at room temperature and incubated with a Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor monoclonal antibody (Product # MA5-13070) at a dilution of 0.5 µg/test for 60 min at room temperature. Cells were then incubated for 40 min at room temperature in the dark using a Dylight 488-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L) secondary antibody and re-suspended in PBS for FACS analysis.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
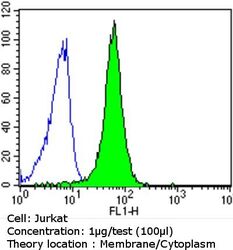
- Experimental details
- Flow cytometry analysis of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Jurkat cells compared to an isotype control (blue). Cells were harvested, adjusted to a concentration of 1-5x10^6 cells/mL, fixed with 2% paraformaldehyde and washed with PBS. Cells were blocked with a 2% solution of BSA-PBS for 30 min at room temperature and incubated with a Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor monoclonal antibody (Product # MA5-13070) at a dilution of 1 µg/test for 60 min at room temperature. Cells were then incubated for 40 min at room temperature in the dark using a Dylight 488-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L) secondary antibody and re-suspended in PBS for FACS analysis.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- Immunoprecipitation of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor using Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (Product # MA5-13070) on Native Human A431 Cells.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
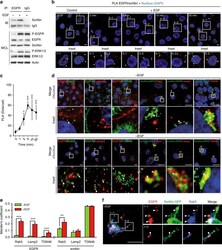
- Experimental details
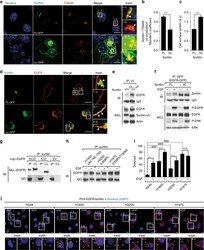
- Fig. 1 EGF promotes the EGFR--sortilin interaction. a A549 cells grown in complete cell culture media were stimulated or not with EGF (50 ng/mL) for 30 min. Immunoprecipitations (IP) were performed using anti-EGFR antibody, and the immunocomplexes were immunoblotted (IB) using anti-sortilin antibody (top). In parallel, immunoblots for P-EGFR, EGFR, sortilin, P-ERK, and ERK were performed on whole-cell lysates (WCL); the isotypic lane Immunoglobulin G (IgG) represents the IP control. b Proximity ligation assays (PLA) were performed on A549 cells, non-stimulated or stimulated with EGF (50 ng/mL) for 2, 5, 15, and 30 min. Red spots indicate sites of proximity ligation assay amplification, reflecting the EGFR--sortilin interaction (white arrows). Scale bar, 10 um. c Quantification of PLA time course, in comparison with non-stimulated cells. d A549 cells were stimulated or not with EGF (50 ng/mL) for 30 min, and then co-immunolabeled for EGFR and markers of the early endosome (Rab5), the late endosome/lysosome (LAMP2) and the trans-Golgi network (TGN46). For sortilin labeling, A549 cells were transiently transfected with sortilin-GFP to adapt a set of functional antibodies, and then immunolabeled for the same markers. Scale bar, 5 um. e Quantitative analysis of EGFR or sortilin-GFP co-localization with the aforementioned organelle-specific markers. f A549 cells were transiently transfected with sortilin-GFP, and then stimulated with EGF (50 ng/mL) for 30 min. Next, cells were fixe
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
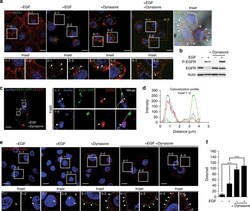
- Experimental details
- Fig. 2 EGFR interacts with sortilin at the cell surface. a A549 cells were pretreated or not with the cell-permeable dynamin inhibitor Dynasore (40 uM) for 2 h, and then stimulated or not with EGF (50 ng/mL) for 15 min. Cells were immunolabeled for EGFR and the early endosome marker EEA1, and then analyzed by confocal microscopy. Scale bar, 10 um. Inset 4-3: Bright-field image of A549 cells; white arrows show EGFR clusters at the cell surface. Scale bar, 10 um. b A549 cells were pretreated or not with Dynasore (40 uM) for 2 h, and then stimulated or not with EGF (50 ng/mL) for 15 min. The cell lysates were analyzed by western blotting for P-EGFR and EGFR. c A549 cells were transfected with EEA1-GFP, pretreated with Dynasore (40 uM) for 2 h, then stimulated with EGF (50 ng/mL) for 30 min. Next, cells were co-immunolabeled for EGFR and sortilin. Scale bar, 10 um. The co-localization profile is shown in d . e Proximity ligation assays (PLA) were performed on A549 cells under the same conditions described above in a . Scale bar, 10 um. f PLA quantification in comparison with A549 non-stimulated cells. All values represent means +- SD, Student's t -test *** P < 0.001. Each experiment has been repeated at least three times
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- Fig. 3 C-terminally truncated sortilin strongly interacts with EGFR at the cell surface independently of ligand stimulation. a HEK293 cells were transiently transfected with either full-length (FL) or C-terminally truncated (Deltac) sortilin-GFP. Cells were fixed and immunolabeled for the trans-Golgi network marker TGN46, and then analyzed by confocal microscope. Scale bar, 10 um. b Bars show the Mander's coefficient, indicating that FL-sortilin-GFP co-localized with TGN46 to a greater degree than Deltac-sortilin-GFP. c Bars show quantification of cell surface GFP intensity. d Strong interaction between EGFR and Deltac-sortilin at the plasma membrane. HEK293 cells were transiently co-transfected with EGFR and FL- or Deltac sortilin-GFP, and then fixed and immunolabeled for EGFR; immunofluorescence was analyzed by confocal microscopy. Scale bar, 10 um. e HEK293 cells were transiently co-transfected with EGFR and FL or Deltac sortilin-v5. Immunoprecipitations (IP) were performed using anti-v5 antibody, and immunocomplexes were analyzed by western blotting using anti-EGFR antibody. In parallel, immunoblots of EGFR and sortilin-v5 were performed on whole-cell lysate (WCL). f HEK293 cells were transiently co-transfected with EGFR-GFP and FL- or Deltac sortilin. Next, cells were stimulated or not with EGF (50 ng/mL) for 30 min and immunoprecipitated using anti-GFP antibody. Immunocomplexes were analyzed by western blotting for sortilin. In parallel, immunoblots of P-EGFR, EGFR
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- Fig. 4 Loss of sortilin greatly perturbs EGFR internalization and dramatically promotes EGFR signaling. a A549 cells expressing shRNA targeting sortilin and control cells (pLKO) were stimulated with EGF (50 ng/mL) for 30 min, and then fixed and immunolabeled for EGFR. Immunofluorescence was analyzed by confocal microscopy. The ratio between whole-cell and intracytoplasmic EGFR intensities, reflecting EGFR membrane retention, is quantified in b . c Sortilin-depleted and control A549 cells (pLKO) were stimulated with EGF (50 ng/mL) over a 60 min time course. At each time point, cell surface EGFR was stained at 4 degC using Alexa Fluor 488 anti-EGFR, and then analyzed by flow cytometry. Curves represent mean fluorescence intensity in sortilin-depleted cells relative to the control. d Cell lysates from sortilin-depleted (sortilin shRNA) or control A549 cells (pLKO) were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. e A549 sortilin-depleted and control cells (pLKO) were stimulated with EGF (50 ng/mL) over a 60 min time course. Cell lysates were analyzed by western blotting for components of the canonical EGFR signaling pathway using the indicated antibodies. f Sortilin-depleted cells were transfected with control siRNA (Si co) or EGFR siRNA. Cell lysates were analyzed by western blotting with the indicated antibodies. g Representative histograms of cell proliferation, as determined by EdU incorporation. Sortilin-depleted cells transfected or not with EGFR siRNA and control A549 cel
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
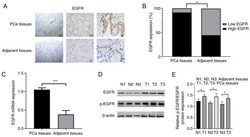
- Figure 2. EGFR expression is upregulated in PCa tissues. (A) Representative images of EGFR staining in PCa and adjacent prostate tissues. Scale bars, 100, 50 and 20 um. (B) The ratio of high EGFR expression and low EGFR expression between PCa and adjacent prostate tissues. (C) EGFR mRNA expression in PCa and adjacent prostate tissues was assessed via reverse transcription-quantitative PCR. (D) Western blotting results of EGFR and p-EGFR protein expression in PCa and adjacent prostate tissues. (E) The gray degree values of p-EGFR/EGFR western blotting results. *P
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
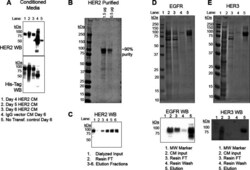
- Figure 2 EGFR family extracellular domain expression and purification in 293-F cells. (A) Time-course western blot (WB, anti-HER2 or anti-His-tag) of conditioned media (CM) indicating that the HER2 protein is expressed and secreted at high levels by day 5 post-transfection. The secreted IgG control vector is detected by the secondary HRP antibody. (B) SDS-PAGE and Coomassie staining of purified HER2 product following Ni 2+ -NTA purification. (C) WB of fractions from Ni 2+ -NTA purification. SDS-PAGE, Coomassie staining, and WB analysis of (D) EGFR and (E) HER3 following Ni 2+ -NTA purification. Lane descriptions are below each panel. FT is flow-through.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
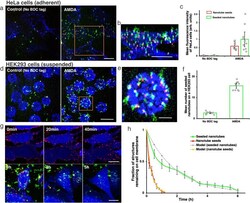
- Experimental details
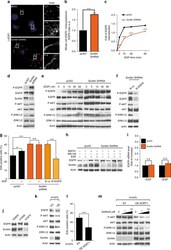
- Fig. 3 Anchoring DNA nanotubes to EGFR receptors using AMDA. a Confocal micrographs of seeded nanotubes anchored to HeLa cells after EGFR AMDA and EGFR AMDA with BDC tag addition omitted (No BDC tag) (Supplementary Note S 26 ). Seeds labeled with atto647 (red) and nanotubes with Cy3 (green), streptavidin with Alexa488 (blue). Scale bar: 20 mum. b Three-dimensional reconstruction of a HeLa cell with seeded nanotubes attached to EGFR. Scale bar: 20 mum. c The average fluorescence intensities of HeLa cells with seeded nanotubes or seeds attached via AMDA and AMDA with BDC tag addition omitted (Supplementary Note S 27 , N = 10 random locations for each case were analyzed). d Three-dimensional projection images of HEK293 cells with attached seeded nanotubes after AMDA and AMDA with BDC tag addition omitted (Supplementary Note S 28 ). Scale bar: 20 mum. e Three-dimensional reconstruction of a HEK293 cell with attached seeded nanotubes. Scale bar: 5 mum. f Average numbers of seeded nanotubes on HEK293 cells after AMDA and after AMDA with BDC tag addition omitted (Supplementary Note S 29 , N = 10 random locations for each case were analyzed). The average numbers of attached seeds are shown in Fig. 2f . g Confocal micrographs of HeLa cells at different times after seed attachment using EGFR AMDA (upper panel) and maximum projection images of HeLa cells at different times after seeded nanotube attachment using EGFR AMDA (lower panel) (Supplementary Notes S 31 , S 32 ). Scale bar: 20 mu
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
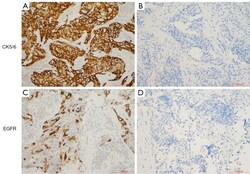
- Experimental details
- Figure 1 CK5/6 and EGFR expression by immunohistochemistry. (A,B) CK5/6 positive/negative staining; (C,D) EGFR positive/negative staining. EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor.
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry