Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [4]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- ELISA [1]
- Immunocytochemistry [3]
- Immunohistochemistry [2]
- Chromatin Immunoprecipitation [2]
- Other assay [2]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- 710048 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- NFkB p65 Recombinant Superclonal™ Antibody (4-2HCLC)
- Antibody type
- Other
- Antigen
- Recombinant full-length protein
- Description
- Recombinant rabbit Superclonal™ antibodies are unique offerings from Thermo Fisher Scientific. They are comprised of a selection of multiple different recombinant monoclonal antibodies, providing the best of both worlds - the sensitivity of polyclonal antibodies with the specificity of monoclonal antibodies - all delivered with the consistency only found in a recombinant antibody. While functionally the same as a polyclonal antibody - recognizing multiple epitope sites on the target and producing higher detection sensitivity for low abundance targets - a recombinant rabbit Superclonal™ antibody has a known mixture of light and heavy chains. The exact population can be produced in every lot, circumventing the biological variability typically associated with polyclonal antibody production. Note: Formerly called “Recombinant polyclonal antibody”, this product is now rebranded as “Recombinant Superclonal™ antibody”. The physical product and the performance remain unchanged.
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse
- Host
- Rabbit
- Isotype
- IgG
- Antibody clone number
- 4-2HCLC
- Vial size
- 100 μg
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/mL
- Storage
- Store at 4°C short term. For long term storage, store at -20°C, avoiding freeze/thaw cycles.
Submitted references Ghrelin ameliorates chronic obstructive pulmonary disease-associated infllammation and autophagy.
Plasma-derived extracellular vesicles from Plasmodium vivax patients signal spleen fibroblasts via NF-kB facilitating parasite cytoadherence.
Systematic Immunotherapy Target Discovery Using Genome-Scale In Vivo CRISPR Screens in CD8 T Cells.
Codonopis bulleynana Forest ex Diels inhibits autophagy and induces apoptosis of colon cancer cells by activating the NF-κB signaling pathway.
Song B, Yan X, Li R, Zhang H
Biotechnology and applied biochemistry 2021 Apr;68(2):356-365
Biotechnology and applied biochemistry 2021 Apr;68(2):356-365
Plasma-derived extracellular vesicles from Plasmodium vivax patients signal spleen fibroblasts via NF-kB facilitating parasite cytoadherence.
Toda H, Diaz-Varela M, Segui-Barber J, Roobsoong W, Baro B, Garcia-Silva S, Galiano A, Gualdrón-López M, Almeida ACG, Brito MAM, de Melo GC, Aparici-Herraiz I, Castro-Cavadía C, Monteiro WM, Borràs E, Sabidó E, Almeida IC, Chojnacki J, Martinez-Picado J, Calvo M, Armengol P, Carmona-Fonseca J, Yasnot MF, Lauzurica R, Marcilla A, Peinado H, Galinski MR, Lacerda MVG, Sattabongkot J, Fernandez-Becerra C, Del Portillo HA
Nature communications 2020 Jun 2;11(1):2761
Nature communications 2020 Jun 2;11(1):2761
Systematic Immunotherapy Target Discovery Using Genome-Scale In Vivo CRISPR Screens in CD8 T Cells.
Dong MB, Wang G, Chow RD, Ye L, Zhu L, Dai X, Park JJ, Kim HR, Errami Y, Guzman CD, Zhou X, Chen KY, Renauer PA, Du Y, Shen J, Lam SZ, Zhou JJ, Lannin DR, Herbst RS, Chen S
Cell 2019 Aug 22;178(5):1189-1204.e23
Cell 2019 Aug 22;178(5):1189-1204.e23
Codonopis bulleynana Forest ex Diels inhibits autophagy and induces apoptosis of colon cancer cells by activating the NF-κB signaling pathway.
Luan Y, Li Y, Zhu L, Zheng S, Mao D, Chen Z, Cao Y
International journal of molecular medicine 2018 Mar;41(3):1305-1314
International journal of molecular medicine 2018 Mar;41(3):1305-1314
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
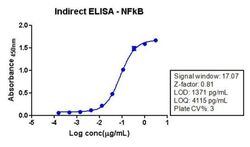
- Experimental details
- Indirect ELISA analysis of NFkB p65 in HeLa cell lysate (1 µg/well) using a NFkB p65 Recombinant Rabbit Superclonal™ Antibody (Product # 710048) and TMB (Product # SB01) as a substrate.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
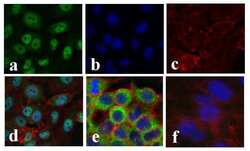
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of NF-kappa-B p65 was done on 70% confluent log phase TNF-Alpha treated HeLa cells (serum starved for 16 hours followed by treatment with 20 ng/mL TNF-Alpha for 1 hour). The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 minutes; permeabilized with 0.25% Triton X-100 for 10 minutes followed by blocking with 5% BSA for 1 hour at room temperature. The cells were incubated with NF-kappa-B p65 Recombinant Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Product # 710048) at 1 µg/mL in 1% BSA and incubated for 3 hours at room temperature and then labeled with Alexa Fluor 488 Goat anti-Rabbit IgG Secondary Antibody (Product # A-11008) at a dilution of 1:400 for 30 minutes at room temperature (Panel a: green). Nuclei (Panel b: blue) were stained with SlowFade Gold Antifade Mountant with DAPI (Product # S36938). F-actin (Panel c: red) was stained with Alexa Fluor 594 Phalloidin (Product # A12381). Panel d shows nuclear localization of SMAD2 upon treatment; Panel e showing cytoplasmic localization in untreated HeLa cells. Panel f is a no primary antibody control. The images were captured at 20X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
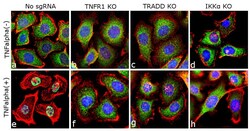
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescence analysis of NFkB p65 was done on 70% confluent log phase ME-180 cells. The cells were either mock treated or treated with TNF-alpha (50 ng/mL for 20 min), fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 minutes, permeabilized with 0.1% Triton™ X-100 for 10 minutes, and blocked with 1% BSA for 1 hour at room temperature. The cells were subsequently labeled with NFkB p65 (Green) Recombinant Rabbit Superclonal™ Antibody (Product # 710048) at 1µg/mL in 0.1% BSA and incubated for 3 hours at room temperature and then labeled with Goat anti-Rabbit IgG (Heavy Chain) Superclonal™ Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor® 488 conjugate (Product # A27034) at a dilution of 1:2000 for 45 minutes at room temperature. Nuclei (Blue) were stained with SlowFade® Gold Antifade Mountant DAPI (S36938). F-actin (Red) was stained with Rhodamine Phalloidin (Product # R415, 1:300). TNFalpha induced nuclear translocation of NFkB, a downstream target in the TNFR1, TRADD and IKK alpha was observed in control cell line (panels a, e) and not in the TNFR1, TRADD and IKK alpha knockout (KO) cell lines (panels b-d; f-h). The images were captured at 40X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
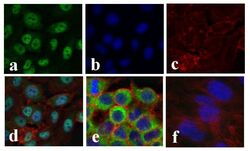
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of NF-kappa-B p65 was done on 70% confluent log phase TNF-Alpha treated HeLa cells (serum starved for 16 hours followed by treatment with 20 ng/mL TNF-Alpha for 1 hour). The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 minutes; permeabilized with 0.25% Triton X-100 for 10 minutes followed by blocking with 5% BSA for 1 hour at room temperature. The cells were incubated with NF-kappa-B p65 Recombinant Rabbit Superclonal™ Antibody (Product # 710048) at 1 µg/mL in 1% BSA and incubated for 3 hours at room temperature and then labeled with Alexa Fluor 488 Goat anti-Rabbit IgG Secondary Antibody (Product # A-11008) at a dilution of 1:400 for 30 minutes at room temperature (Panel a: green). Nuclei (Panel b: blue) were stained with SlowFade Gold Antifade Mountant with DAPI (Product # S36938). F-actin (Panel c: red) was stained with Alexa Fluor 594 Phalloidin (Product # A12381). Panel d shows nuclear localization of SMAD2 upon treatment; Panel e showing cytoplasmic localization in untreated HeLa cells. Panel f is a no primary antibody control. The images were captured at 20X magnification.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
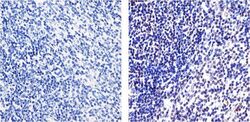
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of NF-kappa-B (p65) showing staining in the nucleus of paraffin-embedded mouse spleen tissue (right) compared to a negative control without primary antibody (left). To expose target proteins, antigen retrieval was performed using 10mM sodium citrate (pH 6.0), microwaved for 8-15 min. Following antigen retrieval, tissues were blocked in 3% H2O2-methanol for 15 min at room temperature, washed with ddH2O and PBS, and then probed with a NF-kappa-B (p65) Recombinant Rabbit Superclonal™ Antibody (Product # 710048) diluted in 3% BSA-PBS at a dilution of 1:20 overnight at 4°C in a humidified chamber. Tissues were washed extensively in PBST and detection was performed using an HRP-conjugated secondary antibody followed by colorimetric detection using a DAB kit. Tissues were counterstained with hematoxylin and dehydrated with ethanol and xylene to prep for mounting.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
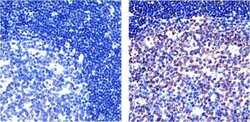
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of NF-kappa-B (p65) showing staining in the cytoplasm and nucleus of paraffin-embedded human tonsil tissue (right) compared to a negative control without primary antibody (left). To expose target proteins, antigen retrieval was performed using 10mM sodium citrate (pH 6.0), microwaved for 8-15 min. Following antigen retrieval, tissues were blocked in 3% H2O2-methanol for 15 min at room temperature, washed with ddH2O and PBS, and then probed with a NF-kappa-B (p65) Recombinant Rabbit Superclonal™ Antibody (Product # 710048) diluted in 3% BSA-PBS at a dilution of 1:20 overnight at 4°C in a humidified chamber. Tissues were washed extensively in PBST and detection was performed using an HRP-conjugated secondary antibody followed by colorimetric detection using a DAB kit. Tissues were counterstained with hematoxylin and dehydrated with ethanol and xylene to prep for mounting.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
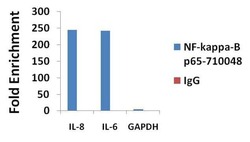
- Experimental details
- ChIP- qPCR analysis of NF-kappa-B-p65 was performed with 3 µg/mL of the NF-kappa-B-p65 Recombinant Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Product # 710048) on sheared chromatin from 2 million HeLa cells treated with TNF-alpha (50 ng/mL for 1h) using the MAGnify Chromatin Immunoprecipitation System (Product # 49-2024). Normal rabbit IgG (3 µg/mL) was used as a negative IP control. The purified DNA from each ChIP sample was analyzed by StepOnePlus Real-Time PCR System (Product # 4376600) with primers for the promoter of active IL-8 and IL-6 gene, used as positive control targets, and the GAPDH gene, used as negative control target. Data is presented as fold enrichment of the antibody signal versus the negative control IgG using the comparative CT method.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
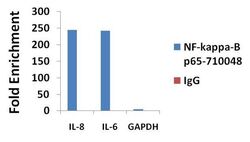
- Experimental details
- ChIP- qPCR analysis of NF-kappa-B-p65 was performed with 3 µg/mL of the NF-kappa-B-p65 Recombinant Rabbit Superclonal™ Antibody (Product # 710048) on sheared chromatin from 2 million HeLa cells treated with TNF-alpha (50 ng/mL for 1h) using the MAGnify Chromatin Immunoprecipitation System (Product # 49-2024). Normal rabbit IgG (3 µg/mL) was used as a negative IP control. The purified DNA from each ChIP sample was analyzed by StepOnePlus Real-Time PCR System (Product # 4376600) with primers for the promoter of active IL-8 and IL-6 gene, used as positive control targets, and the GAPDH gene, used as negative control target. Data is presented as fold enrichment of the antibody signal versus the negative control IgG using the comparative CT method.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
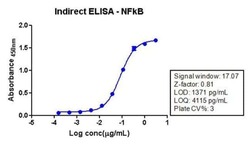
- Experimental details
- Indirect ELISA analysis of NFkB p65 in HeLa cell lysate (1 µg/well) using a NFkB p65 Recombinant Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Product # 710048) and TMB (Product # SB01) as a substrate.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
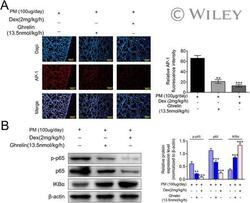
- Experimental details
- 9 FIG Ghrelin inhibited AP-1 and NF-kappaB signaling pathway . ( A ) IF results revealed that ghrelin could inhibited the expression of AP-1 in PM-induced inflammation. ( B ) WB result showed that ghrelin significantly decreased the expression of P65 and incresed IkappaBalpha expression, indicating that classical NF-kappaB signaling pathway was inhibited (mean +- SEM; n = 3; Student's t -test; * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001 vs. control).
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot ELISA
ELISA