14-6731-81
antibody from Invitrogen Antibodies
Targeting: RELA
NFKB3, p65
 Western blot
Western blot Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry Immunoprecipitation
Immunoprecipitation Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry Chromatin Immunoprecipitation
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Other assay
Other assayAntibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [15]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunocytochemistry [1]
- Chromatin Immunoprecipitation [1]
- Other assay [10]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- 14-6731-81 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- NFkB p65 Polyclonal Antibody, eBioscience™
- Antibody type
- Polyclonal
- Antigen
- Other
- Description
- Description: The polyclonal antibody reacts with mouse, rat, and human NFkB p65; the antibody was raised against a peptide mapping to the carboxy terminus of human NFkB p65. Members of the rel/NFkB family of transcription factors are involved in the regulation of cellular responses, such as growth, development, and the inflammatory response. They share a structural motif known as the rel homology region (RHR), the C-terminal one third of which mediates protein dimerization (2, 6, 8). Complexes of p50 (NF-kB1) or p52 (NF-kB2) are generated through the processing of p105 and p100 precursors, respectively. These are usually associated with members of the Rel family (p65, c-Rel, Rel B). The homo- and heterodimer formed through combinations of NFkB/Rel proteins bind distinct kB sites to regulate the transcription of different genes (7, 9). In resting cells, NFkB is retained in the cytoplasm bound to inhibitory proteins of the IkB family. Degradation of IkB proteins occurs with cell activation, via of variety of signals, including inflammatory cytokines and bacterial lipopolysaccharides (LPS) as well as oxidative and fluid mechanical stress. This results in nuclear translocation of NFkB and the transcriptional gene activation of proinflammatory genes (1, 9). It has been suggested that NFkB plays a role in the development of numerous pathological states. Activation of NFkB induces gene programs leading to transcription of factors that promote inflammation, such as leukocyte adhesion molecules, cytokines, and chemokines. It is also thought that there are some substances with possible anti-inflammatory effects that are also NFkB regulated. There is some evidence indicating NFkB as a key factor in the pathophysiology of cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury as well as the development of insulin dependent Diabetes Mellitus (4, 3). Applications Reported: Purified anti-mo/hu/rat NFkB p65 poly has been reported for use in immunoprecipitation, immunoblotting (WB), and immunohistochemical staining. Applications Tested: Purified anti-mo/hu/rat NFkB p65 poly has been tested by immunoblotting (WB) and immunohistochemistry. (1:1000 starting dilution). It is recommended that this antibody be titrated for optimal performance in the assay of interest. Purity: Greater than 90%, as determined by SDS-PAGE. Aggregation: Less than 10%, as determined by HPLC. Filtration: 0.2 µm post-manufacturing filtered.
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat
- Host
- Rabbit
- Isotype
- IgG
- Vial size
- 50 µg
- Concentration
- 0.2 mg/mL
- Storage
- 4° C
Submitted references Butorphanol reduces the neuronal inflammatory response and apoptosis via inhibition of p38/JNK/ATF2/p53 signaling.
Malaria parasite heme biosynthesis promotes and griseofulvin protects against cerebral malaria in mice.
Modulation of allergic inflammation in the lung by a peptide derived from Mycobacteria tuberculosis chaperonin 60.1.
Palmitic acid induces guanylin gene expression through the Toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor-κB pathway in rat macrophages.
Inhibitory effects of quail egg on mast cells degranulation by suppressing PAR2-mediated MAPK and NF-kB activation.
Free immunoglobulin light chain (FLC) promotes murine colitis and colitis-associated colon carcinogenesis by activating the inflammasome.
Anti-hepatitis B virus (HBV) response of imiquimod based toll like receptor 7 ligand in hbv-positive human hepatocelluar carcinoma cell line.
Anti-inhibitory potential of an ethanolic extract of Distromium decumbens on pro-inflammatory cytokine production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa lipopolysaccharide-stimulated nasal polyp-derived fibroblasts.
YCG063 inhibits Pseudomonas aeruginosa LPS-induced inflammation in human retinal pigment epithelial cells through the TLR2-mediated AKT/NF-κB pathway and ROS-independent pathways.
Down-regulation of IKKβ expression in glioma-infiltrating microglia/macrophages is associated with defective inflammatory/immune gene responses in glioblastoma.
3,3'-Diindolylmethane inhibits VEGF expression through the HIF-1α and NF-κB pathways in human retinal pigment epithelial cells under chemical hypoxic conditions.
Transmembrane peptides used to investigate the homo-oligomeric interface and binding hotspot of latent membrane protein 1.
Knockout of the tumor suppressor gene Gprc5a in mice leads to NF-kappaB activation in airway epithelium and promotes lung inflammation and tumorigenesis.
NF-kappaB activation through the alternative pathway correlates with chemoresistance and poor survival in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type.
Alteration of NF-kappaB activity leads to mitochondrial apoptosis after infection with pathological prion protein.
Huang Y, Li S, Chen H, Feng L, Yuan W, Han T
Experimental and therapeutic medicine 2022 Mar;23(3):229
Experimental and therapeutic medicine 2022 Mar;23(3):229
Malaria parasite heme biosynthesis promotes and griseofulvin protects against cerebral malaria in mice.
Chandana M, Anand A, Ghosh S, Das R, Beura S, Jena S, Suryawanshi AR, Padmanaban G, Nagaraj VA
Nature communications 2022 Jul 12;13(1):4028
Nature communications 2022 Jul 12;13(1):4028
Modulation of allergic inflammation in the lung by a peptide derived from Mycobacteria tuberculosis chaperonin 60.1.
Riffo-Vasquez Y, Kanabar V, Keir SD, E-Lacerda RR, Man F, Jackson DJ, Corrigall V, Coates ARM, Page CP
Clinical and experimental allergy : journal of the British Society for Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2020 Apr;50(4):508-519
Clinical and experimental allergy : journal of the British Society for Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2020 Apr;50(4):508-519
Palmitic acid induces guanylin gene expression through the Toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor-κB pathway in rat macrophages.
Akieda-Asai S, Ma H, Date Y
American journal of physiology. Cell physiology 2019 Dec 1;317(6):C1239-C1246
American journal of physiology. Cell physiology 2019 Dec 1;317(6):C1239-C1246
Inhibitory effects of quail egg on mast cells degranulation by suppressing PAR2-mediated MAPK and NF-kB activation.
Lianto P, Ogutu FO, Zhang Y, He F, Che H
Food & nutrition research 2018;62
Food & nutrition research 2018;62
Free immunoglobulin light chain (FLC) promotes murine colitis and colitis-associated colon carcinogenesis by activating the inflammasome.
Ma J, Jiang D, Gong X, Shao W, Zhu Z, Xu W, Qiu X
Scientific reports 2017 Jul 12;7(1):5165
Scientific reports 2017 Jul 12;7(1):5165
Anti-hepatitis B virus (HBV) response of imiquimod based toll like receptor 7 ligand in hbv-positive human hepatocelluar carcinoma cell line.
Das D, Sengupta I, Sarkar N, Pal A, Saha D, Bandopadhyay M, Das C, Narayan J, Singh SP, Chakrabarti S, Chakravarty R
BMC infectious diseases 2017 Jan 14;17(1):76
BMC infectious diseases 2017 Jan 14;17(1):76
Anti-inhibitory potential of an ethanolic extract of Distromium decumbens on pro-inflammatory cytokine production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa lipopolysaccharide-stimulated nasal polyp-derived fibroblasts.
Lee DS, Lee CM, Park SK, Yim MJ, Lee JM, Choi G, Yoo JS, Jung WK, Park S, Seo SK, Park WS, Choi IW
International journal of molecular medicine 2017 Dec;40(6):1950-1956
International journal of molecular medicine 2017 Dec;40(6):1950-1956
YCG063 inhibits Pseudomonas aeruginosa LPS-induced inflammation in human retinal pigment epithelial cells through the TLR2-mediated AKT/NF-κB pathway and ROS-independent pathways.
Paeng SH, Park WS, Jung WK, Lee DS, Kim GY, Choi YH, Seo SK, Jang WH, Choi JS, Lee YM, Park S, Choi IW
International journal of molecular medicine 2015 Sep;36(3):808-16
International journal of molecular medicine 2015 Sep;36(3):808-16
Down-regulation of IKKβ expression in glioma-infiltrating microglia/macrophages is associated with defective inflammatory/immune gene responses in glioblastoma.
Mieczkowski J, Kocyk M, Nauman P, Gabrusiewicz K, Sielska M, Przanowski P, Maleszewska M, Rajan WD, Pszczolkowska D, Tykocki T, Grajkowska W, Kotulska K, Roszkowski M, Kostkiewicz B, Kaminska B
Oncotarget 2015 Oct 20;6(32):33077-90
Oncotarget 2015 Oct 20;6(32):33077-90
3,3'-Diindolylmethane inhibits VEGF expression through the HIF-1α and NF-κB pathways in human retinal pigment epithelial cells under chemical hypoxic conditions.
Park H, Lee DS, Yim MJ, Choi YH, Park S, Seo SK, Choi JS, Jang WH, Yea SS, Park WS, Lee CM, Jung WK, Choi IW
International journal of molecular medicine 2015 Jul;36(1):301-8
International journal of molecular medicine 2015 Jul;36(1):301-8
Transmembrane peptides used to investigate the homo-oligomeric interface and binding hotspot of latent membrane protein 1.
Sammond DW, Joce C, Takeshita R, McQuate SE, Ghosh N, Martin JM, Yin H
Biopolymers 2011 Nov;95(11):772-84
Biopolymers 2011 Nov;95(11):772-84
Knockout of the tumor suppressor gene Gprc5a in mice leads to NF-kappaB activation in airway epithelium and promotes lung inflammation and tumorigenesis.
Deng J, Fujimoto J, Ye XF, Men TY, Van Pelt CS, Chen YL, Lin XF, Kadara H, Tao Q, Lotan D, Lotan R
Cancer prevention research (Philadelphia, Pa.) 2010 Apr;3(4):424-37
Cancer prevention research (Philadelphia, Pa.) 2010 Apr;3(4):424-37
NF-kappaB activation through the alternative pathway correlates with chemoresistance and poor survival in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type.
Liu X, Wang B, Ma X, Guo Y
Japanese journal of clinical oncology 2009 Jul;39(7):418-24
Japanese journal of clinical oncology 2009 Jul;39(7):418-24
Alteration of NF-kappaB activity leads to mitochondrial apoptosis after infection with pathological prion protein.
Bourteele S, Oesterle K, Weinzierl AO, Paxian S, Riemann M, Schmid RM, Planz O
Cellular microbiology 2007 Sep;9(9):2202-17
Cellular microbiology 2007 Sep;9(9):2202-17
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
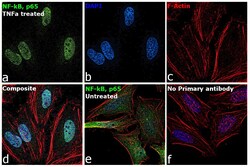
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescence analysis of Transcription factor p65 was performed using HeLa cells (serum-starved) and HeLa cells serum-starved for 16 hours, followed by 20 ng/mL human TNF alpha treatment for 40 minutes. The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 minutes, permeabilized with 0.1% Triton™ X-100 for 15 minutes, and blocked with 2% BSA for 45 minutes at room temperature. The cells were labeled with NFkB p65 Polyclonal Antibody, eBioscience™ (Product # 14-6731-81) at 1:100 dilution in 0.1% BSA, incubated at 4 degree celsius overnight and then labeled with Donkey anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Highly Cross-Adsorbed Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor Plus 488 (Product # A32790), (1:2000 dilution), for 45 minutes at room temperature (Panel a: Green). Nuclei (Panel b:Blue) were stained with ProLong™ Diamond Antifade Mountant with DAPI (Product # P36962). F-actin (Panel c: Red) was stained with Rhodamine Phalloidin (Product # R415, 1:300 dilution). Panel d represents the merged image showing nuclear localization of p65 protein in HeLa treated cells. Panel e represents the merged image of HeLa untreated cells that shows cytoplasmic localization of p65 protein. Panel f represents control cells with no primary antibody to assess background. The images were captured at 60X magnification.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
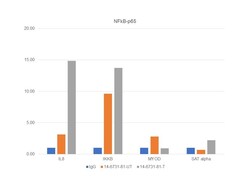
- Experimental details
- Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay of endogenous NFkB p65 was performed using NFkB p65 Polyclonal Antibody, eBioscience™ (Product # 14-6731-81, 5 µg) on sheared chromatin from HeLa cells treated with TNF-alpha (50 ng/mL for 1hr) using the MAGnify ChIP System kit (Product # 49-2024). Chromatin from untreated HeLa cells were prepared the same way. Normal Rabbit IgG was used as a negative IP control. The purified DNA was analyzed by qPCR using primers binding to IL8, IKKB, MYOD and SAT alpha (inactive). Data is presented as fold enrichment of the antibody signal versus the negative control IgG using the comparative CT method.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
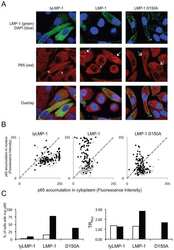
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
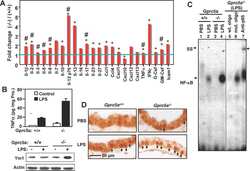
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
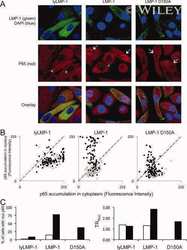
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
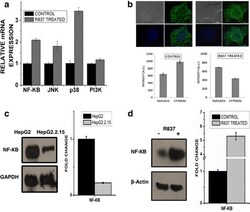
- Experimental details
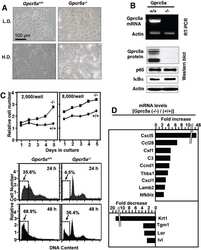
- Fig. 2 TLR7 pathway is activated on stimulation with its specific ligand imiquimod, R837. Chief downstream regulators, especially NF-kB is activated and transclocated to the nucleus on TLR7 activation. a Host immune response on TLR7 activation, using TLR7 ligand. HepG2.2.15 cells were treated with TLR7 agonist, R837 (8mug/ml) for 3 days. mRNA expression of different downstream regulators (NF- KB, JNK, p38 and PI3K) involved in the TLR7 pathway. b Confocal imaging showing nuclear uptake of Nuclear Factor-KB p65 subunit (NF- KB) from cytoplasm in cells where HepG2.2.15 cells are taken as control and HepG2.2.15 cells stimulated with TLR7 ligand, R837 (8mug/ml) for 72 h. c Nuclear Factor-KB p65 subunit (NF-KB) protein expression of HepG2 and HepG2.2.15 cells. d Nuclear Factor-KB p65 subunit (NF- KB) protein expression of HepG2.2.15 cells taken as control and treated with R837 (8mug/ml) for 72 h
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
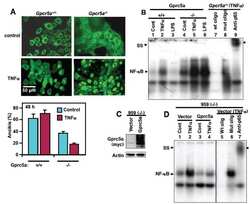
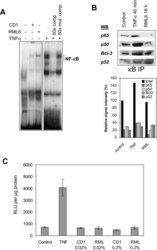
- Fig. 1 No transcriptional NF-kappaB activity after PrP Sc infection. A. Electromobility shift assay revealed NF-kappaB binding activity in PrP Sc -infected neuroblastoma cells (Bos2). Nuclear extracts of Bos2 cells infected with RML6, treated with CD1 or stimulated with 10 ng ml -1 TNF-alpha were incubated with 32 P-labelled double-stranded oligonucleotide specific for NF-kappaB. The TNF-alpha sample was incubated with a 50-fold excess of cold NF-kappaB oligonucleotide as specific competitor or with a mutated oligonucleotide as control. B. kappaB precipitation experiment and detection using antibodies directed against p65, p50, p52 and Bcl-3. kappaB binding proteins were precipitated from nuclear extracts using an agarose-conjugated consensus kappaB oligonucleotide. The precipitates from either untreated controls, TNF-treated or RML6-infected Bos2 cells were divided and analysed in Western blots for the presence of the various NF-kappaB subunits. The immunoblot was quantified by scanning densitometry. The total signal intensities (p65 + p50, +p52 + Bcl-3) for the treated cells relative to the control cells and the portion of each subunits are given in percentage. C. Luciferase reporter gene assay showed no transcriptional NF-kappaB activity after PrP Sc infection (0.2% or 0.02%), the value of relative light unit (RLU) per mug protein being equivalent for RML6- and CD1-treated cells. Mean values and SEM of three independent transfections are shown.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
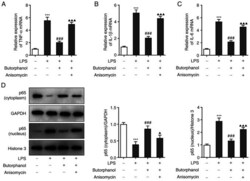
- Butorphanol decreases LPS-induced inflammatory factor release via p38/JNK/ATF2/p53 signaling. (A-C) The expression levels of TNF-alpha, IL-1beta and IL-6 in the above four groups were measured using reverse transcription-quantitative PCR. (D) The expression levels of p65 (cytoplasm) and p65 (nucleus) were determined using western blot analysis. *** P
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
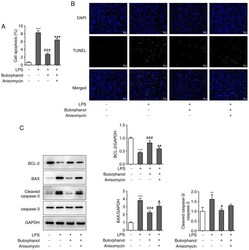
- Butorphanol decreases LPS-induced apoptosis via p38/JNK/ATF2/p53 signaling. (A) Anisomycin increased the number of apoptotic cells. (B) TUNEL assay was used to evaluate cell apoptosis (magnification, x200). (C) Expression levels of apoptosis-related protein were determined using western blot analysis. ** P
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
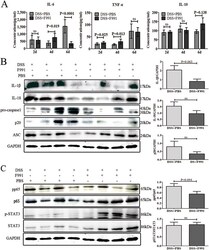
- Figure 3 F991 relieved inflammasome activation in the inflammatory tissue of DSS-induced colitis mice. ( A ) The level of IL-6, TNFalpha, IL-10 in the cultured supernatant of colonic tissue on the 2 nd , 4 th and 6 th day were examined by ELISA. The results are shown as the mean +- SD of 4 mice per group at each time point. ns: no statistical significance , * P < 0.05 , ** P < 0.01 , *** P < 0.001 compared with group DSS + PBS. ( B ) The level of active IL-1beta, IL-18, pro-caspase-1, cleaved caspase-1 (p20) and ASC in the colonic tissues on the 6 th day were determined by western blot. ( C ) The level of phosphorylated p65 (p-p65), and phosphorylated-STAT3 (p-STAT3) in the colonic tissues on the 6 th day were analyzed by western blot. DSS + PBS : mice challenged with DSS and injected with PBS, DSS + F991 : mice challenged with DSS and injected with F991. One representative experiment of three is displayed.
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn