Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [16]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Western blot [1]
- Immunohistochemistry [1]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- 66124-1-Ig - Provider product page

- Provider
- Proteintech Group
- Product name
- APOL1-Specific antibody
- Antibody type
- Monoclonal
- Description
- KD/KO validated APOL1-Specific antibody (Cat. #66124-1-Ig) is a mouse monoclonal antibody that shows reactivity with human and has been validated for the following applications: FC, IF, IHC, IP, WB,ELISA.
- Reactivity
- Human
- Host
- Mouse
- Conjugate
- Unconjugated
- Isotype
- IgG
- Antibody clone number
- 1G12D11
- Vial size
- 20ul, 150ul
Submitted references Identifying endoplasmic reticulum stress-related genes as new diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in clear cell renal cell carcinoma.
APOL1-G2 accelerates nephrocyte cell death by inhibiting the autophagy pathway.
Human Cytomegalovirus UL23 Antagonizes the Antiviral Effect of Interferon-γ by Restraining the Expression of Specific IFN-Stimulated Genes.
Apolipoprotein L1 is increased in frontotemporal lobar degeneration post-mortem brain but not in ante-mortem cerebrospinal fluid.
Antisense oligonucleotides ameliorate kidney dysfunction in podocyte-specific APOL1 risk variant mice.
The key role of NLRP3 and STING in APOL1-associated podocytopathy.
APOL1 risk variants in individuals of African genetic ancestry drive endothelial cell defects that exacerbate sepsis.
Recessive, gain-of-function toxicity in an APOL1 BAC transgenic mouse model mirrors human APOL1 kidney disease.
Kidney Disease-Associated APOL1 Variants Have Dose-Dependent, Dominant Toxic Gain-of-Function.
Alterations in plasma membrane ion channel structures stimulate NLRP3 inflammasome activation in APOL1 risk milieu.
Apolipoprotein L-1 renal risk variants form active channels at the plasma membrane driving cytotoxicity.
Disruption of APOL1-miR193a Axis Induces Disorganization of Podocyte Actin Cytoskeleton.
Disrupted apolipoprotein L1-miR193a axis dedifferentiates podocytes through autophagy blockade in an APOL1 risk milieu.
Role of Apolipoprotein L1 in Human Parietal Epithelial Cell Transition.
Modulation of apolipoprotein L1-microRNA-193a axis prevents podocyte dedifferentiation in high-glucose milieu.
APOL1 risk variants cause podocytes injury through enhancing endoplasmic reticulum stress.
Yu H, Zhang C, Bai X, Yin H, Li X, Zhou X, He W, Kuang Y, Gou X, Li J
Translational andrology and urology 2024 Jan 31;13(1):1-24
Translational andrology and urology 2024 Jan 31;13(1):1-24
APOL1-G2 accelerates nephrocyte cell death by inhibiting the autophagy pathway.
Zhu JY, Lee JG, Fu Y, van de Leemput J, Ray PE, Han Z
Disease models & mechanisms 2023 Dec 1;16(12)
Disease models & mechanisms 2023 Dec 1;16(12)
Human Cytomegalovirus UL23 Antagonizes the Antiviral Effect of Interferon-γ by Restraining the Expression of Specific IFN-Stimulated Genes.
Wang H, Peng W, Wang J, Zhang C, Zhao W, Ran Y, Yang X, Chen J, Li H
Viruses 2023 Apr 20;15(4)
Viruses 2023 Apr 20;15(4)
Apolipoprotein L1 is increased in frontotemporal lobar degeneration post-mortem brain but not in ante-mortem cerebrospinal fluid.
Hok-A-Hin YS, Dijkstra AA, Rábano A, Hoozemans JJ, Castillo L, Seelaar H, van Swieten JC, Pijnenburg YAL, Teunissen CE, Del Campo M
Neurobiology of disease 2022 Oct 1;172:105813
Neurobiology of disease 2022 Oct 1;172:105813
Antisense oligonucleotides ameliorate kidney dysfunction in podocyte-specific APOL1 risk variant mice.
Yang YW, Poudel B, Frederick J, Dhillon P, Shrestha R, Ma Z, Wu J, Okamoto K, Kopp JB, Booten SL, Gattis D, Watt AT, Palmer M, Aghajan M, Susztak K
Molecular therapy : the journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy 2022 Jul 6;30(7):2491-2504
Molecular therapy : the journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy 2022 Jul 6;30(7):2491-2504
The key role of NLRP3 and STING in APOL1-associated podocytopathy.
Wu J, Raman A, Coffey NJ, Sheng X, Wahba J, Seasock MJ, Ma Z, Beckerman P, Laczkó D, Palmer MB, Kopp JB, Kuo JJ, Pullen SS, Boustany-Kari CM, Linkermann A, Susztak K
The Journal of clinical investigation 2021 Oct 15;131(20)
The Journal of clinical investigation 2021 Oct 15;131(20)
APOL1 risk variants in individuals of African genetic ancestry drive endothelial cell defects that exacerbate sepsis.
Wu J, Ma Z, Raman A, Beckerman P, Dhillon P, Mukhi D, Palmer M, Chen HC, Cohen CR, Dunn T, Reilly J, Meyer N, Shashaty M, Arany Z, Haskó G, Laudanski K, Hung A, Susztak K
Immunity 2021 Nov 9;54(11):2632-2649.e6
Immunity 2021 Nov 9;54(11):2632-2649.e6
Recessive, gain-of-function toxicity in an APOL1 BAC transgenic mouse model mirrors human APOL1 kidney disease.
McCarthy GM, Blasio A, Donovan OG, Schaller LB, Bock-Hughes A, Magraner JM, Suh JH, Tattersfield CF, Stillman IE, Shah SS, Zsengeller ZK, Subramanian B, Friedman DJ, Pollak MR
Disease models & mechanisms 2021 Aug 1;14(8)
Disease models & mechanisms 2021 Aug 1;14(8)
Kidney Disease-Associated APOL1 Variants Have Dose-Dependent, Dominant Toxic Gain-of-Function.
Datta S, Kataria R, Zhang JY, Moore S, Petitpas K, Mohamed A, Zahler N, Pollak MR, Olabisi OA
Journal of the American Society of Nephrology : JASN 2020 Sep;31(9):2083-2096
Journal of the American Society of Nephrology : JASN 2020 Sep;31(9):2083-2096
Alterations in plasma membrane ion channel structures stimulate NLRP3 inflammasome activation in APOL1 risk milieu.
Jha A, Kumar V, Haque S, Ayasolla K, Saha S, Lan X, Malhotra A, Saleem MA, Skorecki K, Singhal PC
The FEBS journal 2020 May;287(10):2000-2022
The FEBS journal 2020 May;287(10):2000-2022
Apolipoprotein L-1 renal risk variants form active channels at the plasma membrane driving cytotoxicity.
Giovinazzo JA, Thomson RP, Khalizova N, Zager PJ, Malani N, Rodriguez-Boulan E, Raper J, Schreiner R
eLife 2020 May 19;9
eLife 2020 May 19;9
Disruption of APOL1-miR193a Axis Induces Disorganization of Podocyte Actin Cytoskeleton.
Kumar V, Paliwal N, Ayasolla K, Vashistha H, Jha A, Chandel N, Chowdhary S, Saleem MA, Malhotra A, Chander PN, Skorecki K, Singhal PC
Scientific reports 2019 Mar 5;9(1):3582
Scientific reports 2019 Mar 5;9(1):3582
Disrupted apolipoprotein L1-miR193a axis dedifferentiates podocytes through autophagy blockade in an APOL1 risk milieu.
Kumar V, Ayasolla K, Jha A, Mishra A, Vashistha H, Lan X, Qayyum M, Chinnapaka S, Purohit R, Mikulak J, Saleem MA, Malhotra A, Skorecki K, Singhal PC
American journal of physiology. Cell physiology 2019 Aug 1;317(2):C209-C225
American journal of physiology. Cell physiology 2019 Aug 1;317(2):C209-C225
Role of Apolipoprotein L1 in Human Parietal Epithelial Cell Transition.
Kumar V, Vashistha H, Lan X, Chandel N, Ayasolla K, Shoshtari SSM, Aslam R, Paliwal N, Abbruscato F, Mikulak J, Popik W, Atta MG, Chander PN, Malhotra A, Meyer-Schwesinger C, Skorecki K, Singhal PC
The American journal of pathology 2018 Nov;188(11):2508-2528
The American journal of pathology 2018 Nov;188(11):2508-2528
Modulation of apolipoprotein L1-microRNA-193a axis prevents podocyte dedifferentiation in high-glucose milieu.
Mishra A, Ayasolla K, Kumar V, Lan X, Vashistha H, Aslam R, Hussain A, Chowdhary S, Marashi Shoshtari S, Paliwal N, Popik W, Saleem MA, Malhotra A, Meggs LG, Skorecki K, Singhal PC
American journal of physiology. Renal physiology 2018 May 1;314(5):F832-F843
American journal of physiology. Renal physiology 2018 May 1;314(5):F832-F843
APOL1 risk variants cause podocytes injury through enhancing endoplasmic reticulum stress.
Wen H, Kumar V, Lan X, Shoshtari SSM, Eng JM, Zhou X, Wang F, Wang H, Skorecki K, Xing G, Wu G, Luo H, Malhotra A, Singhal PC
Bioscience reports 2018 Aug 31;38(4)
Bioscience reports 2018 Aug 31;38(4)
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Proteintech Group (provider)
- Main image
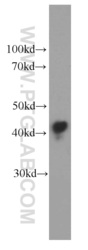
- Experimental details
- human blood tissue were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with 66124-1-Ig(APOL1 antibody) at dilution of 1:20000
- Sample type
- tissue
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Proteintech Group (provider)
- Main image
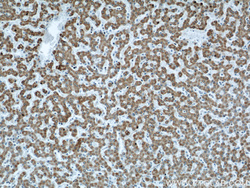
- Experimental details
- The APOL1 antibody from Proteintech is a mouse monoclonal antibody to a fusion protein of human APOL1. This antibody recognizes human antigen. The APOL1 antibody has been validated for the following applications: ELISA, WB, IHC analysis.
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot ELISA
ELISA