Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [23]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunocytochemistry [8]
- Other assay [4]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- MA1-515 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- HIF-1 beta Monoclonal Antibody (2B10)
- Antibody type
- Monoclonal
- Antigen
- Synthetic peptide
- Description
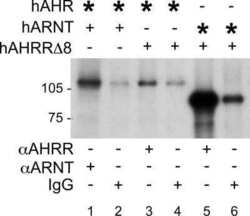
- MA1-515 detects aryl hydrocarbon (Ah) receptor nuclear translocator (ARNT) from human, mouse, rat, and primate tissues. MA1-515 has been successfully used in Western blot, immunofluorescence, gel shift, immunocytochemistry, and immunoprecipitation procedures. By Western blot, this antibody detects an 87 kDa protein representing ARNT in COS cell extract. Immunofluorescence staining of ARNT in VT{2} cells (Hepa 1-C4T mutant deficient in ARNT function but stably transfected with the full length human ARNT cDNA) using MA1-515 yields non-nucleolar, nuclear staining only. MA1-515 immunogen is a synthetic peptide corresponding to residues C N(771) S Y N N E E F P D L T M F P P F S E(789) of human ARNT.
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat
- Host
- Mouse
- Isotype
- IgG
- Antibody clone number
- 2B10
- Vial size
- 100 μL
- Concentration
- 1 mg/mL
- Storage
- -20°C, Avoid Freeze/Thaw Cycles
Submitted references A common functional regulatory variant at a type 2 diabetes locus upregulates ARAP1 expression in the pancreatic beta cell.
Reciprocal regulation of the basic helix-loop-helix/Per-Arnt-Sim partner proteins, Arnt and Arnt2, during neuronal differentiation.
Hypoxia-inducible factor and vascular endothelial growth factor are targets of dietary soy during acute stroke in female rats.
Effect of transient TCDD exposure on immortalized human trophoblast-derived cell lines.
Identification of residues in the N-terminal PAS domains important for dimerization of Arnt and AhR.
Dioxin toxicity in vivo results from an increase in the dioxin-independent transcriptional activity of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor.
Amino acid substitutions in the aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligand binding domain reveal YH439 as an atypical AhR activator.
Evidence for ligand-mediated selective modulation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor activity.
The active form of human aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) repressor lacks exon 8, and its Pro 185 and Ala 185 variants repress both AHR and hypoxia-inducible factor.
Repression of aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) signaling by AHR repressor: role of DNA binding and competition for AHR nuclear translocator.
ARNT gene multiplicity in amphibians: characterization of ARNT2 from the frog Xenopus laevis.
Rescue of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha-deficient tumor growth by wild-type cells is independent of vascular endothelial growth factor.
Recruitment of dioxin receptor to active transcription sites.
Recruitment of dioxin receptor to active transcription sites.
Isoform-specific expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha during the late stages of mouse spermiogenesis.
Identification and functional characterization of hypoxia-inducible factor 2alpha from the estuarine teleost, Fundulus heteroclitus: interaction of HIF-2alpha with two ARNT2 splice variants.
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor/dioxin receptor in human monocytes and macrophages.
A new HIF-1 alpha variant induced by zinc ion suppresses HIF-1-mediated hypoxic responses.
A new HIF-1 alpha variant induced by zinc ion suppresses HIF-1-mediated hypoxic responses.
DNA methylation represses the expression of the human erythropoietin gene by two different mechanisms.
Protection from oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in cortical neuronal cultures by iron chelators is associated with enhanced DNA binding of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 and ATF-1/CREB and increased expression of glycolytic enzymes, p21(waf1/cip1), and erythropoietin.
Up-regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha is not sufficient for hypoxic/anoxic p53 induction.
Physicochemical and immunocytochemical analysis of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator: characterization of two monoclonal antibodies to the aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator.
Kulzer JR, Stitzel ML, Morken MA, Huyghe JR, Fuchsberger C, Kuusisto J, Laakso M, Boehnke M, Collins FS, Mohlke KL
American journal of human genetics 2014 Feb 6;94(2):186-97
American journal of human genetics 2014 Feb 6;94(2):186-97
Reciprocal regulation of the basic helix-loop-helix/Per-Arnt-Sim partner proteins, Arnt and Arnt2, during neuronal differentiation.
Hao N, Bhakti VL, Peet DJ, Whitelaw ML
Nucleic acids research 2013 Jun;41(11):5626-38
Nucleic acids research 2013 Jun;41(11):5626-38
Hypoxia-inducible factor and vascular endothelial growth factor are targets of dietary soy during acute stroke in female rats.
Ma Y, Lovekamp-Swan T, Bekele W, Dohi A, Schreihofer DA
Endocrinology 2013 Apr;154(4):1589-97
Endocrinology 2013 Apr;154(4):1589-97
Effect of transient TCDD exposure on immortalized human trophoblast-derived cell lines.
Fukushima K, Tsukimori K, Li D, Takao T, Morokuma S, Kato K, Seki H, Takeda S, Matsumura S, Wake N
Human & experimental toxicology 2012 Jun;31(6):550-6
Human & experimental toxicology 2012 Jun;31(6):550-6
Identification of residues in the N-terminal PAS domains important for dimerization of Arnt and AhR.
Hao N, Whitelaw ML, Shearwin KE, Dodd IB, Chapman-Smith A
Nucleic acids research 2011 May;39(9):3695-709
Nucleic acids research 2011 May;39(9):3695-709
Dioxin toxicity in vivo results from an increase in the dioxin-independent transcriptional activity of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor.
Céspedes MA, Galindo MI, Couso JP
PloS one 2010 Nov 8;5(11):e15382
PloS one 2010 Nov 8;5(11):e15382
Amino acid substitutions in the aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligand binding domain reveal YH439 as an atypical AhR activator.
Whelan F, Hao N, Furness SG, Whitelaw ML, Chapman-Smith A
Molecular pharmacology 2010 Jun;77(6):1037-46
Molecular pharmacology 2010 Jun;77(6):1037-46
Evidence for ligand-mediated selective modulation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor activity.
Murray IA, Morales JL, Flaveny CA, Dinatale BC, Chiaro C, Gowdahalli K, Amin S, Perdew GH
Molecular pharmacology 2010 Feb;77(2):247-54
Molecular pharmacology 2010 Feb;77(2):247-54
The active form of human aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) repressor lacks exon 8, and its Pro 185 and Ala 185 variants repress both AHR and hypoxia-inducible factor.
Karchner SI, Jenny MJ, Tarrant AM, Evans BR, Kang HJ, Bae I, Sherr DH, Hahn ME
Molecular and cellular biology 2009 Jul;29(13):3465-77
Molecular and cellular biology 2009 Jul;29(13):3465-77
Repression of aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) signaling by AHR repressor: role of DNA binding and competition for AHR nuclear translocator.
Evans BR, Karchner SI, Allan LL, Pollenz RS, Tanguay RL, Jenny MJ, Sherr DH, Hahn ME
Molecular pharmacology 2008 Feb;73(2):387-98
Molecular pharmacology 2008 Feb;73(2):387-98
ARNT gene multiplicity in amphibians: characterization of ARNT2 from the frog Xenopus laevis.
Rowatt AJ, DePowell JJ, Powell WH
Journal of experimental zoology. Part B, Molecular and developmental evolution 2003 Dec 15;300(1):48-57
Journal of experimental zoology. Part B, Molecular and developmental evolution 2003 Dec 15;300(1):48-57
Rescue of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha-deficient tumor growth by wild-type cells is independent of vascular endothelial growth factor.
Höpfl G, Wenger RH, Ziegler U, Stallmach T, Gardelle O, Achermann R, Wergin M, Kaser-Hotz B, Saunders HM, Williams KJ, Stratford IJ, Gassmann M, Desbaillets I
Cancer research 2002 May 15;62(10):2962-70
Cancer research 2002 May 15;62(10):2962-70
Recruitment of dioxin receptor to active transcription sites.
Elbi C, Misteli T, Hager GL
Molecular biology of the cell 2002 Jun;13(6):2001-15
Molecular biology of the cell 2002 Jun;13(6):2001-15
Recruitment of dioxin receptor to active transcription sites.
Elbi C, Misteli T, Hager GL
Molecular biology of the cell 2002 Jun;13(6):2001-15
Molecular biology of the cell 2002 Jun;13(6):2001-15
Isoform-specific expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha during the late stages of mouse spermiogenesis.
Marti HH, Katschinski DM, Wagner KF, Schäffer L, Stier B, Wenger RH
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 2002 Feb;16(2):234-43
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 2002 Feb;16(2):234-43
Identification and functional characterization of hypoxia-inducible factor 2alpha from the estuarine teleost, Fundulus heteroclitus: interaction of HIF-2alpha with two ARNT2 splice variants.
Powell WH, Hahn ME
The Journal of experimental zoology 2002 Apr 15;294(1):17-29
The Journal of experimental zoology 2002 Apr 15;294(1):17-29
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor/dioxin receptor in human monocytes and macrophages.
Komura K, Hayashi S, Makino I, Poellinger L, Tanaka H
Molecular and cellular biochemistry 2001 Oct;226(1-2):107-18
Molecular and cellular biochemistry 2001 Oct;226(1-2):107-18
A new HIF-1 alpha variant induced by zinc ion suppresses HIF-1-mediated hypoxic responses.
Chun YS, Choi E, Yeo EJ, Lee JH, Kim MS, Park JW
Journal of cell science 2001 Nov;114(Pt 22):4051-61
Journal of cell science 2001 Nov;114(Pt 22):4051-61
A new HIF-1 alpha variant induced by zinc ion suppresses HIF-1-mediated hypoxic responses.
Chun YS, Choi E, Yeo EJ, Lee JH, Kim MS, Park JW
Journal of cell science 2001 Nov;114(Pt 22):4051-61
Journal of cell science 2001 Nov;114(Pt 22):4051-61
DNA methylation represses the expression of the human erythropoietin gene by two different mechanisms.
Yin H, Blanchard KL
Blood 2000 Jan 1;95(1):111-9
Blood 2000 Jan 1;95(1):111-9
Protection from oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in cortical neuronal cultures by iron chelators is associated with enhanced DNA binding of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 and ATF-1/CREB and increased expression of glycolytic enzymes, p21(waf1/cip1), and erythropoietin.
Zaman K, Ryu H, Hall D, O'Donovan K, Lin KI, Miller MP, Marquis JC, Baraban JM, Semenza GL, Ratan RR
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 1999 Nov 15;19(22):9821-30
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 1999 Nov 15;19(22):9821-30
Up-regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha is not sufficient for hypoxic/anoxic p53 induction.
Wenger RH, Camenisch G, Desbaillets I, Chilov D, Gassmann M
Cancer research 1998 Dec 15;58(24):5678-80
Cancer research 1998 Dec 15;58(24):5678-80
Physicochemical and immunocytochemical analysis of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator: characterization of two monoclonal antibodies to the aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator.
Hord NG, Perdew GH
Molecular pharmacology 1994 Oct;46(4):618-26
Molecular pharmacology 1994 Oct;46(4):618-26
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
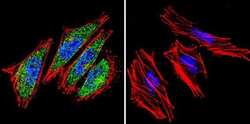
- Experimental details
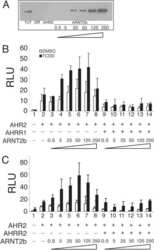
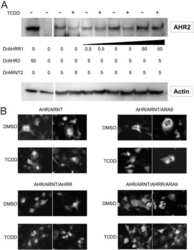
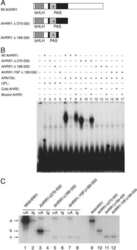
- Immunofluorescent analysis of HIF-1 beta using HIF-1 beta Monoclonal Antibody (2B10) (Product # MA1-515) shows staining in A2058 Cells. HIF-1 beta (green), F-Actin staining with Phalloidin (red) and nuclei with DAPI (blue) is shown. Cells were grown on chamber slides and fixed with formaldehyde prior to staining. Cells were probed without (control) or with an antibody recognizing HIF-1 beta (Product # MA1-515) at a dilution of 1:100 over night at 4 °C, washed with PBS and incubated with a DyLight-488 conjugated secondary antibody (Product # 35552 for GAR, Product # 35503 for GAM). Images were taken at 60X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
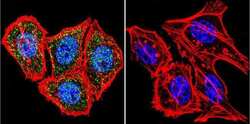
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of HIF-1 beta using HIF-1 beta Monoclonal Antibody (2B10) (Product # MA1-515) shows staining in Hela Cells. HIF-1 beta (green), F-Actin staining with Phalloidin (red) and nuclei with DAPI (blue) is shown. Cells were grown on chamber slides and fixed with formaldehyde prior to staining. Cells were probed without (control) or with an antibody recognizing HIF-1 beta (Product # MA1-515) at a dilution of 1:20 over night at 4 °C, washed with PBS and incubated with a DyLight-488 conjugated secondary antibody (Product # 35552 for GAR, Product # 35503 for GAM). Images were taken at 60X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
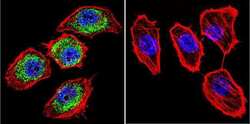
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of HIF-1 beta using HIF-1 beta Monoclonal Antibody (2B10) (Product # MA1-515) shows staining in U251 Cells. HIF-1 beta (green), F-Actin staining with Phalloidin (red) and nuclei with DAPI (blue) is shown. Cells were grown on chamber slides and fixed with formaldehyde prior to staining. Cells were probed without (control) or with an antibody recognizing HIF-1 beta (Product # MA1-515) at a dilution of 1:100 over night at 4 °C, washed with PBS and incubated with a DyLight-488 conjugated secondary antibody (Product # 35552 for GAR, Product # 35503 for GAM). Images were taken at 60X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
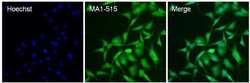
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of HIF-1 beta (green) in NRK cells. The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 minutes, permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 in PBS for 15 minutes, and blocked with 3% BSA in PBS (Product # 37525) for 30 minutes at room temperature. Cells were stained with a HIF-1 beta antibody (Product # MA1-515) at a dilution of 40 µg/mL in staining buffer for 1 hour at room temperature, and then incubated with a Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Superclonal Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor 488 conjugate (Product # A28175) at a dilution of 1:1000 for 1 hour at room temperature (green). Nuclei (blue) were stained with Hoechst 33342 dye (Product # 62249). Images were taken on a Thermo Scientific ToxInsight Instrument at 20X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
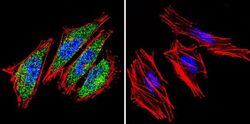
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of HIF-1 beta using HIF-1 beta Monoclonal Antibody (2B10) (Product # MA1-515) shows staining in A2058 Cells. HIF-1 beta (green), F-Actin staining with Phalloidin (red) and nuclei with DAPI (blue) is shown. Cells were grown on chamber slides and fixed with formaldehyde prior to staining. Cells were probed without (control) or with an antibody recognizing HIF-1 beta (Product # MA1-515) at a dilution of 1:100 over night at 4 °C, washed with PBS and incubated with a DyLight-488 conjugated secondary antibody (Product # 35552 for GAR, Product # 35503 for GAM). Images were taken at 60X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
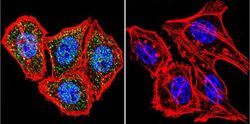
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of HIF-1 beta using HIF-1 beta Monoclonal Antibody (2B10) (Product # MA1-515) shows staining in Hela Cells. HIF-1 beta (green), F-Actin staining with Phalloidin (red) and nuclei with DAPI (blue) is shown. Cells were grown on chamber slides and fixed with formaldehyde prior to staining. Cells were probed without (control) or with an antibody recognizing HIF-1 beta (Product # MA1-515) at a dilution of 1:20 over night at 4 °C, washed with PBS and incubated with a DyLight-488 conjugated secondary antibody (Product # 35552 for GAR, Product # 35503 for GAM). Images were taken at 60X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
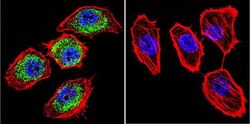
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of HIF-1 beta using HIF-1 beta Monoclonal Antibody (2B10) (Product # MA1-515) shows staining in U251 Cells. HIF-1 beta (green), F-Actin staining with Phalloidin (red) and nuclei with DAPI (blue) is shown. Cells were grown on chamber slides and fixed with formaldehyde prior to staining. Cells were probed without (control) or with an antibody recognizing HIF-1 beta (Product # MA1-515) at a dilution of 1:100 over night at 4 °C, washed with PBS and incubated with a DyLight-488 conjugated secondary antibody (Product # 35552 for GAR, Product # 35503 for GAM). Images were taken at 60X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
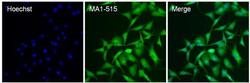
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of HIF-1 beta (green) in NRK cells. The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 minutes, permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 in PBS for 15 minutes, and blocked with 3% BSA in PBS (Product # 37525) for 30 minutes at room temperature. Cells were stained with a HIF-1 beta antibody (Product # MA1-515) at a dilution of 40 µg/mL in staining buffer for 1 hour at room temperature, and then incubated with a Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Superclonal Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor 488 conjugate (Product # A28175) at a dilution of 1:1000 for 1 hour at room temperature (green). Nuclei (blue) were stained with Hoechst 33342 dye (Product # 62249). Images were taken on a Thermo Scientific ToxInsight Instrument at 20X magnification.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry Immunoprecipitation
Immunoprecipitation