Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [2]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Other assay [4]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- PA5-50932 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- CMKLR1 Polyclonal Antibody
- Antibody type
- Polyclonal
- Antigen
- Synthetic peptide
- Description
- CHEMR23 / CMKLR1 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of CHEMR23 / CMKLR1 protein.
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat
- Host
- Rabbit
- Isotype
- IgG
- Vial size
- 100 μL
- Concentration
- 1 mg/mL
- Storage
- -20°C, Avoid Freeze/Thaw Cycles
Submitted references Curcumin inhibits the proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells by targeting the chemerin / CMKLR1 / LCN2 axis.
Resolvin E1 in Follicular Fluid Acts as a Potential Biomarker and Improves Oocyte Developmental Competence by Optimizing Cumulus Cells.
He Y, Wang R, Zhang P, Yan J, Gong N, Li Y, Dong S
Aging 2021 May 24;13(10):13859-13875
Aging 2021 May 24;13(10):13859-13875
Resolvin E1 in Follicular Fluid Acts as a Potential Biomarker and Improves Oocyte Developmental Competence by Optimizing Cumulus Cells.
Zhang Y, Zhu Z, Li H, Zhu M, Peng X, Xin A, Qu R, He W, Fu J, Sun X
Frontiers in endocrinology 2020;11:210
Frontiers in endocrinology 2020;11:210
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
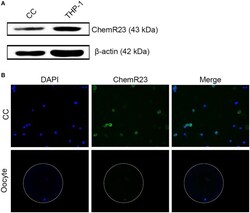
- Figure 2 Identification of RvE1's receptor on cumulus cells (CCs) and oocytes. (A) Detection of ChemR23 expression on CCs by western blot. THP-1 as a positive control; beta-actin as the internal reference. Three independent biological replicates. (B) The presence of ChemR23 (green) on CCs and oocyte was analyzed by fluorescence microscope. The nuclei of CCs and oocyte were stained with DAPI (blue). The outside silhouette of oocyte was presented by a white ring manually. Three independent biological replicates.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
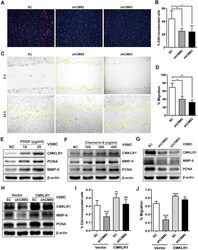
- Figure 2 Downregulation of CMKLR1 inhibit VSMCs proliferation and migration. ( A , B ) Percentage of 5-Ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine (EdU)-incorporated cells following the application of two independent shRNAs targeting CMKLR1 (scramble control, SC; shCMKLR1#2, shCM#2; shCMKLR1#3, shCM#3) to knock down CMKLR1 expression in mice vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs). *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01. ( C , D ) Percentage of cell migration as determined by wound healing assay. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01. ( E ) Western blots showing CMKLR1, MMP-9 and PCNA expressions in cells treated with PDGF (48 h) for different durations. ( F ) Western blots showing CMKLR1, matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) expression in cells treated with chemerin-9 (48 h) for different durations. ( G ) Western blots showing CMKLR1, MMP-9 and PCNA expressions with or without CMKLR1 knockdown. ( H ) Western blots showing CMKLR1, MMP-9 and PCNA expressions following the application of plasmids encoding CMKLR1 to overexpress CMKLR1 expression in VSMCs with or without CMKLR1 knockdown. ( I ) Analysis of the percentage EdU-incorporated cells with or without LCN2 depletion. ****, p < 0.0001; **, p < 0.01; ns, no significant difference. ( J ) Percentage of cell migration as determined by wound healing assay. ****, p < 0.0001; **, p < 0.01.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
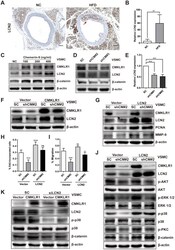
- Figure 3 LCN2 is essential for the inhibition of VSMCs proliferation by CMKLR1 depletion. ( A ) IHC analysis of Lipocalin-2 (LCN2) expression in aorta tissues of mice fed with normal and HFD. Scale bar = 100 mum. Red arrows indicate plaques. ( B ) Chemerin expression score analysis data presented as the means +- SDs. **, p < 0.01. ( C ) Western blots showing LCN2, MMP-9, and beta-catenin expression in cells treated with chemerin-9 (48 h) for different durations. ( D ) Western blot showing LCN2, MMP-9, and beta-catenin expression, with or without CMKLR1 knockdown. ( E ) mRNA expression of LCN2, with or without CMKLR1 depletion, as determined by quantitative real-time PCR. ( F ) Western blots showing CMKLR1 and LCN2 expression following the application of plasmids encoding CMKLR1 to overexpress CMKLR1 expression in VSMCs with or without CMKLR1 depletion. ( G ) Western blots showing CMKLR1, LCN2, PCNA and MMP-9 expression following the application of plasmids encoding LCN2 to overexpress LCN2 expression in VSMCs with or without CMKLR1 depletion. ( H ) Analysis of the percentage EdU-incorporated cells. ****, p < 0.0001; ns, no significant difference. ( I ) Cell migration as determined by wound healing assay. Percentage of cell migration data presented as means +- SDs. ****, p < 0.0001; **, p < 0.01; *, p < 0.05. ( J ) Western blots showing CMKLR1, LCN2, p-AKT, AKT, p-ERK 1/2, ERK 1/2, p-p38, p38, p-PKC and beta-catenin expression following the application of plasmids encoding LCN
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
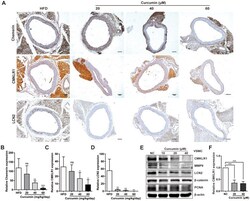
- Figure 5 Curcumin inhibits CMKLR1 and LCN2 expression. ( A ) IHC analysis of chemerin / CMKLR1 and LCN2 expressions in aorta tissues of HFD ApoE -/- mice with or without curcumin treatment. Scale bar = 100 mum. Red arrows indicate plaques. ( B - D ) Chemerin / CMKLR1 and LCN2 expression score analysis data are presented as means +- SDs. n.s., no significant; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001. ( E ) Western blots showing CMKLR1, MMP-9, LCN2, beta-catenin and PCNA expressions in cells treated with curcumin (48 h) for different durations. ( F ) mRNA expression of CMKLR1 with or without curcumin treatment (48 h) as determined by quantitative real-time PCR.
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry Other assay
Other assay