Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [18]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunocytochemistry [2]
- Immunohistochemistry [2]
- Other assay [11]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- 51-6200 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- Connexin 36 Polyclonal Antibody
- Antibody type
- Polyclonal
- Antigen
- Synthetic peptide
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat
- Host
- Rabbit
- Isotype
- IgG
- Vial size
- 50 μg
- Concentration
- 0.25 mg/mL
- Storage
- -20°C
Submitted references An offset ON-OFF receptive field is created by gap junctions between distinct types of retinal ganglion cells.
Inner retinal preservation in the photoinducible I307N rhodopsin mutant mouse, a model of autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa.
Brn3a and Brn3b knockout mice display unvaried retinal fine structure despite major morphological and numerical alterations of ganglion cells.
A Self-Regulating Gap Junction Network of Amacrine Cells Controls Nitric Oxide Release in the Retina.
Glibenclamide Prevents Diabetes in NOD Mice.
Differential expression of astrocytic connexins in a mouse model of prenatal alcohol exposure.
Astrocyte sigma-1 receptors modulate connexin 43 expression leading to the induction of below-level mechanical allodynia in spinal cord injured mice.
Influence of the β2-Subunit of L-Type Voltage-Gated Cav Channels on the Structural and Functional Development of Photoreceptor Ribbon Synapses.
Suppression of spinal connexin 43 expression attenuates mechanical hypersensitivity in rats after an L5 spinal nerve injury.
Connexin and AMPA receptor expression changes over time in the rat olfactory bulb.
Connexins protect mouse pancreatic β cells against apoptosis.
Ultrastructural localization of connexins (Cx36, Cx43, Cx45), glutamate receptors and aquaporin-4 in rodent olfactory mucosa, olfactory nerve and olfactory bulb.
Electrical synapses in retinal ON cone bipolar cells: subtype-specific expression of connexins.
Morphological impairments in retinal neurons of the scotopic visual pathway in a monkey model of Parkinson's disease.
Connexin 36 in photoreceptor cells: studies on transgenic rod-less and cone-less mouse retinas.
Heterogeneous expression of connexin 36 in the olfactory epithelium and glomerular layer of the olfactory bulb.
Immunogold evidence that neuronal gap junctions in adult rat brain and spinal cord contain connexin-36 but not connexin-32 or connexin-43.
Immunogold evidence that neuronal gap junctions in adult rat brain and spinal cord contain connexin-36 but not connexin-32 or connexin-43.
Cooler S, Schwartz GW
Nature neuroscience 2021 Jan;24(1):105-115
Nature neuroscience 2021 Jan;24(1):105-115
Inner retinal preservation in the photoinducible I307N rhodopsin mutant mouse, a model of autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa.
Stefanov A, Novelli E, Strettoi E
The Journal of comparative neurology 2020 Jun 15;528(9):1502-1522
The Journal of comparative neurology 2020 Jun 15;528(9):1502-1522
Brn3a and Brn3b knockout mice display unvaried retinal fine structure despite major morphological and numerical alterations of ganglion cells.
Ghinia MG, Novelli E, Sajgo S, Badea TC, Strettoi E
The Journal of comparative neurology 2019 Jan 1;527(1):187-211
The Journal of comparative neurology 2019 Jan 1;527(1):187-211
A Self-Regulating Gap Junction Network of Amacrine Cells Controls Nitric Oxide Release in the Retina.
Jacoby J, Nath A, Jessen ZF, Schwartz GW
Neuron 2018 Dec 5;100(5):1149-1162.e5
Neuron 2018 Dec 5;100(5):1149-1162.e5
Glibenclamide Prevents Diabetes in NOD Mice.
Lamprianou S, Gysemans C, Bou Saab J, Pontes H, Mathieu C, Meda P
PloS one 2016;11(12):e0168839
PloS one 2016;11(12):e0168839
Differential expression of astrocytic connexins in a mouse model of prenatal alcohol exposure.
Ramani M, Mylvaganam S, Krawczyk M, Wang L, Zoidl C, Brien J, Reynolds JN, Kapur B, Poulter MO, Zoidl G, Carlen PL
Neurobiology of disease 2016 Jul;91:83-93
Neurobiology of disease 2016 Jul;91:83-93
Astrocyte sigma-1 receptors modulate connexin 43 expression leading to the induction of below-level mechanical allodynia in spinal cord injured mice.
Choi SR, Roh DH, Yoon SY, Kwon SG, Choi HS, Han HJ, Beitz AJ, Lee JH
Neuropharmacology 2016 Dec;111:34-46
Neuropharmacology 2016 Dec;111:34-46
Influence of the β2-Subunit of L-Type Voltage-Gated Cav Channels on the Structural and Functional Development of Photoreceptor Ribbon Synapses.
Katiyar R, Weissgerber P, Roth E, Dörr J, Sothilingam V, Garcia Garrido M, Beck SC, Seeliger MW, Beck A, Schmitz F, Flockerzi V
Investigative ophthalmology & visual science 2015 Apr;56(4):2312-24
Investigative ophthalmology & visual science 2015 Apr;56(4):2312-24
Suppression of spinal connexin 43 expression attenuates mechanical hypersensitivity in rats after an L5 spinal nerve injury.
Xu Q, Cheong YK, He SQ, Tiwari V, Liu J, Wang Y, Raja SN, Li J, Guan Y, Li W
Neuroscience letters 2014 Apr 30;566:194-199
Neuroscience letters 2014 Apr 30;566:194-199
Connexin and AMPA receptor expression changes over time in the rat olfactory bulb.
Corthell JT, Fadool DA, Trombley PQ
Neuroscience 2012 Oct 11;222:38-48
Neuroscience 2012 Oct 11;222:38-48
Connexins protect mouse pancreatic β cells against apoptosis.
Klee P, Allagnat F, Pontes H, Cederroth M, Charollais A, Caille D, Britan A, Haefliger JA, Meda P
The Journal of clinical investigation 2011 Dec;121(12):4870-9
The Journal of clinical investigation 2011 Dec;121(12):4870-9
Ultrastructural localization of connexins (Cx36, Cx43, Cx45), glutamate receptors and aquaporin-4 in rodent olfactory mucosa, olfactory nerve and olfactory bulb.
Rash JE, Davidson KG, Kamasawa N, Yasumura T, Kamasawa M, Zhang C, Michaels R, Restrepo D, Ottersen OP, Olson CO, Nagy JI
Journal of neurocytology 2005 Sep;34(3-5):307-41
Journal of neurocytology 2005 Sep;34(3-5):307-41
Electrical synapses in retinal ON cone bipolar cells: subtype-specific expression of connexins.
Han Y, Massey SC
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2005 Sep 13;102(37):13313-8
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2005 Sep 13;102(37):13313-8
Morphological impairments in retinal neurons of the scotopic visual pathway in a monkey model of Parkinson's disease.
Cuenca N, Herrero MT, Angulo A, de Juan E, Martínez-Navarrete GC, López S, Barcia C, Martín-Nieto J
The Journal of comparative neurology 2005 Dec 12;493(2):261-73
The Journal of comparative neurology 2005 Dec 12;493(2):261-73
Connexin 36 in photoreceptor cells: studies on transgenic rod-less and cone-less mouse retinas.
Dang L, Pulukuri S, Mears AJ, Swaroop A, Reese BE, Sitaramayya A
Molecular vision 2004 May 11;10:323-7
Molecular vision 2004 May 11;10:323-7
Heterogeneous expression of connexin 36 in the olfactory epithelium and glomerular layer of the olfactory bulb.
Zhang C, Restrepo D
The Journal of comparative neurology 2003 May 12;459(4):426-39
The Journal of comparative neurology 2003 May 12;459(4):426-39
Immunogold evidence that neuronal gap junctions in adult rat brain and spinal cord contain connexin-36 but not connexin-32 or connexin-43.
Rash JE, Staines WA, Yasumura T, Patel D, Furman CS, Stelmack GL, Nagy JI
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2000 Jun 20;97(13):7573-8
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2000 Jun 20;97(13):7573-8
Immunogold evidence that neuronal gap junctions in adult rat brain and spinal cord contain connexin-36 but not connexin-32 or connexin-43.
Rash JE, Staines WA, Yasumura T, Patel D, Furman CS, Stelmack GL, Nagy JI
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2000 Jun 20;97(13):7573-8
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2000 Jun 20;97(13):7573-8
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
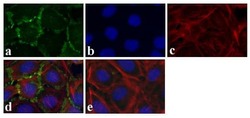
- Experimental details
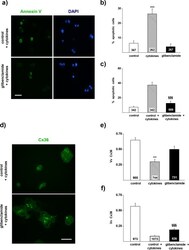
- Immunofluorescence analysis of Connexin 36/GJA9 was done on 70% confluent log phase Caco-2 cells. The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 minutes, permeabilized with 0.25% Triton X-100 for 10 minutes, and blocked with 5% BSA for 1 hour at room temperature. The cells were labeled with Connexin 36/GJA9 Rabbit polyclonal Antibody (Product # 51-6200) at 2 µg/mL in 1% BSA and incubated for 3 hours at room temperature and then labeled with Alexa Fluor 488 Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG Secondary Antibody (Product # A-11008) at a dilution of 1:400 for 30 minutes at room temperature (Panel a: green). Nuclei (Panel b: blue) were stained with SlowFade® Gold Antifade Mountant DAPI (Product # S36938). F-actin (Panel c: red) was stained with Alexa Fluor 594 Phalloidin (Product # A12381). Panel d is a merged image showing junctional localization. Panel e shows no primary antibody control. The images were captured at 20X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
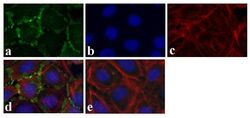
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescence analysis of Connexin 36/GJA9 was done on 70% confluent log phase Caco-2 cells. The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 minutes, permeabilized with 0.25% Triton X-100 for 10 minutes, and blocked with 5% BSA for 1 hour at room temperature. The cells were labeled with Connexin 36/GJA9 Rabbit polyclonal Antibody (Product # 51-6200) at 2 µg/mL in 1% BSA and incubated for 3 hours at room temperature and then labeled with Alexa Fluor 488 Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG Secondary Antibody (Product # A-11008) at a dilution of 1:400 for 30 minutes at room temperature (Panel a: green). Nuclei (Panel b: blue) were stained with SlowFade® Gold Antifade Mountant DAPI (Product # S36938). F-actin (Panel c: red) was stained with Alexa Fluor 594 Phalloidin (Product # A12381). Panel d is a merged image showing junctional localization. Panel e shows no primary antibody control. The images were captured at 20X magnification.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
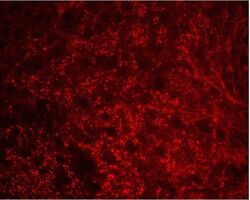
- Experimental details
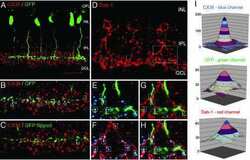
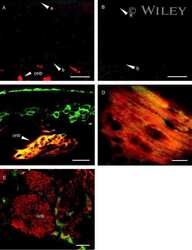
- Connexin 36 Polyclonal Antibody, Rabbit (Product # 51-6200). Mouse inferior olivary nucleus (IO) staining using Product # 51-6200 at 1-2 µg/mL. Imaged by James Nagy (Univ. of Manitoba, Canada).
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
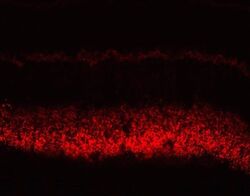
- Experimental details
- Connexin 36 Polyclonal Antibody, Rabbit (Product # 51-6200). Mouse retina staining using Product # 51-6200 at 1-2 µg/mL. Image provided by James Nagy (Univ. of Manitoba, Canada)
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
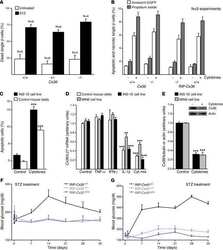
- Fig 1 Glibenclamide reduces the apoptosis and the loss of CVx36 in MIN6 cells exposed to Th1 cytokines. a) Apoptosis of MIN6 cells was evaluated by the proportion of Annexin V-stained cells (green) out of the total number of cells screened (identified by the blue DAPI staining of nuclei). Bar, 25 mum. b) A 18h exposure of MIN6 cells to a mix of IL-1beta, IFN gamma and TNFalpha induced a significant increase in the proportion of Annexin V-labelled cells (hatched bar), compared to the level observed in controls cultured in the absence of cytokines (open bar). Such an increase was not observed in cells exposed to 10 muM glibenclamide (solid bar). c) Comparable effects were seen when MIN6 cells were exposed to 10 muM glibenclamide 6 h before starting the exposure to the cytokines. d) Expression of Cx36 was evaluated by immunostaining, using an antibody that detects the small gap junction plaques made by the concentration of Cx36 within the membrane (yellow-green). Bar, 5 mum. e) A 18h exposure of MIN6 cells to IL-1beta, IFN gamma and TNFalpha (hatched bar) reduced the volume density of immunolabeled Cx36 under the control levels (open bar). Such a decrease was not observed in cells exposed to 10 muM glibenclamide (solid bar). f) . Comparable effects were seen when MIN6 cells were exposed to 10 muM glibenclamide 6 h before starting the exposure to the cytokines. Data are mean + SEM of 3 independent experiments. Numbers within bars indicate the total number of cells scored in ea
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
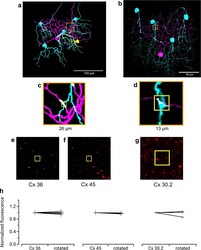
- Experimental details
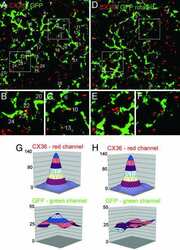
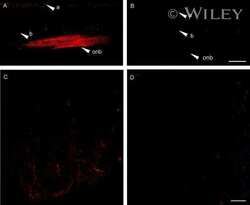
- Extended Data Fig. 4 Immunohistochemistry for three types of Connexin at RGC contact points shows negative results Three connexins were evaluated for presence at the regions of contact between an F-mini-ON and multiple F-mini-OFF RGCs, n = 1 of each experiment. a,b, Full depth maximum intensity projection images of a Neurobiotin-filled F-mini-ON RGC (magenta),the connected F-mini-OFF RGCs (cyan), and a cell of unclassified type due to insufficiently filled dendrites (yellow). Tracing, segmentation, and masking were performed manually. Image brightness was scaled separately by cell type for illustration here but not for analysis. c,d Thin projection images of regions in orange squares in a,b showing an example RGC crossing point with yellow square for spatial reference. Stack depth is 3.5 mum. e-g, The same region and depth as in c,d, showing the IHC channels for the three connexin proteins. h, Quantification of overlap between connexin images and RGC contact region masks. Values are similar before and after a 90 degree rotation of the connexin image. Points mark the overlap of the single F-mini-ON RGC with each F-mini-OFF RGC in the image.
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry