Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [20]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Other assay [22]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- 40-3700 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- TXNIP Polyclonal Antibody
- Antibody type
- Polyclonal
- Antigen
- Synthetic peptide
- Reactivity
- Human, Bovine
- Host
- Rabbit
- Isotype
- IgG
- Vial size
- 100 μg
- Concentration
- 0.25 mg/mL
- Storage
- -20°C
Submitted references Vitamin D Prevents High Glucose-Induced Lipid Droplets Accumulation in Cultured Endothelial Cells: The Role of Thioredoxin Interacting Protein.
Metformin Protects ARPE-19 Cells from Glyoxal-Induced Oxidative Stress.
Deletion of Thioredoxin-Interacting Protein (TXNIP) Abrogates High Fat Diet-induced Retinal Leukostasis, Barrier Dysfunction and Microvascular Degeneration in a Mouse Obesity Model.
miR-20b and miR-451a Are Involved in Gastric Carcinogenesis through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway: Data from Gastric Cancer Patients, Cell Lines and Ins-Gas Mouse Model.
TXNIP induces growth arrest and enhances ABT263-induced apoptosis in mixed-lineage leukemia-rearranged acute myeloid leukemia cells.
Modeling G2019S-LRRK2 Sporadic Parkinson's Disease in 3D Midbrain Organoids.
Absence of TXNIP in Humans Leads to Lactic Acidosis and Low Serum Methionine Linked to Deficient Respiration on Pyruvate.
Thioredoxin-interacting protein promotes high-glucose-induced macrovascular endothelial dysfunction.
High fat diet dysregulates microRNA-17-5p and triggers retinal inflammation: Role of endoplasmic-reticulum-stress.
Uncoupling protein 2 modulation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in astrocytes and its implications in depression.
Thioredoxin interacting protein (TXNIP) is a novel tumor suppressor in thyroid cancer.
Variations of thioredoxin system contributes to increased susceptibility to apoptosis in cardiomyocytes of type 2 diabetic rats.
Tight coordination of protein translation and HSF1 activation supports the anabolic malignant state.
A role for thioredoxin-interacting protein (Txnip) in cellular creatine homeostasis.
Thioredoxin interacting protein promotes endothelial cell inflammation in response to disturbed flow by increasing leukocyte adhesion and repressing Kruppel-like factor 2.
A role for mitochondria in NLRP3 inflammasome activation.
Thioredoxin-interacting protein mediates TRX1 translocation to the plasma membrane in response to tumor necrosis factor-α: a key mechanism for vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 transactivation by reactive oxygen species.
Thioredoxin-interacting protein links oxidative stress to inflammasome activation.
Acquired vorinostat resistance shows partial cross-resistance to 'second-generation' HDAC inhibitors and correlates with loss of histone acetylation and apoptosis but not with altered HDAC and HAT activities.
Expression, localization, and function of the thioredoxin system in diabetic nephropathy.
Scrimieri R, Cazzaniga A, Castiglioni S, Maier JAM
Biomedicines 2021 Dec 10;9(12)
Biomedicines 2021 Dec 10;9(12)
Metformin Protects ARPE-19 Cells from Glyoxal-Induced Oxidative Stress.
Qu S, Zhang C, Liu D, Wu J, Tian H, Lu L, Xu GT, Liu F, Zhang J
Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity 2020;2020:1740943
Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity 2020;2020:1740943
Deletion of Thioredoxin-Interacting Protein (TXNIP) Abrogates High Fat Diet-induced Retinal Leukostasis, Barrier Dysfunction and Microvascular Degeneration in a Mouse Obesity Model.
Mohamed IN, Sheibani N, El-Remessy AB
International journal of molecular sciences 2020 Jun 1;21(11)
International journal of molecular sciences 2020 Jun 1;21(11)
miR-20b and miR-451a Are Involved in Gastric Carcinogenesis through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway: Data from Gastric Cancer Patients, Cell Lines and Ins-Gas Mouse Model.
Streleckiene G, Inciuraite R, Juzenas S, Salteniene V, Steponaitiene R, Gyvyte U, Kiudelis G, Leja M, Ruzgys P, Satkauskas S, Kupcinskiene E, Franke S, Thon C, Link A, Kupcinskas J, Skieceviciene J
International journal of molecular sciences 2020 Jan 29;21(3)
International journal of molecular sciences 2020 Jan 29;21(3)
TXNIP induces growth arrest and enhances ABT263-induced apoptosis in mixed-lineage leukemia-rearranged acute myeloid leukemia cells.
Noura M, Matsuo H, Koyama A, Adachi S, Masutani H
FEBS open bio 2020 Aug;10(8):1532-1541
FEBS open bio 2020 Aug;10(8):1532-1541
Modeling G2019S-LRRK2 Sporadic Parkinson's Disease in 3D Midbrain Organoids.
Kim H, Park HJ, Choi H, Chang Y, Park H, Shin J, Kim J, Lengner CJ, Lee YK, Kim J
Stem cell reports 2019 Mar 5;12(3):518-531
Stem cell reports 2019 Mar 5;12(3):518-531
Absence of TXNIP in Humans Leads to Lactic Acidosis and Low Serum Methionine Linked to Deficient Respiration on Pyruvate.
Katsu-Jiménez Y, Vázquez-Calvo C, Maffezzini C, Halldin M, Peng X, Freyer C, Wredenberg A, Giménez-Cassina A, Wedell A, Arnér ESJ
Diabetes 2019 Apr;68(4):709-723
Diabetes 2019 Apr;68(4):709-723
Thioredoxin-interacting protein promotes high-glucose-induced macrovascular endothelial dysfunction.
Li X, Kover KL, Heruth DP, Watkins DJ, Guo Y, Moore WV, He LG, Zang M, Clements MA, Yan Y
Biochemical and biophysical research communications 2017 Nov 4;493(1):291-297
Biochemical and biophysical research communications 2017 Nov 4;493(1):291-297
High fat diet dysregulates microRNA-17-5p and triggers retinal inflammation: Role of endoplasmic-reticulum-stress.
Coucha M, Mohamed IN, Elshaer SL, Mbata O, Bartasis ML, El-Remessy AB
World journal of diabetes 2017 Feb 15;8(2):56-65
World journal of diabetes 2017 Feb 15;8(2):56-65
Uncoupling protein 2 modulation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in astrocytes and its implications in depression.
Du RH, Wu FF, Lu M, Shu XD, Ding JH, Wu G, Hu G
Redox biology 2016 Oct;9:178-187
Redox biology 2016 Oct;9:178-187
Thioredoxin interacting protein (TXNIP) is a novel tumor suppressor in thyroid cancer.
Morrison JA, Pike LA, Sams SB, Sharma V, Zhou Q, Severson JJ, Tan AC, Wood WM, Haugen BR
Molecular cancer 2014 Mar 19;13:62
Molecular cancer 2014 Mar 19;13:62
Variations of thioredoxin system contributes to increased susceptibility to apoptosis in cardiomyocytes of type 2 diabetic rats.
Zhao X, Zhang Y, Li X, Wang R, Jiao X
Acta biochimica et biophysica Sinica 2014 Apr;46(4):318-29
Acta biochimica et biophysica Sinica 2014 Apr;46(4):318-29
Tight coordination of protein translation and HSF1 activation supports the anabolic malignant state.
Santagata S, Mendillo ML, Tang YC, Subramanian A, Perley CC, Roche SP, Wong B, Narayan R, Kwon H, Koeva M, Amon A, Golub TR, Porco JA Jr, Whitesell L, Lindquist S
Science (New York, N.Y.) 2013 Jul 19;341(6143):1238303
Science (New York, N.Y.) 2013 Jul 19;341(6143):1238303
A role for thioredoxin-interacting protein (Txnip) in cellular creatine homeostasis.
Zervou S, Ray T, Sahgal N, Sebag-Montefiore L, Cross R, Medway DJ, Ostrowski PJ, Neubauer S, Lygate CA
American journal of physiology. Endocrinology and metabolism 2013 Jul 15;305(2):E263-70
American journal of physiology. Endocrinology and metabolism 2013 Jul 15;305(2):E263-70
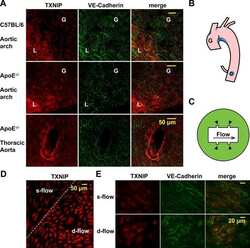
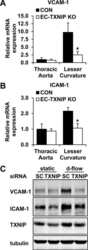
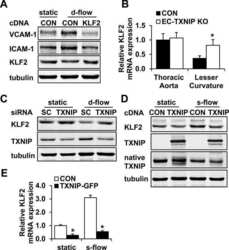
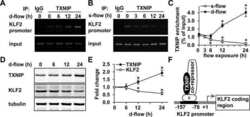
Thioredoxin interacting protein promotes endothelial cell inflammation in response to disturbed flow by increasing leukocyte adhesion and repressing Kruppel-like factor 2.
Wang XQ, Nigro P, World C, Fujiwara K, Yan C, Berk BC
Circulation research 2012 Feb 17;110(4):560-8
Circulation research 2012 Feb 17;110(4):560-8
A role for mitochondria in NLRP3 inflammasome activation.
Zhou R, Yazdi AS, Menu P, Tschopp J
Nature 2011 Jan 13;469(7329):221-5
Nature 2011 Jan 13;469(7329):221-5
Thioredoxin-interacting protein mediates TRX1 translocation to the plasma membrane in response to tumor necrosis factor-α: a key mechanism for vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 transactivation by reactive oxygen species.
World C, Spindel ON, Berk BC
Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology 2011 Aug;31(8):1890-7
Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology 2011 Aug;31(8):1890-7
Thioredoxin-interacting protein links oxidative stress to inflammasome activation.
Zhou R, Tardivel A, Thorens B, Choi I, Tschopp J
Nature immunology 2010 Feb;11(2):136-40
Nature immunology 2010 Feb;11(2):136-40
Acquired vorinostat resistance shows partial cross-resistance to 'second-generation' HDAC inhibitors and correlates with loss of histone acetylation and apoptosis but not with altered HDAC and HAT activities.
Dedes KJ, Dedes I, Imesch P, von Bueren AO, Fink D, Fedier A
Anti-cancer drugs 2009 Jun;20(5):321-33
Anti-cancer drugs 2009 Jun;20(5):321-33
Expression, localization, and function of the thioredoxin system in diabetic nephropathy.
Advani A, Gilbert RE, Thai K, Gow RM, Langham RG, Cox AJ, Connelly KA, Zhang Y, Herzenberg AM, Christensen PK, Pollock CA, Qi W, Tan SM, Parving HH, Kelly DJ
Journal of the American Society of Nephrology : JASN 2009 Apr;20(4):730-41
Journal of the American Society of Nephrology : JASN 2009 Apr;20(4):730-41
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
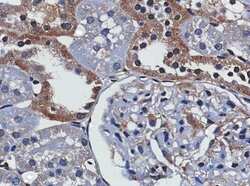
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
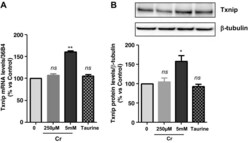
- Fig. 2. A : verification of gene array result by qRT-PCR. Cells were exposed to either 250 muM or 5 mM Cr. While 250 muM Cr did not change thioredoxin-interacting protein (Txnip) mRNA (107 +- 3.7; P = 0.449), saturating Cr caused a rise in Txnip mRNA levels in agreement to the gene array observation ( n = 3 from 3 independent experiments; 161 +- 2; P = 0.0016). Moreover, the induction of Txnip expression was specific for Cr and did not occur at 5 mM taurine ( n = 3; 106; P = 0.5481). B : Txnip protein levels were elevated by 5 mM Cr, at 3 h ( n = 3/treatment; 145 +- 11; P = 0.0139), whereas neither 250 muM Cr nor taurine changed protein expression. ns, Nonsignificant P > 0.05, * P < 0.05, and ** P < 0.005.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
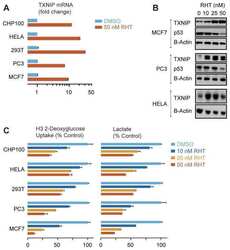
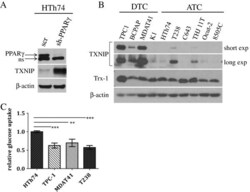
- Figure 1 TXNIP is highly expressed in DTC cell lines and low or undetectable in ATC cell lines, and glucose uptake is inversely proportional to TXNIP expression levels. (A) HTh74 cells were transduced with lentivirus expressing a PPARgamma-specific shRNA or scrambled control, and stable pools were generated under antibiotic selection. Western blot analysis of nuclear lysates (top immunoblot) reveals PPARgamma expression levels in the transduced cells. Using Western blot analysis of whole cell lysates, TXNIP and beta-actin (loading control) were detected using specific antibodies. Nonspecific band is indicated by ""ns"". (B) Western blot analysis for TXNIP, Trx-1, and beta-actin (loading control) were performed on whole cell lysates prepared from a panel of DTC and ATC cell lines grown under standard conditions. (C) Glucose uptake assays were performed. Each condition was performed in triplicate per experiment, and each experiment was performed at least three times. Nonspecific glucose uptake as determined by parallel treatment of a subset with cytochalasin B was subtracted from measurements. Data from all experiments were combined, and glucose uptake from each cell line was normalized to levels of HTh74 (average set at 1). Normalized averages are plotted, and error bars indicate SEM. ***p
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
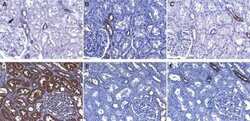
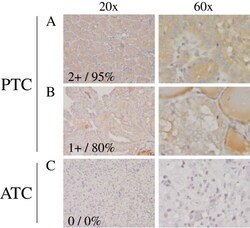
- Figure 2 TXNIP is expressed in primary DTC tumors but is low or undetectable in ATC tumors. Immunohistochemistry was performed using a TXNIP-specific primary antibody or normal mouse IgG control and a horseradish peroxidase tagged secondary antibody on a panel of 13 PTC and 8 ATC patient specimens. Two representative PTC (A-B) and one ATC (C) specimen stains are shown at 20X and 60X power. Positive staining is indicated by brown coloring, though staining of colloid is nonspecific. Staining was quantitated by a pathologist (S. B. S.), and intensity of staining was scored from absent (0) to high to (3+), followed by percent of tumor positivity.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
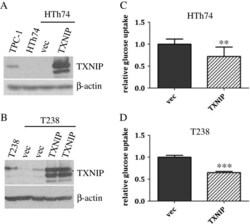
- Figure 3 TXNIP overexpression in ATC HTh74 and T238 cells attenuates glucose uptake. HTh74 and T238 cells were transduced with retrovirus encoding human TXNIP or vector control as well as a selectable antibiotic resistance marker, and stable pools were generated under antibiotic selection. Western blot analysis of whole cell lysates with TXNIP- and beta-actin-specific antibodies is shown for HTh74 (A) and T238 (B) . Glucose uptake assays were performed as described in Figure 1 using the HTh74 stable cell lines (C) and T238 stable cell lines (D) . Data from all experiments were combined, and glucose uptake from each cell line was normalized to vector control levels (average set at 1). **p = 0.001, ***p
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
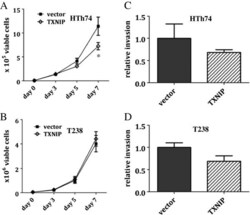
- Figure 4 TXNIP overexpression inhibits in vitro growth of ATC HTh74 cells. Viable cell proliferation assays were performed for stable HTh74 (A) and T238 (B) cell lines. Briefly, 50,000 cells were plated in 6-cm plates, trypsinized and viable cell counts were determined using the ViCell automated cell counting system. Each time point was performed in duplicate, and lysates were prepared from the day 7 time point to confirm high TXNIP expression using Western blot analysis. Each experiment was performed at least three times. Mean and SEM are plotted. Closed squares () indicate vector control cells, and open diamonds (*) indicate cells with TXNIP overexpression. In vitro invasion assays were performed on the TXNIP-overexpressing stable HTh74 (C) and T238 (D) cell lines as described in the Methods section. Results from three independent experiments were combined and normalized to the vector control average and graphed with mean plus SEM. *p
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
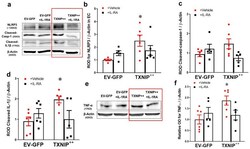
- Figure 5 Overexpression of TXNIP activates NLRP3-inflammasome and EC inflammation in an IL-1beta-dependent fashion. Representative WB blots ( a , e ) and statistical analysis of protein expression detected from REC lysates, of endothelial ( b ) NLRP3, ( c ) cleaved caspase-1, ( d ) cleaved IL-1beta, and ( f ) TNF-alpha, showing significant increases in NLRP3, cleaved IL-1beta and TNF-alpha and a trend towards increased expression of cleaved caspase-1 in the TXNIP overexpressing (TXNIP ++ + vehicle) group compared with the EV-GFP + vehicle control group. Treatment of TXNIP-overexpressing REC with 100 ng/mL of IL-1RA (TXNIP ++ + IL-1RA) suppressed the effect of TXNIP overexpression on inflammasome activation and TNF-alpha expression. Two-way ANOVA showed significant interaction between IL-1RA and TXNIP overexpression across NLRP3 and cleaved IL-1beta expression levels ( n = 5-6, each measurement was performed in triplicate using two different cell preparations; * p < 0.05 vs. EV-GFP + vehicle group).
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
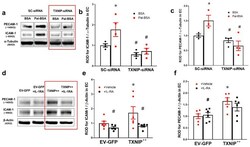
- Figure 6 Silencing of TXNIP abolishes, while its overexpression induces, REC adhesion molecule upregulation in an IL-1beta-dependent fashion. ( a ) Representative WB blots (boxes denote separate lanes from the same gel) and statistical analyses of ( b ) ICAM-1 and ( c ) PECAM-1 protein expression showed higher levels in cells incubated with PAL-BSA compared with BSA controls in the scrambled-siRNA group. Silencing TXNIP expression using siRNA abolished such responses. Two-way ANOVA showed significant interaction between Pal-BSA and silencing TXNIP expression across PECAM-1 levels ( n = 3-4, each measurement was performed in duplicate using two different cell preparations; * p < 0.05 vs. SCsiRNA + BSA, # vs. SCsiRNA + Pal-BSA). ( d ) Representative blots and WB analysis of ( e ) ICAM-1 and ( f ) PECAM-1 protein expression showed higher levels in TXNIP overexpression (TXNIP ++ + vehicle) group compared with EV-GFP + vehicle control group, respectively. Treatment of TXNIP-overexpressing REC with 100 ng/mL of IL-1RA (TXNIP ++ + IL-1RA) suppressed the effect of TXNIP overexpression on expression of REC adhesion molecules ( n = 5-6, each measurement was performed in triplicate using two different cell preparations; * p < 0.05 vs. EV-GFP+ vehicle, # vs. TXNIP + + + vehicle).
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
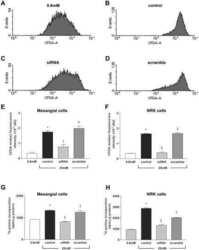
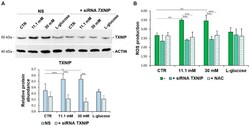
- Figure 2 TXNIP upregulation is responsible for ROS accumulation in HUVEC cultured in high glucose levels. ( A ) HUVEC were cultured in medium containing 5 mM (CTR), 11.1 mM or 30 mM of d -glucose after TXNIP silencing. A scrambled non-silencing sequence (NS) was used as a control for silencing. Western blot (upper panel) was performed on cell lysates using specific antibodies against TXNIP. Actin was used an equal loading control. A representative blot is shown. Densitometric analysis (lower panel) was performed using Image J Lab software on three different blots, and the results are the mean of three independent experiments +- SD. ( B ) HUVEC were cultured in medium containing 5 mM (CTR), 11.1 mM or 30 mM of d -glucose (-) and either after TXNIP silencing or the addition of NAC 5 mM. l -glucose (30 mM) was used as a control of osmolarity. ROS production was evaluated by DCFH, as described in the methods. The results are the mean of three experiments performed in triplicate +- SD. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
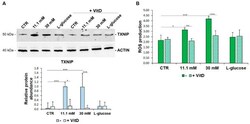
- Figure 3 VitD prevents TXNIP upregulation and ROS accumulation in HUVEC cultured in high glucose conditions. ( A ) Western blot (upper panel) was performed on cell lysates using specific antibodies against TXNIP. Actin was used as an equal loading control. A representative blot is shown. Densitometric analysis (lower panel) was performed using Image J Lab software on three different blots, and the results are the mean of three independent experiments +- SD. ( B ) HUVEC were cultured in medium containing 5 mM (CTR), 11.1 mM, or 30 mM of d -glucose in the absence (-) or in the presence of VitD 20 nM. l -glucose (30 mM) was used as a control of osmolarity. ROS production was evaluated by DCFH, as described in the methods. The results are the mean of three experiments performed triplicate +- SD. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
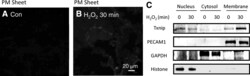
- Figure 2. TXNIP translocates to the plasma membrane following H 2 O 2 stimulation, assayed by plasma membrane sheet. A and B, TXNIP present in plasma membrane sheets was detected by immunoepifluorescence microscopy for the indicated time. Con indicates control. C, Western blot analysis of cell fractionation indicated that the majority of TXNIP under basal conditions is nuclear and translocates to the membrane with H 2 O 2 treatment. Western blotting of organelle-specific markers demonstrated the purity of cell fractions.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
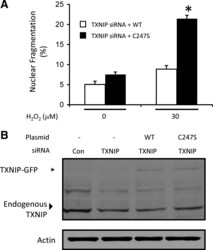
- Figure 6. TXNIP promotes cell survival that requires TXNIP-TRX1 binding. A, Apoptosis assayed by nuclear morphology of EC transfected with TXNIP siRNA, rescued with either TXNIP-WT-GFP or TXNIP-Cys247Ser-GFP, and treated with H 2 O 2 for 6 hours. &ast P
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- Figure 7 PTEN and TXNIP proteins level changes after exogenous miR-20b expression inhibition. PTEN ( A ) and TXNIP ( B ) protein expression comparison 48 h and 72 h after transfection in AGS and MKN28 cell cultures transfected with anti-miR-20b and miR-control. Significant PTEN protein level increase was determined 72 h after transfection in AGS cell culture and TXNIP- 72 h after transfection in MKN28 cell culture. Representative pictures of PTEN and TXNIP proteins signals detected by Western Blot presented at the bottom of a figure (* p < 0.05). Data from four independent experiments.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
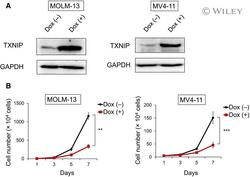
- 2 Fig. Doxycycline-induced TXNIP suppresses proliferation of MLL-r AML cells. (A) Expression of TXNIP in doxycycline (dox)-on-dependent TXNIP-overexpressed MOLM-13 and MV4-11 cells. Cells were treated with or without 3 mu m doxycycline. Seventy-two hours after treatment, cell lysates were prepared and analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. GAPDH was used as loading control. Images are representative images of three reproducible independent results. (B) Growth curves of dox-on-dependent TXNIP-overexpressed MOLM-13 and MV4-11 cells treated with or without doxycycline ( n = 3). Data are expressed as the mean +- SEM values. ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, by 2-tailed Student's t- test.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
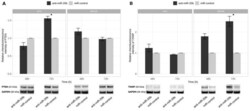
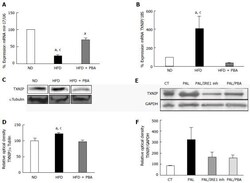
- Figure 4 Dysregulation of realtime polymerase chain reaction. It shows significant (A) reduction in miR-17-5p and (B) increase in TXNIP mRNA levels in mice kept on HFD for 4 wk compared to ND, which were reversed with PBA treatment ( n = 3-4); C: Representative western blot were cut from the same membrane for TXNIP and alphatubulin from retina (D) Statistical analysis showed an upregulation in TXNIP expression in HFD mice compared to ND, PBA treatment ified this effect ( n = 4-5) ( a P < 0.05 vs ND, c P < 0.05 vs HFD + PBA) (E) Representative western blot of TXNIP and GAPDH from rMC1 treated with palmitate (pal), after the addition of IRE inhibitor or PBA; D: Statistical analysis showed a trend increase in TXNIP expression, which is reversed by IRE inhibitor or PBA ( P = 0.076, n = 3). HFD: High fat diet; ND: Normal diet; PBA: Phenyl-butyric acid; TXNIP: Thioredoxin-interacting protein; CT: Control; PAL: Palmitate; PAL/IRE1: Palmitate + inositol requiring enzyme 1; PAL/PBA: Palmitate + phenyl-butyric acid.
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Immunoprecipitation
Immunoprecipitation Other assay
Other assay