Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [11]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Flow cytometry [2]
- Other assay [3]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- 14-0497-37 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- Integrin beta 5 Monoclonal Antibody (KN52), eBioscience™
- Antibody type
- Monoclonal
- Antigen
- Other
- Description
- Description: The KN52 antibody reacts with human integrin beta 5, an approximately 100,000 Mr (reduced) and 95,000 Mr (nonreduced) a member of the integrin family. Only a single alpha chain, the alpha v subunit, associates with the integrin beta 5 to form the vitronectin receptor complex. Integrin alpha v/beta 5 complex also binds to the basic domain of Tat (he sequence RKKRRQRRR). The integrin beta 5 is found on carcinoma cell lines, hepatoma and fibroblast cell lines, and is absent from lymphoblastoid cells and platelets. The KN52 monoclonal antibody has been shown to inhibit migration. Applications Reported: This KN52 antibody has been reported for use in flow cytometric analysis. Applications Tested: This KN52 antibody has been tested by flow cytometric analysis of Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO), A549 and normal human peripheral blood cells. This can be used at less than or equal to 0.25 µg per test. A test is defined as the amount (µg) of antibody that will stain a cell sample in a final volume of 100 µL. Cell number should be determined empirically but can range from 10^5 to 10^8 cells/test. It is recommended that the antibody be carefully titrated for optimal performance in the assay of interest. Purity: Greater than 90%, as determined by SDS-PAGE. Aggregation: Less than 10%, as determined by HPLC. Filtration: 0.2 µm post-manufacturing filtered.
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Hamster
- Host
- Mouse
- Isotype
- IgG
- Antibody clone number
- KN52
- Vial size
- 2 mg
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/mL
- Storage
- 4°C
Submitted references Melanoma-Secreted Amyloid Beta Suppresses Neuroinflammation and Promotes Brain Metastasis.
Diverse Requirements for Microglial Survival, Specification, and Function Revealed by Defined-Medium Cultures.
A novel method for culturing stellate astrocytes reveals spatially distinct Ca2+ signaling and vesicle recycling in astrocytic processes.
Complex I assembly into supercomplexes determines differential mitochondrial ROS production in neurons and astrocytes.
Astrocyte NMDA receptors' activity sustains neuronal survival through a Cdk5-Nrf2 pathway.
The matricellular protein CCN1 mediates neutrophil efferocytosis in cutaneous wound healing.
Inhibition of a novel specific neuroglial integrin signaling pathway increases STAT3-mediated CNTF expression.
Recombinant fibronectin matrix mimetics specify integrin adhesion and extracellular matrix assembly.
Development of a method for the purification and culture of rodent astrocytes.
Homing of mouse spermatogonial stem cells to germline niche depends on beta1-integrin.
Macrophage-derived SPARC bridges tumor cell-extracellular matrix interactions toward metastasis.
Kleffman K, Levinson G, Rose IVL, Blumenberg LM, Shadaloey SAA, Dhabaria A, Wong E, Galán-Echevarría F, Karz A, Argibay D, Von Itter R, Floristán A, Baptiste G, Eskow NM, Tranos JA, Chen J, Vega Y Saenz de Miera EC, Call M, Rogers R, Jour G, Wadghiri YZ, Osman I, Li YM, Mathews P, DeMattos RB, Ueberheide B, Ruggles KV, Liddelow SA, Schneider RJ, Hernando E
Cancer discovery 2022 May 2;12(5):1314-1335
Cancer discovery 2022 May 2;12(5):1314-1335
Diverse Requirements for Microglial Survival, Specification, and Function Revealed by Defined-Medium Cultures.
Bohlen CJ, Bennett FC, Tucker AF, Collins HY, Mulinyawe SB, Barres BA
Neuron 2017 May 17;94(4):759-773.e8
Neuron 2017 May 17;94(4):759-773.e8
A novel method for culturing stellate astrocytes reveals spatially distinct Ca2+ signaling and vesicle recycling in astrocytic processes.
Wolfes AC, Ahmed S, Awasthi A, Stahlberg MA, Rajput A, Magruder DS, Bonn S, Dean C
The Journal of general physiology 2017 Jan;149(1):149-170
The Journal of general physiology 2017 Jan;149(1):149-170
Complex I assembly into supercomplexes determines differential mitochondrial ROS production in neurons and astrocytes.
Lopez-Fabuel I, Le Douce J, Logan A, James AM, Bonvento G, Murphy MP, Almeida A, Bolaños JP
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2016 Nov 15;113(46):13063-13068
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2016 Nov 15;113(46):13063-13068
Astrocyte NMDA receptors' activity sustains neuronal survival through a Cdk5-Nrf2 pathway.
Jimenez-Blasco D, Santofimia-Castaño P, Gonzalez A, Almeida A, Bolaños JP
Cell death and differentiation 2015 Nov;22(11):1877-89
Cell death and differentiation 2015 Nov;22(11):1877-89
The matricellular protein CCN1 mediates neutrophil efferocytosis in cutaneous wound healing.
Jun JI, Kim KH, Lau LF
Nature communications 2015 Jun 16;6:7386
Nature communications 2015 Jun 16;6:7386
Inhibition of a novel specific neuroglial integrin signaling pathway increases STAT3-mediated CNTF expression.
Keasey MP, Kang SS, Lovins C, Hagg T
Cell communication and signaling : CCS 2013 May 21;11:35
Cell communication and signaling : CCS 2013 May 21;11:35
Recombinant fibronectin matrix mimetics specify integrin adhesion and extracellular matrix assembly.
Roy DC, Hocking DC
Tissue engineering. Part A 2013 Feb;19(3-4):558-70
Tissue engineering. Part A 2013 Feb;19(3-4):558-70
Development of a method for the purification and culture of rodent astrocytes.
Foo LC, Allen NJ, Bushong EA, Ventura PB, Chung WS, Zhou L, Cahoy JD, Daneman R, Zong H, Ellisman MH, Barres BA
Neuron 2011 Sep 8;71(5):799-811
Neuron 2011 Sep 8;71(5):799-811
Homing of mouse spermatogonial stem cells to germline niche depends on beta1-integrin.
Kanatsu-Shinohara M, Takehashi M, Takashima S, Lee J, Morimoto H, Chuma S, Raducanu A, Nakatsuji N, Fässler R, Shinohara T
Cell stem cell 2008 Nov 6;3(5):533-42
Cell stem cell 2008 Nov 6;3(5):533-42
Macrophage-derived SPARC bridges tumor cell-extracellular matrix interactions toward metastasis.
Sangaletti S, Di Carlo E, Gariboldi S, Miotti S, Cappetti B, Parenza M, Rumio C, Brekken RA, Chiodoni C, Colombo MP
Cancer research 2008 Nov 1;68(21):9050-9
Cancer research 2008 Nov 1;68(21):9050-9
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
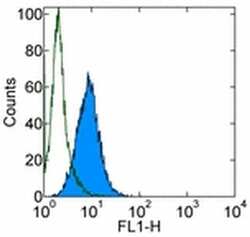
- Experimental details
- Staining of Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cell line with 0.25 µg of Mouse IgG1kappa Isotype Control Purified (Product # 14-4714-82) (open histogram) or 0.25 µg of Anti-Integrin beta 5 Purified (filled histogram) followed by Anti-Mouse IgG FITC (Product # 11-4011-85). Total viable cells were used for analysis.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
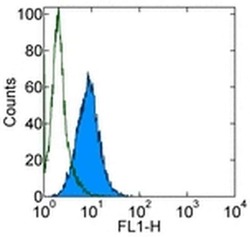
- Experimental details
- Staining of Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cell line with 0.25 µg of Mouse IgG1kappa Isotype Control Purified (Product # 14-4714-82) (open histogram) or 0.25 µg of Anti-Integrin beta 5 Purified (filled histogram) followed by Anti-Mouse IgG FITC (Product # 11-4011-85). Total viable cells were used for analysis.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
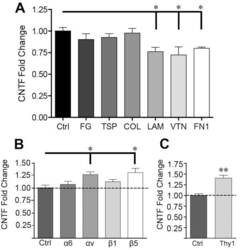
- Experimental details
- Figure 1 CNTF is repressed by ECM and specific alphavbeta5 integrin and neuronal Thy-1 ligand. A ) C6 astroglioma cells grown for 4 h on laminin (LAM), fibronectin (FN1) and vitronectin (VTN) had lower levels of CNTF mRNA compared to poly-d-lysine control (Ctrl, set at 1.00) as quantified by qRT-PCR. Fibrinogen (FG), thrombospondin (TSP), and collagen (COL) had no significant effect. Because of the binding specificity this suggests that a limited number of integrins repress CNTF. B ) Neutralizing antibodies against alphav or beta5, but not alpha6 or beta1 induce CNTF mRNA expression relative to IgG (Ctrl) in C6 cells after 4 hours. Antibody selection was guided by elimination of unlikely candidates (Table 1 ). The beta5 subunit is only found in alphavbeta5. C ) Neutralizing antibody against Thy-1, an alphavbeta5 ligand, induces CNTF mRNA expression in primary astrocyte-neuron co-cultures compared to IgG (Ctrl). Data represent means (+- SEM) of 3-4 ( A ) or 6 ( B , C ) independent experiments and are fold changes expressed relative to controls.
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Flow cytometry
Flow cytometry