Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [55]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunocytochemistry [6]
- Immunohistochemistry [3]
- Other assay [22]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- MA3-930 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- ATP1B1 Monoclonal Antibody (M17-P5-F11)
- Antibody type
- Monoclonal
- Antigen
- Purifed from natural sources
- Description
- MA3-930 detects sodium/potassium ATPase beta 1 from mouse, human, sheep, canine, and pig tissues. This antibody does not recognize the beta 1 or beta 2 subunit in rat. MA3-930 has been successfully used in Western blot and immunohistochemistry and immunocytochemistry procedures. By Western blot, this antibody detects an ~42 kDa protein in liver samples and ~55 kDa in kidney samples representing beta sodium/potassium ATPase in sheep liver extract. Immunohistochemical staining of the sodium/potassium ATPase with MA3-930 yields a pattern consistent with plasma membrane localization. The MA3-930 antigen is purified lamb kidney sodium/potassium ATPase beta. This antibody recognizes and epitope between amino acid residues 195-199 of sheep sodium/potassium ATPase beta 1.
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Canine, Porcine
- Host
- Mouse
- Isotype
- IgG
- Antibody clone number
- M17-P5-F11
- Vial size
- 100 μg
- Concentration
- 1 mg/mL
- Storage
- -20°C, Avoid Freeze/Thaw Cycles
Submitted references Expression of TXNRD1, HSPA4L and ATP1B1 Genes Associated with the Freezability of Boar Sperm.
Skeletal muscle proteins important for work capacity are altered with type 2 diabetes - Effect of 10-20-30 training.
Multiple Na,K-ATPase Subunits Colocalize in the Brush Border of Mouse Choroid Plexus Epithelial Cells.
Effects of testosterone suppression, hindlimb immobilization, and recovery on [(3)H]ouabain binding site content and Na(+), K(+)-ATPase isoforms in rat soleus muscle.
Cycling with blood flow restriction improves performance and muscle K(+) regulation and alters the effect of anti-oxidant infusion in humans.
Skeletal muscle and performance adaptations to high-intensity training in elite male soccer players: speed endurance runs versus small-sided game training.
Effect of tapering after a period of high-volume sprint interval training on running performance and muscular adaptations in moderately trained runners.
The Human "Cochlear Battery" - Claudin-11 Barrier and Ion Transport Proteins in the Lateral Wall of the Cochlea.
Muscle ion transporters and antioxidative proteins have different adaptive potential in arm than in leg skeletal muscle with exercise training.
Genome-wide association study identifies three novel loci in Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy.
Effect of increased and maintained frequency of speed endurance training on performance and muscle adaptations in runners.
Intense interval training in healthy older adults increases skeletal muscle [(3)H]ouabain-binding site content and elevates Na(+),K(+)-ATPase α(2) isoform abundance in Type II fibers.
Dissociation between short-term unloading and resistance training effects on skeletal muscle Na+,K+-ATPase, muscle function, and fatigue in humans.
Cell specific differences in the protein abundances of GAPDH and Na(+),K(+)-ATPase in skeletal muscle from aged individuals.
The O-glycosylated ectodomain of FXYD5 impairs adhesion by disrupting cell-cell trans-dimerization of Na,K-ATPase β1 subunits.
Effect of speed endurance and strength training on performance, running economy and muscular adaptations in endurance-trained runners.
Muscle variables of importance for physiological performance in competitive football.
Mechanisms underlying enhancements in muscle force and power output during maximal cycle ergometer exercise induced by chronic β2-adrenergic stimulation in men.
Single-fiber expression and fiber-specific adaptability to short-term intense exercise training of Na+-K+-ATPase α- and β-isoforms in human skeletal muscle.
The effects of knee injury on skeletal muscle function, Na+, K+-ATPase content, and isoform abundance.
Concurrent speed endurance and resistance training improves performance, running economy, and muscle NHE1 in moderately trained runners.
A polymorphic 3'UTR element in ATP1B1 regulates alternative polyadenylation and is associated with blood pressure.
Effect of intensified training on muscle ion kinetics, fatigue development, and repeated short-term performance in endurance-trained cyclists.
The effects of osteoarthritis and age on skeletal muscle strength, Na+-K+-ATPase content, gene and isoform expression.
Fibre type-specific change in FXYD1 phosphorylation during acute intense exercise in humans.
Unchanged [3H]ouabain binding site content but reduced Na+-K+ pump α2-protein abundance in skeletal muscle in older adults.
Impaired exercise performance and muscle Na(+),K(+)-pump activity in renal transplantation and haemodialysis patients.
Four weeks of normobaric "live high-train low" do not alter muscular or systemic capacity for maintaining pH and K⁺ homeostasis during intense exercise.
The 10-20-30 training concept improves performance and health profile in moderately trained runners.
Subunit isoform selectivity in assembly of Na,K-ATPase α-β heterodimers.
Influence of chronic and acute spinal cord injury on skeletal muscle Na+-K+-ATPase and phospholemman expression in humans.
Effect of exercise and training on phospholemman phosphorylation in human skeletal muscle.
Relationship between performance at different exercise intensities and skeletal muscle characteristics.
Epithelial junctions depend on intercellular trans-interactions between the Na,K-ATPase β₁ subunits.
Diverse pathways for maturation of the Na,K-ATPase β1 and β2 subunits in the endoplasmic reticulum of Madin-Darby canine kidney cells.
Effect of 2-wk intensified training and inactivity on muscle Na+-K+ pump expression, phospholemman (FXYD1) phosphorylation, and performance in soccer players.
Ubiquitination participates in the lysosomal degradation of Na,K-ATPase in steady-state conditions.
Reduced volume and increased training intensity elevate muscle Na+-K+ pump alpha2-subunit expression as well as short- and long-term work capacity in humans.
Regulation of Na,K-ATPase subunit abundance by translational repression.
beta-Subunit overexpression alters the stoicheometry of assembled Na-K-ATPase subunits in MDCK cells.
Reduced volume but increased training intensity elevates muscle Na+-K+ pump alpha1-subunit and NHE1 expression as well as short-term work capacity in humans.
Effect of dexamethasone on skeletal muscle Na+,K+ pump subunit specific expression and K+ homeostasis during exercise in humans.
Human copper transporter hCTR1 mediates basolateral uptake of copper into enterocytes: implications for copper homeostasis.
Selective basolateral localization of overexpressed Na-K-ATPase beta1- and beta2- subunits is disrupted by butryate treatment of MDCK cells.
Muscle Na+-K+-ATPase activity and isoform adaptations to intense interval exercise and training in well-trained athletes.
Prolonged submaximal exercise induces isoform-specific Na+-K+-ATPase mRNA and protein responses in human skeletal muscle.
The role of the beta1 subunit of the Na,K-ATPase and its glycosylation in cell-cell adhesion.
Oligomerization of the Na,K-ATPase in cell membranes.
Intense exercise up-regulates Na+,K+-ATPase isoform mRNA, but not protein expression in human skeletal muscle.
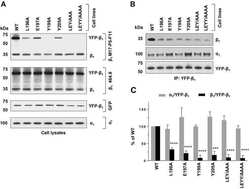
Mutational analysis of alpha-beta subunit interactions in the delivery of Na,K-ATPase heterodimers to the plasma membrane.
Molecular and functional studies of electrogenic Na(+) transport in the distal colon and rectum of young and elderly subjects.
Na pump isoforms in human erythroid progenitor cells and mature erythrocytes.
Plasma membrane depolarization without repolarization is an early molecular event in anti-Fas-induced apoptosis.
Determination of Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase alpha- and beta-isoforms and kinetic properties in mammalian liver.
Determination of Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase alpha- and beta-isoforms and kinetic properties in mammalian liver.
Mańkowska A, Gilun P, Zasiadczyk Ł, Sobiech P, Fraser L
International journal of molecular sciences 2022 Aug 18;23(16)
International journal of molecular sciences 2022 Aug 18;23(16)
Skeletal muscle proteins important for work capacity are altered with type 2 diabetes - Effect of 10-20-30 training.
Baasch-Skytte T, Gunnarsson TP, Fiorenza M, Bangsbo J
Physiological reports 2021 Jan;9(1):e14681
Physiological reports 2021 Jan;9(1):e14681
Multiple Na,K-ATPase Subunits Colocalize in the Brush Border of Mouse Choroid Plexus Epithelial Cells.
Baasch Christensen I, Cheng L, Brewer JR, Bartsch U, Fenton RA, H Damkier H, Praetorius J
International journal of molecular sciences 2021 Feb 4;22(4)
International journal of molecular sciences 2021 Feb 4;22(4)
Effects of testosterone suppression, hindlimb immobilization, and recovery on [(3)H]ouabain binding site content and Na(+), K(+)-ATPase isoforms in rat soleus muscle.
Altarawneh MM, Hanson ED, Betik AC, Petersen AC, Hayes A, McKenna MJ
Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985) 2020 Mar 1;128(3):501-513
Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985) 2020 Mar 1;128(3):501-513
Cycling with blood flow restriction improves performance and muscle K(+) regulation and alters the effect of anti-oxidant infusion in humans.
Christiansen D, Eibye KH, Rasmussen V, Voldbye HM, Thomassen M, Nyberg M, Gunnarsson TGP, Skovgaard C, Lindskrog MS, Bishop DJ, Hostrup M, Bangsbo J
The Journal of physiology 2019 May;597(9):2421-2444
The Journal of physiology 2019 May;597(9):2421-2444
Skeletal muscle and performance adaptations to high-intensity training in elite male soccer players: speed endurance runs versus small-sided game training.
Fransson D, Nielsen TS, Olsson K, Christensson T, Bradley PS, Fatouros IG, Krustrup P, Nordsborg NB, Mohr M
European journal of applied physiology 2018 Jan;118(1):111-121
European journal of applied physiology 2018 Jan;118(1):111-121
Effect of tapering after a period of high-volume sprint interval training on running performance and muscular adaptations in moderately trained runners.
Skovgaard C, Almquist NW, Kvorning T, Christensen PM, Bangsbo J
Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985) 2018 Feb 1;124(2):259-267
Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985) 2018 Feb 1;124(2):259-267
The Human "Cochlear Battery" - Claudin-11 Barrier and Ion Transport Proteins in the Lateral Wall of the Cochlea.
Liu W, Schrott-Fischer A, Glueckert R, Benav H, Rask-Andersen H
Frontiers in molecular neuroscience 2017;10:239
Frontiers in molecular neuroscience 2017;10:239
Muscle ion transporters and antioxidative proteins have different adaptive potential in arm than in leg skeletal muscle with exercise training.
Mohr M, Nielsen TS, Weihe P, Thomsen JA, Aquino G, Krustrup P, Nordsborg NB
Physiological reports 2017 Oct;5(19)
Physiological reports 2017 Oct;5(19)
Genome-wide association study identifies three novel loci in Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy.
Afshari NA, Igo RP Jr, Morris NJ, Stambolian D, Sharma S, Pulagam VL, Dunn S, Stamler JF, Truitt BJ, Rimmler J, Kuot A, Croasdale CR, Qin X, Burdon KP, Riazuddin SA, Mills R, Klebe S, Minear MA, Zhao J, Balajonda E, Rosenwasser GO, Baratz KH, Mootha VV, Patel SV, Gregory SG, Bailey-Wilson JE, Price MO, Price FW Jr, Craig JE, Fingert JH, Gottsch JD, Aldave AJ, Klintworth GK, Lass JH, Li YJ, Iyengar SK
Nature communications 2017 Mar 30;8:14898
Nature communications 2017 Mar 30;8:14898
Effect of increased and maintained frequency of speed endurance training on performance and muscle adaptations in runners.
Skovgaard C, Almquist NW, Bangsbo J
Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985) 2017 Jan 1;122(1):48-59
Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985) 2017 Jan 1;122(1):48-59
Intense interval training in healthy older adults increases skeletal muscle [(3)H]ouabain-binding site content and elevates Na(+),K(+)-ATPase α(2) isoform abundance in Type II fibers.
Wyckelsma VL, Levinger I, Murphy RM, Petersen AC, Perry BD, Hedges CP, Anderson MJ, McKenna MJ
Physiological reports 2017 Apr;5(7)
Physiological reports 2017 Apr;5(7)
Dissociation between short-term unloading and resistance training effects on skeletal muscle Na+,K+-ATPase, muscle function, and fatigue in humans.
Perry BD, Wyckelsma VL, Murphy RM, Steward CH, Anderson M, Levinger I, Petersen AC, McKenna MJ
Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985) 2016 Nov 1;121(5):1074-1086
Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985) 2016 Nov 1;121(5):1074-1086
Cell specific differences in the protein abundances of GAPDH and Na(+),K(+)-ATPase in skeletal muscle from aged individuals.
Wyckelsma VL, McKenna MJ, Levinger I, Petersen AC, Lamboley CR, Murphy RM
Experimental gerontology 2016 Mar;75:8-15
Experimental gerontology 2016 Mar;75:8-15
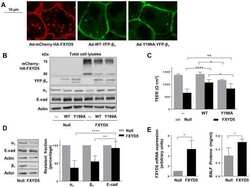
The O-glycosylated ectodomain of FXYD5 impairs adhesion by disrupting cell-cell trans-dimerization of Na,K-ATPase β1 subunits.
Tokhtaeva E, Sun H, Deiss-Yehiely N, Wen Y, Soni PN, Gabrielli NM, Marcus EA, Ridge KM, Sachs G, Vazquez-Levin M, Sznajder JI, Vagin O, Dada LA
Journal of cell science 2016 Jun 15;129(12):2394-406
Journal of cell science 2016 Jun 15;129(12):2394-406
Effect of speed endurance and strength training on performance, running economy and muscular adaptations in endurance-trained runners.
Vorup J, Tybirk J, Gunnarsson TP, Ravnholt T, Dalsgaard S, Bangsbo J
European journal of applied physiology 2016 Jul;116(7):1331-41
European journal of applied physiology 2016 Jul;116(7):1331-41
Muscle variables of importance for physiological performance in competitive football.
Mohr M, Thomassen M, Girard O, Racinais S, Nybo L
European journal of applied physiology 2016 Feb;116(2):251-62
European journal of applied physiology 2016 Feb;116(2):251-62
Mechanisms underlying enhancements in muscle force and power output during maximal cycle ergometer exercise induced by chronic β2-adrenergic stimulation in men.
Hostrup M, Kalsen A, Onslev J, Jessen S, Haase C, Habib S, Ørtenblad N, Backer V, Bangsbo J
Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985) 2015 Sep 1;119(5):475-86
Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985) 2015 Sep 1;119(5):475-86
Single-fiber expression and fiber-specific adaptability to short-term intense exercise training of Na+-K+-ATPase α- and β-isoforms in human skeletal muscle.
Wyckelsma VL, McKenna MJ, Serpiello FR, Lamboley CR, Aughey RJ, Stepto NK, Bishop DJ, Murphy RM
Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985) 2015 Mar 15;118(6):699-706
Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985) 2015 Mar 15;118(6):699-706
The effects of knee injury on skeletal muscle function, Na+, K+-ATPase content, and isoform abundance.
Perry BD, Levinger P, Morris HG, Petersen AC, Garnham AP, Levinger I, McKenna MJ
Physiological reports 2015 Feb 1;3(2)
Physiological reports 2015 Feb 1;3(2)
Concurrent speed endurance and resistance training improves performance, running economy, and muscle NHE1 in moderately trained runners.
Skovgaard C, Christensen PM, Larsen S, Andersen TR, Thomassen M, Bangsbo J
Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985) 2014 Nov 15;117(10):1097-109
Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985) 2014 Nov 15;117(10):1097-109
A polymorphic 3'UTR element in ATP1B1 regulates alternative polyadenylation and is associated with blood pressure.
Prasad MK, Bhalla K, Pan ZH, O'Connell JR, Weder AB, Chakravarti A, Tian B, Chang YP
PloS one 2013;8(10):e76290
PloS one 2013;8(10):e76290
Effect of intensified training on muscle ion kinetics, fatigue development, and repeated short-term performance in endurance-trained cyclists.
Gunnarsson TP, Christensen PM, Thomassen M, Nielsen LR, Bangsbo J
American journal of physiology. Regulatory, integrative and comparative physiology 2013 Oct 1;305(7):R811-21
American journal of physiology. Regulatory, integrative and comparative physiology 2013 Oct 1;305(7):R811-21
The effects of osteoarthritis and age on skeletal muscle strength, Na+-K+-ATPase content, gene and isoform expression.
Perry BD, Levinger P, Serpiello FR, Caldow MK, Cameron-Smith D, Bartlett JR, Feller JA, Bergman NR, Levinger I, McKenna MJ
Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985) 2013 Nov;115(10):1443-9
Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985) 2013 Nov;115(10):1443-9
Fibre type-specific change in FXYD1 phosphorylation during acute intense exercise in humans.
Thomassen M, Murphy RM, Bangsbo J
The Journal of physiology 2013 Mar 15;591(6):1523-33
The Journal of physiology 2013 Mar 15;591(6):1523-33
Unchanged [3H]ouabain binding site content but reduced Na+-K+ pump α2-protein abundance in skeletal muscle in older adults.
McKenna MJ, Perry BD, Serpiello FR, Caldow MK, Levinger P, Cameron-Smith D, Levinger I
Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985) 2012 Nov;113(10):1505-11
Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985) 2012 Nov;113(10):1505-11
Impaired exercise performance and muscle Na(+),K(+)-pump activity in renal transplantation and haemodialysis patients.
Petersen AC, Leikis MJ, McMahon LP, Kent AB, Murphy KT, Gong X, McKenna MJ
Nephrology, dialysis, transplantation : official publication of the European Dialysis and Transplant Association - European Renal Association 2012 May;27(5):2036-43
Nephrology, dialysis, transplantation : official publication of the European Dialysis and Transplant Association - European Renal Association 2012 May;27(5):2036-43
Four weeks of normobaric "live high-train low" do not alter muscular or systemic capacity for maintaining pH and K⁺ homeostasis during intense exercise.
Nordsborg NB, Siebenmann C, Jacobs RA, Rasmussen P, Diaz V, Robach P, Lundby C
Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985) 2012 Jun;112(12):2027-36
Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985) 2012 Jun;112(12):2027-36
The 10-20-30 training concept improves performance and health profile in moderately trained runners.
Gunnarsson TP, Bangsbo J
Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985) 2012 Jul;113(1):16-24
Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985) 2012 Jul;113(1):16-24
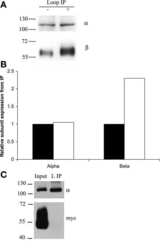
Subunit isoform selectivity in assembly of Na,K-ATPase α-β heterodimers.
Tokhtaeva E, Clifford RJ, Kaplan JH, Sachs G, Vagin O
The Journal of biological chemistry 2012 Jul 27;287(31):26115-25
The Journal of biological chemistry 2012 Jul 27;287(31):26115-25
Influence of chronic and acute spinal cord injury on skeletal muscle Na+-K+-ATPase and phospholemman expression in humans.
Boon H, Kostovski E, Pirkmajer S, Song M, Lubarski I, Iversen PO, Hjeltnes N, Widegren U, Chibalin AV
American journal of physiology. Endocrinology and metabolism 2012 Apr 1;302(7):E864-71
American journal of physiology. Endocrinology and metabolism 2012 Apr 1;302(7):E864-71
Effect of exercise and training on phospholemman phosphorylation in human skeletal muscle.
Benziane B, Widegren U, Pirkmajer S, Henriksson J, Stepto NK, Chibalin AV
American journal of physiology. Endocrinology and metabolism 2011 Sep;301(3):E456-66
American journal of physiology. Endocrinology and metabolism 2011 Sep;301(3):E456-66
Relationship between performance at different exercise intensities and skeletal muscle characteristics.
Iaia FM, Perez-Gomez J, Thomassen M, Nordsborg NB, Hellsten Y, Bangsbo J
Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985) 2011 Jun;110(6):1555-63
Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985) 2011 Jun;110(6):1555-63
Epithelial junctions depend on intercellular trans-interactions between the Na,K-ATPase β₁ subunits.
Tokhtaeva E, Sachs G, Souda P, Bassilian S, Whitelegge JP, Shoshani L, Vagin O
The Journal of biological chemistry 2011 Jul 22;286(29):25801-12
The Journal of biological chemistry 2011 Jul 22;286(29):25801-12
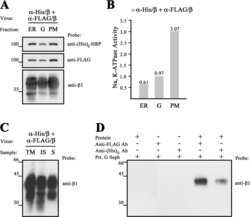
Diverse pathways for maturation of the Na,K-ATPase β1 and β2 subunits in the endoplasmic reticulum of Madin-Darby canine kidney cells.
Tokhtaeva E, Sachs G, Vagin O
The Journal of biological chemistry 2010 Dec 10;285(50):39289-302
The Journal of biological chemistry 2010 Dec 10;285(50):39289-302
Effect of 2-wk intensified training and inactivity on muscle Na+-K+ pump expression, phospholemman (FXYD1) phosphorylation, and performance in soccer players.
Thomassen M, Christensen PM, Gunnarsson TP, Nybo L, Bangsbo J
Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985) 2010 Apr;108(4):898-905
Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985) 2010 Apr;108(4):898-905
Ubiquitination participates in the lysosomal degradation of Na,K-ATPase in steady-state conditions.
Lecuona E, Sun H, Vohwinkel C, Ciechanover A, Sznajder JI
American journal of respiratory cell and molecular biology 2009 Dec;41(6):671-9
American journal of respiratory cell and molecular biology 2009 Dec;41(6):671-9
Reduced volume and increased training intensity elevate muscle Na+-K+ pump alpha2-subunit expression as well as short- and long-term work capacity in humans.
Bangsbo J, Gunnarsson TP, Wendell J, Nybo L, Thomassen M
Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985) 2009 Dec;107(6):1771-80
Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985) 2009 Dec;107(6):1771-80
Regulation of Na,K-ATPase subunit abundance by translational repression.
Clifford RJ, Kaplan JH
The Journal of biological chemistry 2009 Aug 21;284(34):22905-15
The Journal of biological chemistry 2009 Aug 21;284(34):22905-15
beta-Subunit overexpression alters the stoicheometry of assembled Na-K-ATPase subunits in MDCK cells.
Clifford RJ, Kaplan JH
American journal of physiology. Renal physiology 2008 Nov;295(5):F1314-23
American journal of physiology. Renal physiology 2008 Nov;295(5):F1314-23
Reduced volume but increased training intensity elevates muscle Na+-K+ pump alpha1-subunit and NHE1 expression as well as short-term work capacity in humans.
Iaia FM, Thomassen M, Kolding H, Gunnarsson T, Wendell J, Rostgaard T, Nordsborg N, Krustrup P, Nybo L, Hellsten Y, Bangsbo J
American journal of physiology. Regulatory, integrative and comparative physiology 2008 Mar;294(3):R966-74
American journal of physiology. Regulatory, integrative and comparative physiology 2008 Mar;294(3):R966-74
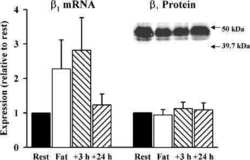
Effect of dexamethasone on skeletal muscle Na+,K+ pump subunit specific expression and K+ homeostasis during exercise in humans.
Nordsborg N, Ovesen J, Thomassen M, Zangenberg M, Jøns C, Iaia FM, Nielsen JJ, Bangsbo J
The Journal of physiology 2008 Mar 1;586(5):1447-59
The Journal of physiology 2008 Mar 1;586(5):1447-59
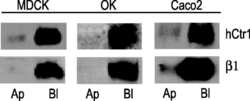
Human copper transporter hCTR1 mediates basolateral uptake of copper into enterocytes: implications for copper homeostasis.
Zimnicka AM, Maryon EB, Kaplan JH
The Journal of biological chemistry 2007 Sep 7;282(36):26471-80
The Journal of biological chemistry 2007 Sep 7;282(36):26471-80
Selective basolateral localization of overexpressed Na-K-ATPase beta1- and beta2- subunits is disrupted by butryate treatment of MDCK cells.
Laughery MD, Clifford RJ, Chi Y, Kaplan JH
American journal of physiology. Renal physiology 2007 Jun;292(6):F1718-25
American journal of physiology. Renal physiology 2007 Jun;292(6):F1718-25
Muscle Na+-K+-ATPase activity and isoform adaptations to intense interval exercise and training in well-trained athletes.
Aughey RJ, Murphy KT, Clark SA, Garnham AP, Snow RJ, Cameron-Smith D, Hawley JA, McKenna MJ
Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985) 2007 Jul;103(1):39-47
Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985) 2007 Jul;103(1):39-47
Prolonged submaximal exercise induces isoform-specific Na+-K+-ATPase mRNA and protein responses in human skeletal muscle.
Murphy KT, Petersen AC, Goodman C, Gong X, Leppik JA, Garnham AP, Cameron-Smith D, Snow RJ, McKenna MJ
American journal of physiology. Regulatory, integrative and comparative physiology 2006 Feb;290(2):R414-24
American journal of physiology. Regulatory, integrative and comparative physiology 2006 Feb;290(2):R414-24
The role of the beta1 subunit of the Na,K-ATPase and its glycosylation in cell-cell adhesion.
Vagin O, Tokhtaeva E, Sachs G
The Journal of biological chemistry 2006 Dec 22;281(51):39573-87
The Journal of biological chemistry 2006 Dec 22;281(51):39573-87
Oligomerization of the Na,K-ATPase in cell membranes.
Laughery M, Todd M, Kaplan JH
The Journal of biological chemistry 2004 Aug 27;279(35):36339-48
The Journal of biological chemistry 2004 Aug 27;279(35):36339-48
Intense exercise up-regulates Na+,K+-ATPase isoform mRNA, but not protein expression in human skeletal muscle.
Murphy KT, Snow RJ, Petersen AC, Murphy RM, Mollica J, Lee JS, Garnham AP, Aughey RJ, Leppik JA, Medved I, Cameron-Smith D, McKenna MJ
The Journal of physiology 2004 Apr 15;556(Pt 2):507-19
The Journal of physiology 2004 Apr 15;556(Pt 2):507-19
Mutational analysis of alpha-beta subunit interactions in the delivery of Na,K-ATPase heterodimers to the plasma membrane.
Laughery MD, Todd ML, Kaplan JH
The Journal of biological chemistry 2003 Sep 12;278(37):34794-803
The Journal of biological chemistry 2003 Sep 12;278(37):34794-803
Molecular and functional studies of electrogenic Na(+) transport in the distal colon and rectum of young and elderly subjects.
Greig ER, Mathialahan T, Boot-Handford RP, Sandle GI
Gut 2003 Nov;52(11):1607-15
Gut 2003 Nov;52(11):1607-15
Na pump isoforms in human erythroid progenitor cells and mature erythrocytes.
Hoffman JF, Wickrema A, Potapova O, Milanick M, Yingst DR
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2002 Oct 29;99(22):14572-7
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2002 Oct 29;99(22):14572-7
Plasma membrane depolarization without repolarization is an early molecular event in anti-Fas-induced apoptosis.
Bortner CD, Gomez-Angelats M, Cidlowski JA
The Journal of biological chemistry 2001 Feb 9;276(6):4304-14
The Journal of biological chemistry 2001 Feb 9;276(6):4304-14
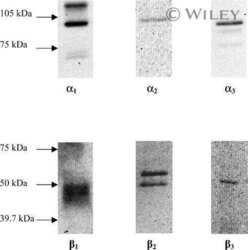
Determination of Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase alpha- and beta-isoforms and kinetic properties in mammalian liver.
Sun Y, Ball WJ Jr
The American journal of physiology 1992 Jun;262(6 Pt 1):C1491-9
The American journal of physiology 1992 Jun;262(6 Pt 1):C1491-9
Determination of Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase alpha- and beta-isoforms and kinetic properties in mammalian liver.
Sun Y, Ball WJ Jr
The American journal of physiology 1992 Jun;262(6 Pt 1):C1491-9
The American journal of physiology 1992 Jun;262(6 Pt 1):C1491-9
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
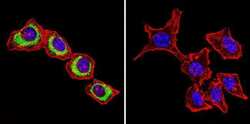
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of Sodiµm/Potassium ATPase beta using Anti-Sodiµm/Potassium ATPase beta Monoclonal Antibody (M17-P5-F11) (Product # MA3-930) shows staining in Hela Cells. Sodiµm/Potassium ATPase beta staining (green), F-Actin staining with Phalloidin (red) and nuclei with DAPI (blue) is shown. Cells were grown on chamber slides and fixed with formaldehyde prior to staining. Cells were probed without (control) or with or an antibody recognizing Sodiµm/Potassium ATPase beta (Product # MA3-930) at a dilution of 1:200 over night at 4°C, washed with PBS and incubated with a DyLight-488 conjugated secondary antibody (Product # 35503, Goat Anti-Mouse). Images were taken at 60X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
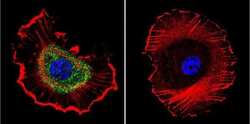
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of Sodiµm/Potassium ATPase beta using Anti-Sodiµm/Potassium ATPase beta Monoclonal Antibody (M17-P5-F11) (Product # MA3-930) shows staining in MCF-7 Cells. Sodiµm/Potassium ATPase beta staining (green), F-Actin staining with Phalloidin (red) and nuclei with DAPI (blue) is shown. Cells were grown on chamber slides and fixed with formaldehyde prior to staining. Cells were probed without (control) or with or an antibody recognizing Sodiµm/Potassium ATPase beta (Product # MA3-930) at a dilution of 1:200 over night at 4°C, washed with PBS and incubated with a DyLight-488 conjugated secondary antibody (Product # 35503, Goat Anti-Mouse). Images were taken at 60X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
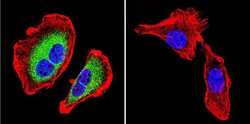
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of Sodiµm/Potassium ATPase beta using Anti-Sodiµm/Potassium ATPase beta Monoclonal Antibody (M17-P5-F11) (Product # MA3-930) shows staining in U251 Cells. Sodiµm/Potassium ATPase beta staining (green), F-Actin staining with Phalloidin (red) and nuclei with DAPI (blue) is shown. Cells were grown on chamber slides and fixed with formaldehyde prior to staining. Cells were probed without (control) or with or an antibody recognizing Sodiµm/Potassium ATPase beta (Product # MA3-930) at a dilution of 1:200 over night at 4°C, washed with PBS and incubated with a DyLight-488 conjugated secondary antibody (Product # 35503, Goat Anti-Mouse). Images were taken at 60X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
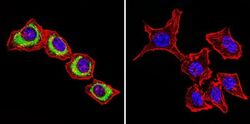
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of Sodiµm/Potassium ATPase beta using Anti-Sodiµm/Potassium ATPase beta Monoclonal Antibody (M17-P5-F11) (Product # MA3-930) shows staining in Hela Cells. Sodiµm/Potassium ATPase beta staining (green), F-Actin staining with Phalloidin (red) and nuclei with DAPI (blue) is shown. Cells were grown on chamber slides and fixed with formaldehyde prior to staining. Cells were probed without (control) or with or an antibody recognizing Sodiµm/Potassium ATPase beta (Product # MA3-930) at a dilution of 1:200 over night at 4°C, washed with PBS and incubated with a DyLight-488 conjugated secondary antibody (Product # 35503, Goat Anti-Mouse). Images were taken at 60X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
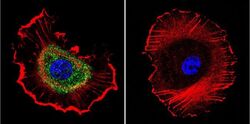
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of Sodiµm/Potassium ATPase beta using Anti-Sodiµm/Potassium ATPase beta Monoclonal Antibody (M17-P5-F11) (Product # MA3-930) shows staining in MCF-7 Cells. Sodiµm/Potassium ATPase beta staining (green), F-Actin staining with Phalloidin (red) and nuclei with DAPI (blue) is shown. Cells were grown on chamber slides and fixed with formaldehyde prior to staining. Cells were probed without (control) or with or an antibody recognizing Sodiµm/Potassium ATPase beta (Product # MA3-930) at a dilution of 1:200 over night at 4°C, washed with PBS and incubated with a DyLight-488 conjugated secondary antibody (Product # 35503, Goat Anti-Mouse). Images were taken at 60X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
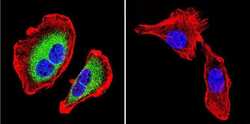
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of Sodiµm/Potassium ATPase beta using Anti-Sodiµm/Potassium ATPase beta Monoclonal Antibody (M17-P5-F11) (Product # MA3-930) shows staining in U251 Cells. Sodiµm/Potassium ATPase beta staining (green), F-Actin staining with Phalloidin (red) and nuclei with DAPI (blue) is shown. Cells were grown on chamber slides and fixed with formaldehyde prior to staining. Cells were probed without (control) or with or an antibody recognizing Sodiµm/Potassium ATPase beta (Product # MA3-930) at a dilution of 1:200 over night at 4°C, washed with PBS and incubated with a DyLight-488 conjugated secondary antibody (Product # 35503, Goat Anti-Mouse). Images were taken at 60X magnification.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
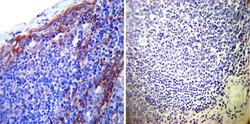
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemistry was performed on normal deparaffinized Human tonsil tissue tissues. To expose target proteins, heat induced antigen retrieval was performed using 10mM sodium citrate (pH6.0) buffer, microwaved for 8-15 minutes. Following antigen retrieval tissues were blocked in 3% BSA-PBS for 30 minutes at room temperature. Tissues were then probed at a dilution of 1:200 with a mouse monoclonal antibody recognizing Sodiµm/Potassium ATPase beta (Product # MA3-930) or without primary antibody (negative control) overnight at 4°C in a humidified chamber. Tissues were washed extensively with PBST and endogenous peroxidase activity was quenched with a peroxidase suppressor. Detection was performed using a biotin-conjugated secondary antibody and SA-HRP, followed by colorimetric detection using DAB. Tissues were counterstained with hematoxylin and prepped for mounting.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
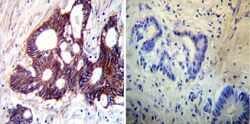
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemistry was performed on cancer biopsies of deparaffinized Human colon carcinoma tissues. To expose target proteins, heat induced antigen retrieval was performed using 10mM sodium citrate (pH6.0) buffer, microwaved for 8-15 minutes. Following antigen retrieval tissues were blocked in 3% BSA-PBS for 30 minutes at room temperature. Tissues were then probed at a dilution of 1:200 with a mouse monoclonal antibody recognizing Sodiµm/Potassium ATPase beta (Product # MA3-930) or without primary antibody (negative control) overnight at 4°C in a humidified chamber. Tissues were washed extensively with PBST and endogenous peroxidase activity was quenched with a peroxidase suppressor. Detection was performed using a biotin-conjugated secondary antibody and SA-HRP, followed by colorimetric detection using DAB. Tissues were counterstained with hematoxylin and prepped for mounting.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
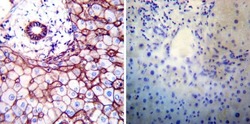
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemistry was performed on normal deparaffinized Human liver tissue tissues. To expose target proteins, heat induced antigen retrieval was performed using 10mM sodium citrate (pH6.0) buffer, microwaved for 8-15 minutes. Following antigen retrieval tissues were blocked in 3% BSA-PBS for 30 minutes at room temperature. Tissues were then probed at a dilution of 1:200 with a mouse monoclonal antibody recognizing Sodiµm/Potassium ATPase beta (Product # MA3-930) or without primary antibody (negative control) overnight at 4°C in a humidified chamber. Tissues were washed extensively with PBST and endogenous peroxidase activity was quenched with a peroxidase suppressor. Detection was performed using a biotin-conjugated secondary antibody and SA-HRP, followed by colorimetric detection using DAB. Tissues were counterstained with hematoxylin and prepped for mounting.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
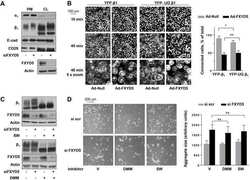
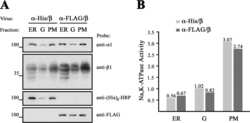
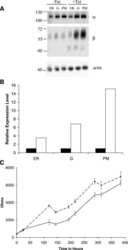
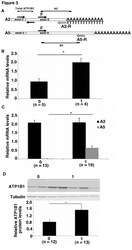
- Figure 3 The T 12 GT 3 GT 6 allele regulates the polyadenylation of ATP1B1 mRNA in human tissues A) Schematic of the primer design used to distinguish between the A2- and A5- polyadenylated mRNAs. The A2-R primer had a 5' T 15 tail to selectively amplify A2-polyadenylated mRNA. Total ATP1B1 mRNA was measured using primers that amplified across the exon 5/exon 6 junction. B) Real-time PCR of mRNA from human kidneys. The A2-polyadenylated transcript was quantified relative to total ATP1B1 mRNA. 0 and 1 indicate subjects without the T 12 GT 3 GT 6 allele and with 1 copy of the T 12 GT 3 GT 6 allele, respectively. Error bars represent standard errors. * p < 0.0001. C) Real-time PCR of mRNA from human lymphocytes. Expression of the A2- and A5-polyadenylated mRNAs relative to total ATP1B1 mRNA in lymphocytes from subjects with 0 or at least 1 copy of the T 12 GT 3 GT 6 allele. * p = 0.0001 between the A5-polyadenylated transcript levels in the 2 groups. Data represent the average across samples from each genotype group with standard error. D) Expression of ATP1B1 protein in lymphocytes from individuals with 0 or at least 1 copy of the T 12 GT 3 GT 6 allele. Tubulin was used as a loading control. The graph quantifies the average level of ATP1B1 protein relative to tubulin with standard error. * p = 0.05.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
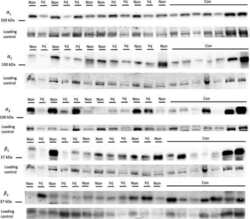
- Experimental details
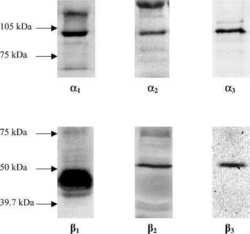
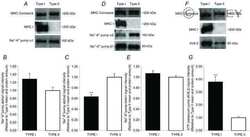
- Figure 4 Representative western blot images for each NKA isoform analyzed ( alpha 1-3 and beta 1-2 ), including example of the coomassie stain used to normalize blot density to the total protein content of the sample. ""Inj"" represents the injured leg from the KI group, ""Non"" represents the noninjured leg from the KI group, and ""CON"" represents the control group.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
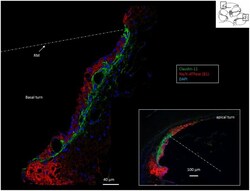
- Experimental details
- FIGURE 2 Confocal immunofluorescence of Na/K-ATPase (beta1 isoform) and Claudin-11 in the lateral wall of the basal and apical (inset) turns. Claudin-11 is expressed basally from the superior epithelium of the SP to the suprastrial space insulating the K + secreting marginal cell layer. Non-polarized beta1 Na/K-ATPase activity is high in type II and type V fibrocytes conceivably reflecting the uptake and recirculation of K + . RM, Reissner's membrane.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
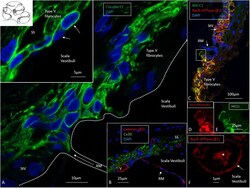
- Experimental details
- FIGURE 4 Confocal and super-resolution (SIM) microscopy of the suprastrial space (SS). (A) Insulating type V fibrocytes express Claudin-11. The left inset shows cells facing the scala vestibuli (arrows). (B) Cx30 expression also reaches the SS reflecting conceivable transcellular recirculation of K + from SV back to the StV. Laminin beta2 stains the basal lamina of the RM and capillaries. (C) Polarized expression of NKCC1 and Na/K-ATPase (beta1) in the StV and non-polarized manifestation in the suprastrial space may reflect the alternate directions of ion flow. Framed area is magnified in (D,E) and show expression of the NKCC1 and Na/K-ATPase (beta1) membrane transporters facing SV. (F) The type V fibrocyte facing the SV shows both intracellular ( * ) and membrane expression (arrow) of Na/K-ATPase (SR-SIM). StV, stria vascularis; RM, Reissner's membrane; V, stria vessel; SV, scala vestibuli.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
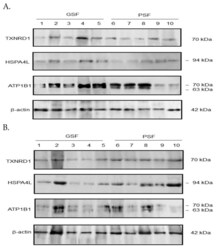
- Experimental details
- Western blotting analysis showing protein expression of TXNRD1, HSPA4L and ATP1B1 in ( A ) the fresh pre-freeze (PF) and ( B ) frozen-thawed (FT) sperm from boars of the good and poor semen freezability (GSF and PSF, respectively) groups.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
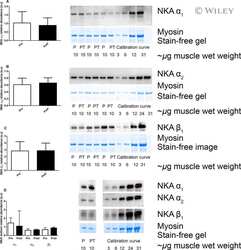
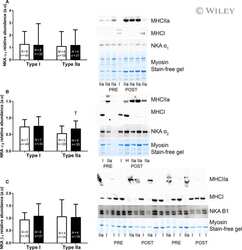
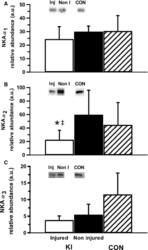
- Figure 2 Muscle NKA alpha 1 (A), alpha 2 (B), and alpha 3 (C) isoform relative abundance from the vastus lateralis of the injured and noninjured legs of participants with knee injury (KI) and from a single leg of age- and BMI-matched controls (CON). Representative western blots are included; Inj represents the knee-injured leg, Non-I represents the noninjured leg, and CON represents the control group. Unfilled bars represent the injured leg from KI, filled bars represent the noninjured leg from KI and the hatched bars represent CON. *Less than noninjured leg ( P < 0.05), ‡ Moderate effect size compared to noninjured leg. Values are Mean +- SD, n = 6 for each leg KI, n = 7 CON.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
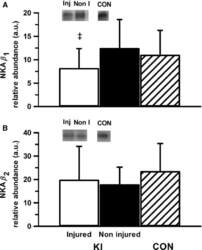
- Figure 3 Muscle NKA beta 1 (A) and beta 2 (B) isoform relative abundance from the vastus lateralis of the injured and noninjured legs of participants with knee injury (KI) and from a single leg of age- and BMI-matched controls (CON). Representative western blots are included; ""Inj"" represents the knee-injured leg, ""Non-I"" represents the noninjured leg, and ""CON ""represents the control group. Hollow bars represent the injured leg from KI, filled bars represent the noninjured leg from KI and the hatched bars represent the CON. ‡ Moderate effect size compared to noninjured leg in KI. Values are Mean +- SD, n = 6 for each leg KI, n = 7 CON.
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry Immunoprecipitation
Immunoprecipitation