Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [38]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunocytochemistry [6]
- Immunohistochemistry [1]
- Flow cytometry [6]
- Other assay [6]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- MA5-11828 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- CD24 Monoclonal Antibody (SN3)
- Antibody type
- Monoclonal
- Antigen
- Other
- Description
- MA5-11828 targets CD24 in FACS, IHC (F), ICC/IF and WB applications and shows reactivity with Human and Mouse samples. This antibody detects a few non-specific bands in BAF-3 cell lysates. The MA5-11828 immunogen is cell membrane antigen preparation isolated from NALM-1 human pre-B leukemia cell line.
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse
- Host
- Mouse
- Isotype
- IgG
- Antibody clone number
- SN3
- Vial size
- 500 μL
- Concentration
- 0.2 mg/mL
- Storage
- 4°C
Submitted references Transmissible gastroenteritis virus targets Paneth cells to inhibit the self-renewal and differentiation of Lgr5 intestinal stem cells via Notch signaling.
Advanced High-Content-Screening Applications of Clonogenicity in Cancer.
Highly versatile cancer photoimmunotherapy using photosensitizer-conjugated avidin and biotin-conjugated targeting antibodies.
Zika virus as an oncolytic treatment of human neuroblastoma cells requires CD24.
Secreted Frizzled-related protein 4 (sFRP4) chemo-sensitizes cancer stem cells derived from human breast, prostate, and ovary tumor cell lines.
A CD44v(+) subpopulation of breast cancer stem-like cells with enhanced lung metastasis capacity.
Humoral Dysregulation Associated with Increased Systemic Inflammation among Injection Heroin Users.
CD24 Expression May Play a Role as a Predictive Indicator and a Modulator of Cisplatin Treatment Response in Head and Neck Squamous Cellular Carcinoma.
Increased Steady-State Memory B Cell Subsets Among High-Risk Participants in an HIV Vaccine Trial.
Differential expression of ligands for NKG2D and DNAM-1 receptors by epithelial ovarian cancer-derived exosomes and its influence on NK cell cytotoxicity.
CD24 Overexpression Is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Luminal A and Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.
Addition of niclosamide to palladium(II) saccharinate complex of terpyridine results in enhanced cytotoxic activity inducing apoptosis on cancer stem cells of breast cancer.
The clinicopathological and prognostic significance of CD24, CD44, CD133, ALDH1 expressions in invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast: CD44/CD24 expression in breast cancer.
Diversity, cellular origin and autoreactivity of antibody-secreting cell population expansions in acute systemic lupus erythematosus.
Fibromatosis-like metaplastic carcinoma of the breast has a claudin-low immunohistochemical phenotype.
CD24 and CD44 in salivary gland pleomorphic adenoma and in human salivary gland morphogenesis: differential markers of glandular structure or stem cell indicators?
Profiling of normal and malignant breast tissue show CD44high/CD24low phenotype as a predominant stem/progenitor marker when used in combination with Ep-CAM/CD49f markers.
Genomic and phenotypic profiles of two Brazilian breast cancer cell lines derived from primary human tumors.
Multiparameter flow cytometry and bioanalytics for B cell profiling in systemic lupus erythematosus.
CD24 expression as a marker for predicting clinical outcome in human gliomas.
Autoimmunity, intestinal lymphoid hyperplasia, and defects in mucosal B-cell homeostasis in patients with PTEN hamartoma tumor syndrome.
Characterization of sphere-propagating cells with stem-like properties from DU145 prostate cancer cells.
Acetaminophen-induced differentiation of human breast cancer stem cells and inhibition of tumor xenograft growth in mice.
Different prognostic significance of CD24 and CD44 expression in breast cancer according to hormone receptor status.
CD24 is a novel predictor for poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma after surgery.
Association of breast cancer stem cells identified by aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 expression with resistance to sequential Paclitaxel and epirubicin-based chemotherapy for breast cancers.
CD24 expression is a novel prognostic factor in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Laser capture microdissection-microarray analysis of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis glomeruli.
Cytoplasmic CD24 expression is a novel prognostic factor in diffuse-type gastric adenocarcinoma.
A new population of cells lacking expression of CD27 represents a notable component of the B cell memory compartment in systemic lupus erythematosus.
A new population of cells lacking expression of CD27 represents a notable component of the B cell memory compartment in systemic lupus erythematosus.
The role of extracellular factors in human metastatic chordoma cell growth in vitro.
Identification and purification of classical Hodgkin cells from lymph nodes by flow cytometry and flow cytometric cell sorting.
CD24 expression is a prognostic factor in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.
Cytoplasmic CD24 expression in colorectal cancer independently correlates with shortened patient survival.
Expression profiling of microdissected matched prostate cancer samples reveals CD166/MEMD and CD24 as new prognostic markers for patient survival.
Molecular and prognostic distinction between serous ovarian carcinomas of varying grade and malignant potential.
CD24 expression is a significant predictor of PSA relapse and poor prognosis in low grade or organ confined prostate cancer.
Wu A, Yu B, Zhang K, Xu Z, Wu D, He J, Luo J, Luo Y, Yu J, Zheng P, Che L, Mao X, Huang Z, Wang L, Zhao J, Chen D
Cell death & disease 2020 Jan 20;11(1):40
Cell death & disease 2020 Jan 20;11(1):40
Advanced High-Content-Screening Applications of Clonogenicity in Cancer.
Esquer H, Zhou Q, Abraham AD, LaBarbera DV
SLAS discovery : advancing life sciences R & D 2020 Aug;25(7):734-743
SLAS discovery : advancing life sciences R & D 2020 Aug;25(7):734-743
Highly versatile cancer photoimmunotherapy using photosensitizer-conjugated avidin and biotin-conjugated targeting antibodies.
Shirasu N, Shibaguchi H, Yamada H, Kuroki M, Yasunaga S
Cancer cell international 2019;19:299
Cancer cell international 2019;19:299
Zika virus as an oncolytic treatment of human neuroblastoma cells requires CD24.
Mazar J, Li Y, Rosado A, Phelan P, Kedarinath K, Parks GD, Alexander KA, Westmoreland TJ
PloS one 2018;13(7):e0200358
PloS one 2018;13(7):e0200358
Secreted Frizzled-related protein 4 (sFRP4) chemo-sensitizes cancer stem cells derived from human breast, prostate, and ovary tumor cell lines.
Deshmukh A, Kumar S, Arfuso F, Newsholme P, Dharmarajan A
Scientific reports 2017 May 23;7(1):2256
Scientific reports 2017 May 23;7(1):2256
A CD44v(+) subpopulation of breast cancer stem-like cells with enhanced lung metastasis capacity.
Hu J, Li G, Zhang P, Zhuang X, Hu G
Cell death & disease 2017 Mar 16;8(3):e2679
Cell death & disease 2017 Mar 16;8(3):e2679
Humoral Dysregulation Associated with Increased Systemic Inflammation among Injection Heroin Users.
Piepenbrink MS, Samuel M, Zheng B, Carter B, Fucile C, Bunce C, Kiebala M, Khan AA, Thakar J, Maggirwar SB, Morse D, Rosenberg AF, Haughey NJ, Valenti W, Keefer MC, Kobie JJ
PloS one 2016;11(7):e0158641
PloS one 2016;11(7):e0158641
CD24 Expression May Play a Role as a Predictive Indicator and a Modulator of Cisplatin Treatment Response in Head and Neck Squamous Cellular Carcinoma.
Modur V, Joshi P, Nie D, Robbins KT, Khan AU, Rao K
PloS one 2016;11(6):e0156651
PloS one 2016;11(6):e0156651
Increased Steady-State Memory B Cell Subsets Among High-Risk Participants in an HIV Vaccine Trial.
Keefer MC, Zheng B, Rosenberg AF, Kobie JJ
AIDS research and human retroviruses 2016 Oct Nov;32(10-11):1143-1148
AIDS research and human retroviruses 2016 Oct Nov;32(10-11):1143-1148
Differential expression of ligands for NKG2D and DNAM-1 receptors by epithelial ovarian cancer-derived exosomes and its influence on NK cell cytotoxicity.
Labani-Motlagh A, Israelsson P, Ottander U, Lundin E, Nagaev I, Nagaeva O, Dehlin E, Baranov V, Mincheva-Nilsson L
Tumour biology : the journal of the International Society for Oncodevelopmental Biology and Medicine 2016 Apr;37(4):5455-66
Tumour biology : the journal of the International Society for Oncodevelopmental Biology and Medicine 2016 Apr;37(4):5455-66
CD24 Overexpression Is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Luminal A and Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.
Kwon MJ, Han J, Seo JH, Song K, Jeong HM, Choi JS, Kim YJ, Lee SH, Choi YL, Shin YK
PloS one 2015;10(10):e0139112
PloS one 2015;10(10):e0139112
Addition of niclosamide to palladium(II) saccharinate complex of terpyridine results in enhanced cytotoxic activity inducing apoptosis on cancer stem cells of breast cancer.
Karakas D, Cevatemre B, Aztopal N, Ari F, Yilmaz VT, Ulukaya E
Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry 2015 Sep 1;23(17):5580-6
Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry 2015 Sep 1;23(17):5580-6
The clinicopathological and prognostic significance of CD24, CD44, CD133, ALDH1 expressions in invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast: CD44/CD24 expression in breast cancer.
Kapucuoğlu N, Bozkurt KK, Başpınar Ş, Koçer M, Eroğlu HE, Akdeniz R, Akçil M
Pathology, research and practice 2015 Oct;211(10):740-7
Pathology, research and practice 2015 Oct;211(10):740-7
Diversity, cellular origin and autoreactivity of antibody-secreting cell population expansions in acute systemic lupus erythematosus.
Tipton CM, Fucile CF, Darce J, Chida A, Ichikawa T, Gregoretti I, Schieferl S, Hom J, Jenks S, Feldman RJ, Mehr R, Wei C, Lee FE, Cheung WC, Rosenberg AF, Sanz I
Nature immunology 2015 Jul;16(7):755-65
Nature immunology 2015 Jul;16(7):755-65
Fibromatosis-like metaplastic carcinoma of the breast has a claudin-low immunohistochemical phenotype.
Rito M, Schmitt F, Pinto AE, André S
Virchows Archiv : an international journal of pathology 2014 Aug;465(2):185-91
Virchows Archiv : an international journal of pathology 2014 Aug;465(2):185-91
CD24 and CD44 in salivary gland pleomorphic adenoma and in human salivary gland morphogenesis: differential markers of glandular structure or stem cell indicators?
Ianez RC, Coutinho-Camillo CM, Buim ME, Pinto CA, Soares FA, Lourenço SV
Histopathology 2013 Jun;62(7):1075-82
Histopathology 2013 Jun;62(7):1075-82
Profiling of normal and malignant breast tissue show CD44high/CD24low phenotype as a predominant stem/progenitor marker when used in combination with Ep-CAM/CD49f markers.
Ghebeh H, Sleiman GM, Manogaran PS, Al-Mazrou A, Barhoush E, Al-Mohanna FH, Tulbah A, Al-Faqeeh K, Adra CN
BMC cancer 2013 Jun 14;13:289
BMC cancer 2013 Jun 14;13:289
Genomic and phenotypic profiles of two Brazilian breast cancer cell lines derived from primary human tumors.
Corrêa NC, Kuasne H, Faria JA, Seixas CC, Santos IG, Abreu FB, Nonogaki S, Rocha RM, Aparecida Borges Silva G, Gobbi H, Rogatto SR, Goes AM, Gomes DA
Oncology reports 2013 Apr;29(4):1299-307
Oncology reports 2013 Apr;29(4):1299-307
Multiparameter flow cytometry and bioanalytics for B cell profiling in systemic lupus erythematosus.
Kaminski DA, Wei C, Rosenberg AF, Lee FE, Sanz I
Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, N.J.) 2012;900:109-34
Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, N.J.) 2012;900:109-34
CD24 expression as a marker for predicting clinical outcome in human gliomas.
Deng J, Gao G, Wang L, Wang T, Yu J, Zhao Z
Journal of biomedicine & biotechnology 2012;2012:517172
Journal of biomedicine & biotechnology 2012;2012:517172
Autoimmunity, intestinal lymphoid hyperplasia, and defects in mucosal B-cell homeostasis in patients with PTEN hamartoma tumor syndrome.
Heindl M, Händel N, Ngeow J, Kionke J, Wittekind C, Kamprad M, Rensing-Ehl A, Ehl S, Reifenberger J, Loddenkemper C, Maul J, Hoffmeister A, Aretz S, Kiess W, Eng C, Uhlig HH
Gastroenterology 2012 May;142(5):1093-1096.e6
Gastroenterology 2012 May;142(5):1093-1096.e6
Characterization of sphere-propagating cells with stem-like properties from DU145 prostate cancer cells.
Rybak AP, He L, Kapoor A, Cutz JC, Tang D
Biochimica et biophysica acta 2011 May;1813(5):683-94
Biochimica et biophysica acta 2011 May;1813(5):683-94
Acetaminophen-induced differentiation of human breast cancer stem cells and inhibition of tumor xenograft growth in mice.
Takehara M, Hoshino T, Namba T, Yamakawa N, Mizushima T
Biochemical pharmacology 2011 May 1;81(9):1124-35
Biochemical pharmacology 2011 May 1;81(9):1124-35
Different prognostic significance of CD24 and CD44 expression in breast cancer according to hormone receptor status.
Kim HJ, Kim MJ, Ahn SH, Son BH, Kim SB, Ahn JH, Noh WC, Gong G
Breast (Edinburgh, Scotland) 2011 Feb;20(1):78-85
Breast (Edinburgh, Scotland) 2011 Feb;20(1):78-85
CD24 is a novel predictor for poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma after surgery.
Yang XR, Xu Y, Yu B, Zhou J, Li JC, Qiu SJ, Shi YH, Wang XY, Dai Z, Shi GM, Wu B, Wu LM, Yang GH, Zhang BH, Qin WX, Fan J
Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2009 Sep 1;15(17):5518-27
Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2009 Sep 1;15(17):5518-27
Association of breast cancer stem cells identified by aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 expression with resistance to sequential Paclitaxel and epirubicin-based chemotherapy for breast cancers.
Tanei T, Morimoto K, Shimazu K, Kim SJ, Tanji Y, Taguchi T, Tamaki Y, Noguchi S
Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2009 Jun 15;15(12):4234-41
Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2009 Jun 15;15(12):4234-41
CD24 expression is a novel prognostic factor in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Sano A, Kato H, Sakurai S, Sakai M, Tanaka N, Inose T, Saito K, Sohda M, Nakajima M, Nakajima T, Kuwano H
Annals of surgical oncology 2009 Feb;16(2):506-14
Annals of surgical oncology 2009 Feb;16(2):506-14
Laser capture microdissection-microarray analysis of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis glomeruli.
Bennett MR, Czech KA, Arend LJ, Witte DP, Devarajan P, Potter SS
Nephron. Experimental nephrology 2007;107(1):e30-40
Nephron. Experimental nephrology 2007;107(1):e30-40
Cytoplasmic CD24 expression is a novel prognostic factor in diffuse-type gastric adenocarcinoma.
Chou YY, Jeng YM, Lee TT, Hu FC, Kao HL, Lin WC, Lai PL, Hu RH, Yuan RH
Annals of surgical oncology 2007 Oct;14(10):2748-58
Annals of surgical oncology 2007 Oct;14(10):2748-58
A new population of cells lacking expression of CD27 represents a notable component of the B cell memory compartment in systemic lupus erythematosus.
Wei C, Anolik J, Cappione A, Zheng B, Pugh-Bernard A, Brooks J, Lee EH, Milner EC, Sanz I
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2007 May 15;178(10):6624-33
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2007 May 15;178(10):6624-33
A new population of cells lacking expression of CD27 represents a notable component of the B cell memory compartment in systemic lupus erythematosus.
Wei C, Anolik J, Cappione A, Zheng B, Pugh-Bernard A, Brooks J, Lee EH, Milner EC, Sanz I
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2007 May 15;178(10):6624-33
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2007 May 15;178(10):6624-33
The role of extracellular factors in human metastatic chordoma cell growth in vitro.
Ostroumov E, Hunter CJ
Spine 2007 Dec 15;32(26):2957-64
Spine 2007 Dec 15;32(26):2957-64
Identification and purification of classical Hodgkin cells from lymph nodes by flow cytometry and flow cytometric cell sorting.
Fromm JR, Kussick SJ, Wood BL
American journal of clinical pathology 2006 Nov;126(5):764-80
American journal of clinical pathology 2006 Nov;126(5):764-80
CD24 expression is a prognostic factor in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.
Su MC, Hsu C, Kao HL, Jeng YM
Cancer letters 2006 Apr 8;235(1):34-9
Cancer letters 2006 Apr 8;235(1):34-9
Cytoplasmic CD24 expression in colorectal cancer independently correlates with shortened patient survival.
Weichert W, Denkert C, Burkhardt M, Gansukh T, Bellach J, Altevogt P, Dietel M, Kristiansen G
Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2005 Sep 15;11(18):6574-81
Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2005 Sep 15;11(18):6574-81
Expression profiling of microdissected matched prostate cancer samples reveals CD166/MEMD and CD24 as new prognostic markers for patient survival.
Kristiansen G, Pilarsky C, Wissmann C, Kaiser S, Bruemmendorf T, Roepcke S, Dahl E, Hinzmann B, Specht T, Pervan J, Stephan C, Loening S, Dietel M, Rosenthal A
The Journal of pathology 2005 Feb;205(3):359-76
The Journal of pathology 2005 Feb;205(3):359-76
Molecular and prognostic distinction between serous ovarian carcinomas of varying grade and malignant potential.
Meinhold-Heerlein I, Bauerschlag D, Hilpert F, Dimitrov P, Sapinoso LM, Orlowska-Volk M, Bauknecht T, Park TW, Jonat W, Jacobsen A, Sehouli J, Luttges J, Krajewski M, Krajewski S, Reed JC, Arnold N, Hampton GM
Oncogene 2005 Feb 3;24(6):1053-65
Oncogene 2005 Feb 3;24(6):1053-65
CD24 expression is a significant predictor of PSA relapse and poor prognosis in low grade or organ confined prostate cancer.
Kristiansen G, Pilarsky C, Pervan J, Stürzebecher B, Stephan C, Jung K, Loening S, Rosenthal A, Dietel M
The Prostate 2004 Feb 1;58(2):183-92
The Prostate 2004 Feb 1;58(2):183-92
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
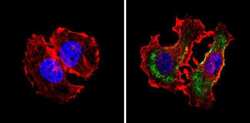
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of CD24 (green) showing staining in the cytoplasm of MCF-7 cells (right) compared to a negative control without primary antibody (left). Formalin-fixed cells were permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 in TBS for 5-10 minutes and blocked with 3% BSA-PBS for 30 minutes at room temperature. Cells were probed with a CD24 monoclonal antibody (Product # MA5-11828) in 3% BSA-PBS at a dilution of 1:20 and incubated overnight at 4 ºC in a humidified chamber. Cells were washed with PBST and incubated with a DyLight-conjugated secondary antibody in PBS at room temperature in the dark. F-actin (red) was stained with a fluorescent red phalloidin and nuclei (blue) were stained with Hoechst or DAPI. Images were taken at a magnification of 60x.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
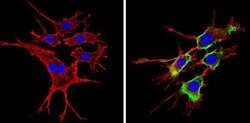
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of CD24 (green) showing staining in the cytoplasm of NIH-3T3 cells (right) compared to a negative control without primary antibody (left). Formalin-fixed cells were permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 in TBS for 5-10 minutes and blocked with 3% BSA-PBS for 30 minutes at room temperature. Cells were probed with a CD24 monoclonal antibody (Product # MA5-11828) in 3% BSA-PBS at a dilution of 1:20 and incubated overnight at 4 ºC in a humidified chamber. Cells were washed with PBST and incubated with a DyLight-conjugated secondary antibody in PBS at room temperature in the dark. F-actin (red) was stained with a fluorescent red phalloidin and nuclei (blue) were stained with Hoechst or DAPI. Images were taken at a magnification of 60x.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
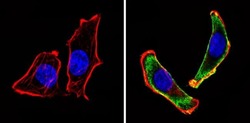
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of CD24 (green) showing staining in the cytoplasm of U251 cells (right) compared to a negative control without primary antibody (left). Formalin-fixed cells were permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 in TBS for 5-10 minutes and blocked with 3% BSA-PBS for 30 minutes at room temperature. Cells were probed with a CD24 monoclonal antibody (Product # MA5-11828) in 3% BSA-PBS at a dilution of 1:20 and incubated overnight at 4 ºC in a humidified chamber. Cells were washed with PBST and incubated with a DyLight-conjugated secondary antibody in PBS at room temperature in the dark. F-actin (red) was stained with a fluorescent red phalloidin and nuclei (blue) were stained with Hoechst or DAPI. Images were taken at a magnification of 60x.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
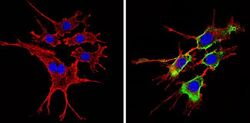
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of CD24 (green) showing staining in the cytoplasm of NIH-3T3 cells (right) compared to a negative control without primary antibody (left). Formalin-fixed cells were permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 in TBS for 5-10 minutes and blocked with 3% BSA-PBS for 30 minutes at room temperature. Cells were probed with a CD24 monoclonal antibody (Product # MA5-11828) in 3% BSA-PBS at a dilution of 1:20 and incubated overnight at 4 ºC in a humidified chamber. Cells were washed with PBST and incubated with a DyLight-conjugated secondary antibody in PBS at room temperature in the dark. F-actin (red) was stained with a fluorescent red phalloidin and nuclei (blue) were stained with Hoechst or DAPI. Images were taken at a magnification of 60x.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
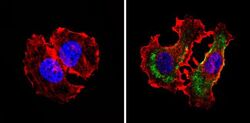
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of CD24 (green) showing staining in the cytoplasm of MCF-7 cells (right) compared to a negative control without primary antibody (left). Formalin-fixed cells were permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 in TBS for 5-10 minutes and blocked with 3% BSA-PBS for 30 minutes at room temperature. Cells were probed with a CD24 monoclonal antibody (Product # MA5-11828) in 3% BSA-PBS at a dilution of 1:20 and incubated overnight at 4 ºC in a humidified chamber. Cells were washed with PBST and incubated with a DyLight-conjugated secondary antibody in PBS at room temperature in the dark. F-actin (red) was stained with a fluorescent red phalloidin and nuclei (blue) were stained with Hoechst or DAPI. Images were taken at a magnification of 60x.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
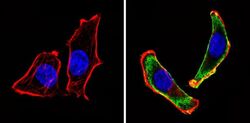
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of CD24 (green) showing staining in the cytoplasm of U251 cells (right) compared to a negative control without primary antibody (left). Formalin-fixed cells were permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 in TBS for 5-10 minutes and blocked with 3% BSA-PBS for 30 minutes at room temperature. Cells were probed with a CD24 monoclonal antibody (Product # MA5-11828) in 3% BSA-PBS at a dilution of 1:20 and incubated overnight at 4 ºC in a humidified chamber. Cells were washed with PBST and incubated with a DyLight-conjugated secondary antibody in PBS at room temperature in the dark. F-actin (red) was stained with a fluorescent red phalloidin and nuclei (blue) were stained with Hoechst or DAPI. Images were taken at a magnification of 60x.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
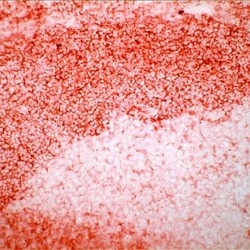
- Experimental details
- Frozen human tonsil section stained with CD24 antibody using UltraVision LP and AEC chromogen. Note membrane staining of lymphocytes.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
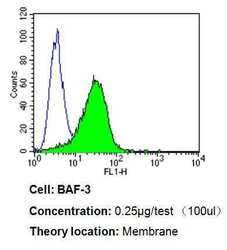
- Experimental details
- Flow cytometry analysis of CD24 in BAF-3 cells compared to an isotype control (blue). Cells were harvested, adjusted to a concentration of 1-5x10^6 cells/mL, fixed with 2% paraformaldehyde, washed with PBS, and incubated with CD24 monoclonal antibody (Product # MA5-11828) at a dilution of 0.25 µg/test for 60 min at room temperature. Cells were then blocked in a solution of 2% BSA-PBS for 30 min at room temperature, incubated for 40 min at room temperature in the dark using a Dylight 488-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L) secondary antibody, and re-suspended in PBS for FACS analysis.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
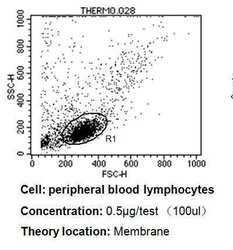
- Experimental details
- Flow cytometry analysis of CD24 in PBMC cells compared to an isotype control (blue). Human blood was collected, combined with a hydrophilic polysaccharide, centrifuged, transferred to a conical tube and washed with PBS. 50 µL of cell solution was added to each tube at a dilution of 2x10^7 cells/mL, followed by the addition of 50 µL of isotype control and primary antibody (Product # MA5-11828) at a dilution of 0.5 µg/test. Cells were incubated for 30 min at 4°C and washed with a cell buffer, followed by incubation with a DyLight 488-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L) secondary for 30 min at 4°C in the dark. FACS analysis was performed using 400 µL of cell buffer.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
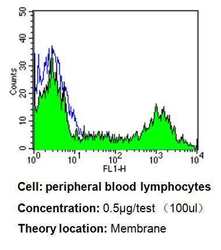
- Experimental details
- Flow cytometry analysis of CD24 in PBMC cells compared to an isotype control (blue). Human blood was collected, combined with a hydrophilic polysaccharide, centrifuged, transferred to a conical tube and washed with PBS. 50 µL of cell solution was added to each tube at a dilution of 2x10^7 cells/mL, followed by the addition of 50 µL of isotype control and primary antibody (Product # MA5-11828) at a dilution of 0.5 µg/test. Cells were incubated for 30 min at 4°C and washed with a cell buffer, followed by incubation with a DyLight 488-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L) secondary for 30 min at 4°C in the dark. FACS analysis was performed using 400 µL of cell buffer.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
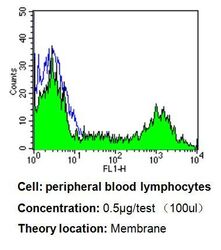
- Experimental details
- Flow cytometry analysis of CD24 in PBMC cells compared to an isotype control (blue). Human blood was collected, combined with a hydrophilic polysaccharide, centrifuged, transferred to a conical tube and washed with PBS. 50 µL of cell solution was added to each tube at a dilution of 2x10^7 cells/mL, followed by the addition of 50 µL of isotype control and primary antibody (Product # MA5-11828) at a dilution of 0.5 µg/test. Cells were incubated for 30 min at 4°C and washed with a cell buffer, followed by incubation with a DyLight 488-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L) secondary for 30 min at 4°C in the dark. FACS analysis was performed using 400 µL of cell buffer.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
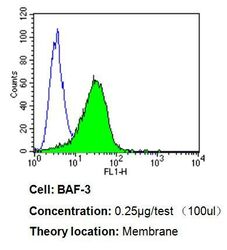
- Experimental details
- Flow cytometry analysis of CD24 in BAF-3 cells compared to an isotype control (blue). Cells were harvested, adjusted to a concentration of 1-5x10^6 cells/mL, fixed with 2% paraformaldehyde, washed with PBS, and incubated with CD24 monoclonal antibody (Product # MA5-11828) at a dilution of 0.25 µg/test for 60 min at room temperature. Cells were then blocked in a solution of 2% BSA-PBS for 30 min at room temperature, incubated for 40 min at room temperature in the dark using a Dylight 488-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L) secondary antibody, and re-suspended in PBS for FACS analysis.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
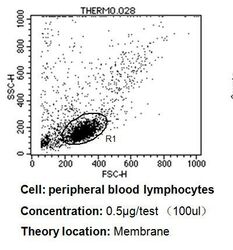
- Experimental details
- Flow cytometry analysis of CD24 in PBMC cells compared to an isotype control (blue). Human blood was collected, combined with a hydrophilic polysaccharide, centrifuged, transferred to a conical tube and washed with PBS. 50 µL of cell solution was added to each tube at a dilution of 2x10^7 cells/mL, followed by the addition of 50 µL of isotype control and primary antibody (Product # MA5-11828) at a dilution of 0.5 µg/test. Cells were incubated for 30 min at 4°C and washed with a cell buffer, followed by incubation with a DyLight 488-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L) secondary for 30 min at 4°C in the dark. FACS analysis was performed using 400 µL of cell buffer.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
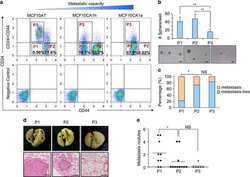
- Figure 5 CD44v3-10 expression is positively correlated with poor prognosis in breast tumors. ( a ) Representative immunofluorescence analyses of total CD44, CD44v and CD24 in human breast cancer samples. White and yellow arrows denote CD24 - /CD44 + /CD44v + and CD24 - /CD44 + /CD44v - cells, respectively. Insets in white and yellow boxes show representative CD24 - /CD44 + /CD44v + and CD24 - /CD44 + /CD44v - cells, respectively. ( b ) CD44v3-10 and CD44s expression ratios analyzed by qPCR in human breast cancer samples, results are expressed as mean+-S.D., n =3. ( c ) Distant metastasis-free survival (DMFS) analysis of the patients in the KM-Plotter database stratified by ESRP1 expression, ( n =1610). ( d ) Correlation of ESRP1 expression and CD44v3-10/CD44s expression ratios in Qilu clinical samples ( n =45). ( e-g ) Distant metastasis-free survival (DMFS) analysis of Qilu clinical samples stratified by expression levels of CD44v3-10 ( e ), total CD44 ( f ) and CD44s ( g ) ( n =63). Scale bars, 10 mu m (insets) and 20 mu m (others)
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
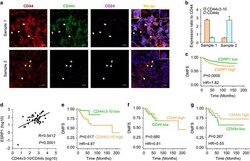
- Experimental details
- Fig 3 Analysis of CD24 expression in human neuroblastoma cells. A) Schematic of the alignment of CD24 splice variants 1 and 7. B & C) Absolute quantification of CD24 expression by quantitative real-time PCR of total RNA acquired from neuroblastoma cells, measuring CD24 splice variants 1 (B) and 7 (C). Copy number values were normalized to the corresponding GAPDH values to determine the relative copy number. ** p > 0.05, Student's t-test. D) Western blot analysis of CD24 expression in the total cell lysates of neuroblastoma cells. GAPDH was used as a loading control. All results are representative of the combined data of experiments performed in triplicate, with error bars representing standard deviation.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
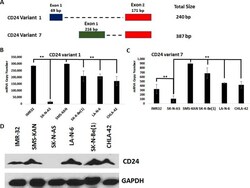
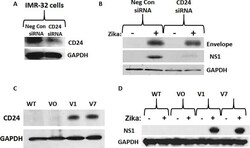
- Fig 4 Analysis of the role of CD24 in Zika-virus infected neuroblastoma cells. A) Western blot analysis of siRNA-mediated knock-down of CD24 expression in IMR-32 cells. Samples include Negative Control siRNA and CD24 siRNA. B) Western blot analysis of the expression of Envelope protein and NS1 (Non-Structural 1) protein in IMR-32 cells after siRNA-mediated knock-down of CD24 expression, 96 hours after Zika infection (MOI = 10). Samples include control cells treated with non-infected conditioned media and infected IMR-32 cells transfected with either Negative Control siRNA or CD24 siRNA. C) Western blot analysis of CD24 expression in the human neuroblastoma cell line SK-N-AS, comparing wild type (WT) to stably selected ""Vector Only"" (VO), CD24 variant 1 (V1), and CD24 variant 7 (V7). D) Western blot analysis of Zika NS1 protein expression 96 hours after Zika infection in CD24-stably expressing SK-N-AS cells, comparing wild type (WT) to stably selected Vector Only (VO), CD24 variant 1 (V1), and CD24 variant 7 (V7). GAPDH was used as a load control for all experiments. All results are representative of the combined data of experiments performed in triplicate.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
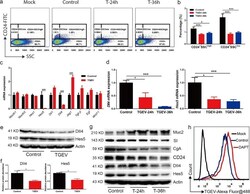
- Fig. 3 TGEV infection results in CD24 + SSC high cells (Paneth cells) loss and Notch signaling inactivation. a Representative FACS of CD24 in TGEV-infected IPEC-J2 cells. b Quantification of CD24 + SSC high (Paneth cells) and CD24 + SSC low (enteroendocrine cells) number in TGEV-infected IPEC-J2 cells. c Jejunum from TGEV-infected piglets were analyzed by quantitative PCR (qPCR) for makers of ISCs niche signaling (Notch, Wnt, and EGF signaling). d Representative Notch factors mRNA change in TGEV-infected IPEC-J2 cells. e Western blot for Notch effector Hes5 and Notch ligand DII4 in jejunum from TGEV-infected piglets. f Quantitation of bands to demonstrate the protein level of DII4 and Hes5. g Representative Notch factors (DII4 and Hes5) and intestinal epithelial cells markers Muc2, SI, CgA, and CD24 were tested by western blot in TGEV-infected IPEC-J2 cells. h TGEV content was tested by FACS in 24 h post TGEV-infected IPEC-J2 cells, which were pre-treated by DAPT for 12 h before TGEV infection, and DAPT continued addition during TGEV infection period.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
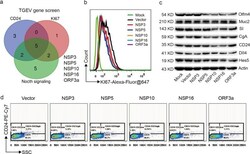
- Fig. 6 TGEV-encoded NSP10 and NSP16 mediate cell proliferation and Lgr5 ISCs fate. a Cell proliferation (KI67), CD24 cells number and Notch signaling factors DII4 and Hes5 were analyzed in TGEV gene stable cell lines. Venn diagram depicts the numbers of decreased cell proliferation and CD24 cells number and down-regulated Notch signaling identified by using FACS and western blot. b FACS for KI67 in TGEV NSPs stable cell lines. c Notch factor and intestinal epithelium markers Muc2, SI, CgA, and CD24 were tested by western blot in TGEV NSPs stable cell lines. d FACS for CD24 in TGEV NSPs stable cell lines.
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry