Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [1]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Other assay [4]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- PA5-68941 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- ZNF589 Polyclonal Antibody
- Antibody type
- Polyclonal
- Antigen
- Synthetic peptide
- Description
- This target displays homology in the following species: Human: 100%
- Reactivity
- Human
- Host
- Rabbit
- Isotype
- IgG
- Vial size
- 100 μL
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/mL
- Storage
- -20°C, Avoid Freeze/Thaw Cycles
Submitted references A heterochromatin inducing protein differentially recognizes self versus foreign genomes.
Burton EM, Akinyemi IA, Frey TR, Xu H, Li X, Su LJ, Zhi J, McIntosh MT, Bhaduri-McIntosh S
PLoS pathogens 2021 Mar;17(3):e1009447
PLoS pathogens 2021 Mar;17(3):e1009447
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
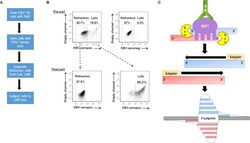
- Experimental details
- Fig 1 ChIP-exo in sorted-refractory cells to map genome-wide SZF1-binding sites. ( A ) Experimental design for isolation of EBV-positive refractory and lytic cells for ChIP (chromatin immunoprecipitation)-exo protocol. ( B ) Pre-sort and post-sort analysis of FACS separation of refractory and lytic cells. EBV-positive HH514-16 BL cells were treated with NaB for 24 hours and harvested for flow sorting. (B, top) Reference EBV-seropositive serum was used to demarcate lytic cells and EBV-seronegative serum was used as negative control for gating purposes. (B, bottom) Post-sort analysis was performed to confirm purity and efficacy of sort. ( C ) Illustration of ChIP-exo protocol for SZF1 in sorted cells. DNA immunoprecipitated by anti-SZF1 antibody is treated with a 5''-to-3'' exonuclease (Exo) while still in the immunoprecipitate. The 5'' ends of digested DNA are concentrated at a fixed distance from the sites of crosslinking (i.e. footprint) and are detected by deep sequencing.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
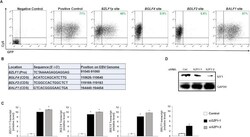
- Experimental details
- Fig 2 Effects of EBV genome-derived candidate SZF1-binding sites on extrachromosomal gene expression. ( A ) Candidate SZF1-binding site fragments from the EBV genome were cloned into pEGFP-N1 vector. SZF1-binding site pEGFP-N1 vectors or control pEGPFn1 vector (positive control) were transfected into HEK293T cells and assayed for relative GFP expression by flow cytometry. In addition, Cy5-non-targeting siRNA was co-transfected to monitor transfection efficiency between samples. Empty vector and non-fluorescent, non-targeting control siRNA-transfected 293T cells were used as negative control and for gating purposes. Percent cells expressing GFP are labeled in green. ( B ) Sequences of candidate SZF1-binding sites identified via ChIP-exo and tested in panel A. Positions on the EBV genome and with respect to nearby ""target"" genes are also shown; Pro, promoter; CDS, coding sequence. ( C ) Knockdown of SZF1 using two separate siRNAs or a control non-targeting siRNA was performed in HH514-16 BL cells. After 24 hours, NaB was added to activate EBV lytic cycle. After another 24 hours, cells were harvested for RNA extraction and RT-qPCR analysis was performed for relative EBV lytic transcripts in control non-targeting siRNA-transfected cells (white bar) versus two distinct siRNAs targeting SZF1 (black and grey bars). Data represent averages of three independent experiments; error bars, SEM; *, p
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
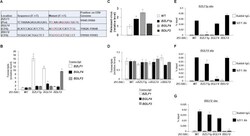
- Experimental details
- Fig 3 Mutations in candidate SZF1-binding sites derepress EBV lytic genes. ( A ) Synonymous point mutations were made in candidate SZF1-binding sites on the p2089 BACmid via red recombineering. Mutant residues are shown in red. ( B ) After transfection and hygromycin selection (~ 2 weeks later), 293-BAC cells harboring wild-type p2089 BACmid or BACmids with mutant SZF1-binding sites were harvested for RNA extraction and RT-qPCR analysis for relative expression of EBV lytic genes (from each kinetic class: BZLF1 , immediate early; BGLF4 , early; BDLF2 , late), compared to wild-type BAC sample. ( C ) Supernatants from 293-BAC cells harboring p2089-BACs bearing BZLF1 promoter, BGLF4 coding sequence, or BDLF2 coding sequence SZF1-binding site mutations were harvested and analyzed via qPCR for relative amounts of released DNase-resistant virus compared to the wild-type 293-BAC sample. ( D ) 293-BAC cells harboring wild-type p2089-BAC or p2089 BACmids that underwent reversion (r) mutations for their respective SZF1-binding sites were tested by RT-qPCR of lytic genes BZLF1 , BGLF4 , and BDLF2 relative to wild-type 293-BAC. ( E-G ) SZF1-ChIP was performed on wild-type 293-BAC samples or 293-BACs harboring SZF1-binding site mutations; precipitated chromatin was analyzed via qPCR using primers to amplify PCR products flanking the putative BZLF1 promoter sequence (E), the BGLF4 coding sequence site (F), or the BDLF2 coding sequence site (G). ChIP-PCR results were analyzed relative to 1%
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
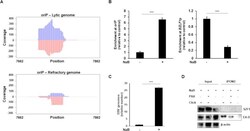
- Experimental details
- Fig 8 SZF1 is enriched at oriP on the lytic genome but is not associated with actively replicating viral DNA. A. Read coverage at EBV oriP. Plots show the read distributions at oriP under lytic and refractory conditions. Coverage of the reads from lytic and refractory genomes were determined with Bedtools software (v2.30.0) and plotted in R. Lytic reads were normalized to refractory EBV genome copy number, Rightward and leftward strands are indicated by blue and red, respectively. Genome position numbers corresponding to the reference genome NC_007605 are indicated. B-D. EBV-positive cells were untreated or exposed to NaB for 36 hours (or 24 hours in C) and subjected to (B) ChIP with anti-SZF1 antibody or control antibody followed by qPCR amplification of oriP and BZLF1 p and analysis of data by normalizing to 2% input and IgG control, (C) isolation of intracellular DNA and qPCR amplification of BALF5 gene, or (D) isolation of proteins on nascent DNA (iPOND) followed by western blotting with indicated antibodies. Data in B and C represent averages of two independent experiments; error bars, SEM; ***, p < 0.001; iPOND was performed twice.
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Other assay
Other assay