HPA031755
antibody from Atlas Antibodies
Targeting: SON
BASS1, C21orf50, DBP-5, FLJ21099, FLJ33914, KIAA1019, NREBP
Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [5]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunocytochemistry [1]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- HPA031755 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Atlas Antibodies
- Proper citation
- Atlas Antibodies Cat#HPA031755, RRID:AB_2674029
- Product name
- Anti-SON
- Antibody type
- Polyclonal
- Description
- Polyclonal Antibody against Human SON, Gene description: SON DNA binding protein, Alternative Gene Names: BASS1, C21orf50, DBP-5, FLJ21099, FLJ33914, KIAA1019, NREBP, Validated applications: ICC, WB, Uniprot ID: P18583, Storage: Store at +4°C for short term storage. Long time storage is recommended at -20°C.
- Reactivity
- Human
- Host
- Rabbit
- Conjugate
- Unconjugated
- Isotype
- IgG
- Vial size
- 100 µl
- Concentration
- 0.2 mg/ml
- Storage
- Store at +4°C for short term storage. Long time storage is recommended at -20°C.
- Handling
- The antibody solution should be gently mixed before use.
Submitted references Spatial 3D genome organization controls the activity of bivalent chromatin during human neurogenesis.
Stress-induced nuclear speckle reorganization is linked to activation of immediate early gene splicing
Mammalian nuclear speckles exhibit stable association with chromatin: a biochemical study
Prion-like low complexity regions enable avid virus-host interactions during HIV-1 infection.
HIV-1 replication complexes accumulate in nuclear speckles and integrate into speckle-associated genomic domains
Ahanger SH, Zhang C, Semenza ER, Gil E, Cole MA, Wang L, Kriegstein AR, Lim DA
bioRxiv : the preprint server for biology 2024 Aug 1;
bioRxiv : the preprint server for biology 2024 Aug 1;
Stress-induced nuclear speckle reorganization is linked to activation of immediate early gene splicing
Sung H, Schott J, Boss P, Lehmann J, Hardt M, Lindner D, Messens J, Bogeski I, Ohler U, Stoecklin G
Journal of Cell Biology 2023;222(12)
Journal of Cell Biology 2023;222(12)
Mammalian nuclear speckles exhibit stable association with chromatin: a biochemical study
Raina K, Rao B
Nucleus 2022;13(1):58-73
Nucleus 2022;13(1):58-73
Prion-like low complexity regions enable avid virus-host interactions during HIV-1 infection.
Wei G, Iqbal N, Courouble VV, Francis AC, Singh PK, Hudait A, Annamalai AS, Bester S, Huang SW, Shkriabai N, Briganti L, Haney R, KewalRamani VN, Voth GA, Engelman AN, Melikyan GB, Griffin PR, Asturias F, Kvaratskhelia M
Nature communications 2022 Oct 6;13(1):5879
Nature communications 2022 Oct 6;13(1):5879
HIV-1 replication complexes accumulate in nuclear speckles and integrate into speckle-associated genomic domains
Francis A, Marin M, Singh P, Achuthan V, Prellberg M, Palermino-Rowland K, Lan S, Tedbury P, Sarafianos S, Engelman A, Melikyan G
Nature Communications 2020;11(1)
Nature Communications 2020;11(1)
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Atlas Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
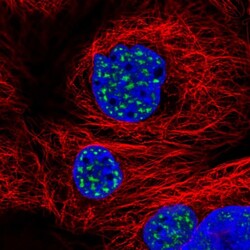
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent staining of human cell line A-431 shows localization to nuclear speckles.
- Sample type
- Human
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry