Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [1]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunocytochemistry [1]
- Other assay [1]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- PA5-29931 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- Rhotekin Polyclonal Antibody
- Antibody type
- Polyclonal
- Antigen
- Recombinant full-length protein
- Description
- Recommended positive controls: 293T, A431, Jurkat, Raji, mouse brain, NCI-H929, human Rhotekin-transfected 293T. Predicted reactivity: Mouse (93%), Rat (96%), Rhesus Monkey (99%), Bovine (94%). Store product as a concentrated solution. Centrifuge briefly prior to opening the vial.
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse
- Host
- Rabbit
- Isotype
- IgG
- Vial size
- 100 μL
- Concentration
- 0.54 mg/mL
- Storage
- Store at 4°C short term. For long term storage, store at -20°C, avoiding freeze/thaw cycles.
Submitted references S100A4 is activated by RhoA and catalyses the polymerization of non-muscle myosin, adhesion complex assembly and contraction in airway smooth muscle.
Zhang W, Gunst SJ
The Journal of physiology 2020 Oct;598(20):4573-4590
The Journal of physiology 2020 Oct;598(20):4573-4590
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
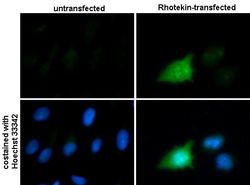
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of Rhotekin showing staining in the cytoplasm of HeLa cells. Rhotekin-transfected (right) or untransfected (left) HeLa cells were fixed in ice-cold MeOH for 5 min and stained using a Rhotekin polyclonal antibody (Product # PA5-29931) diluted at 1:500. Blue: Hoechst 33342 staining.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
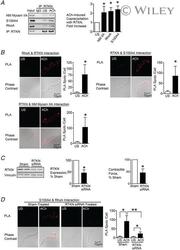
- Experimental details
- 5 Figure Rhotekin couples RhoA to S100A4 and NM myosin II in SM cells and tissues stimulated with ACh A , rhotekin (RTKN) was immunoprecipitated from tissue extracts and immunocomplexes were blotted for RhoA, S100A4, RTKN and NM myosin IIA. Stimulation for 5 min with 10 -5 M ACh significantly increased the coprecipitation of NM myosin IIA ( n = 6, p = 0.0070), RhoA ( n = 3, p = 0.0359) and S100A4 ( n = 9, p = 0.0001) with RTKN. B , in situ PLA was used to determine the interaction of RTKN and RhoA, S100A4 and NM myosin IIA in freshly dissociated tracheal SM cells. Stimulation with ACh caused a significant increase in the number of PLA complexes between all four proteins (RTKN-RhoA, n = 20, p = 0.0001; RTKN-S100A4, n = 20, p = 0.0001; RTKN-NM myosin IIA, n = 31, p = 0.0001). C , tracheal SM tissues were treated with RTKN siRNA. Depletion of RTKN significantly inhibited protein expression ( n = 10, p = 0.0001) and also inhibited tension development in response to 10 -5 M ACh stimulation ( n = 16, p = 0.0001). D , PLA shows interactions between S100A4 and RhoA in cells dissociated from sham-treated tissues and from RTKN-depleted tissues. ACh stimulation of sham-treated cells resulted in a significant increase in the interactions between S100A4 and RhoA (US, n = 16; ACh, n = 20). RTKN depletion inhibited the ACh-induced increase of the interaction between S100A4 and RhoA ( p = 0.0001) (US, n = 18; ACh, n = 19). Data analysed by a paired Student's t test ( A and C ), an unpaired S
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry