Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [6]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunocytochemistry [2]
- Other assay [7]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- PA5-17308 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- alpha Actinin 1 Polyclonal Antibody
- Antibody type
- Polyclonal
- Antigen
- Synthetic peptide
- Description
- It is not recommended to aliquot this antibody.
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat, Hamster
- Host
- Rabbit
- Isotype
- IgG
- Vial size
- 100 μL
- Concentration
- 5 μg/mL
- Storage
- -20°C
Submitted references Saffron: A Multitask Neuroprotective Agent for Retinal Degenerative Diseases.
Variants in exons 5 and 6 of ACTB cause syndromic thrombocytopenia.
Increased free Zn(2+) correlates induction of sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum stress via altered expression levels of Zn(2+) -transporters in heart failure.
Generation of two human isogenic iPSC lines from fetal dermal fibroblasts.
Myogenic differentiation potential of human tonsil-derived mesenchymal stem cells and their potential for use to promote skeletal muscle regeneration.
Use of Adeno-Associated Virus to Enrich Cardiomyocytes Derived from Human Stem Cells.
Di Marco S, Carnicelli V, Franceschini N, Di Paolo M, Piccardi M, Bisti S, Falsini B
Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland) 2019 Jul 17;8(7)
Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland) 2019 Jul 17;8(7)
Variants in exons 5 and 6 of ACTB cause syndromic thrombocytopenia.
Latham SL, Ehmke N, Reinke PYA, Taft MH, Eicke D, Reindl T, Stenzel W, Lyons MJ, Friez MJ, Lee JA, Hecker R, Frühwald MC, Becker K, Neuhann TM, Horn D, Schrock E, Niehaus I, Sarnow K, Grützmann K, Gawehn L, Klink B, Rump A, Chaponnier C, Figueiredo C, Knöfler R, Manstein DJ, Di Donato N
Nature communications 2018 Oct 12;9(1):4250
Nature communications 2018 Oct 12;9(1):4250
Increased free Zn(2+) correlates induction of sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum stress via altered expression levels of Zn(2+) -transporters in heart failure.
Olgar Y, Durak A, Tuncay E, Bitirim CV, Ozcinar E, Inan MB, Tokcaer-Keskin Z, Akcali KC, Akar AR, Turan B
Journal of cellular and molecular medicine 2018 Mar;22(3):1944-1956
Journal of cellular and molecular medicine 2018 Mar;22(3):1944-1956
Generation of two human isogenic iPSC lines from fetal dermal fibroblasts.
Tandon R, Brändl B, Baryshnikova N, Landshammer A, Steenpaß L, Keminer O, Pless O, Müller FJ
Stem cell research 2018 Dec;33:120-124
Stem cell research 2018 Dec;33:120-124
Myogenic differentiation potential of human tonsil-derived mesenchymal stem cells and their potential for use to promote skeletal muscle regeneration.
Park S, Choi Y, Jung N, Yu Y, Ryu KH, Kim HS, Jo I, Choi BO, Jung SC
International journal of molecular medicine 2016 May;37(5):1209-20
International journal of molecular medicine 2016 May;37(5):1209-20
Use of Adeno-Associated Virus to Enrich Cardiomyocytes Derived from Human Stem Cells.
Guan X, Wang Z, Czerniecki S, Mack D, François V, Blouin V, Moullier P, Childers MK
Human gene therapy. Clinical development 2015 Sep;26(3):194-201
Human gene therapy. Clinical development 2015 Sep;26(3):194-201
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
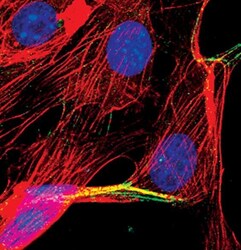
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of Alpha-Actinin in NIH/3T3 cells using an Alpha-Actinin polyclonal antibody (Product # PA5-17308) (green). Actin filaments are labeled with a fluorescent red phalloidin. DNA is labeled using a fluorescent blue dye.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of Alpha-Actinin in NIH/3T3 cells using an Alpha-Actinin polyclonal antibody (Product # PA5-17308) (green). Actin filaments are labeled with a fluorescent red phalloidin. DNA is labeled using a fluorescent blue dye.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
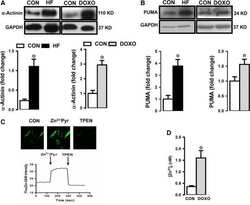
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
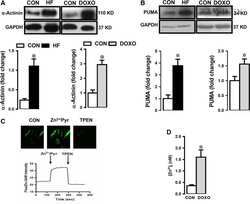
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
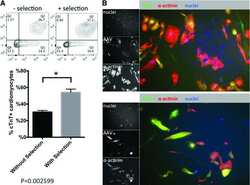
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
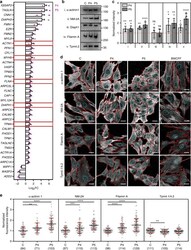
- Fig. 5 Select thrombocytopenia-associated ABPs are recruited to basal beta-CYA-rich filaments. a ABP transcripts significantly deregulated (log 2 fold change +- s.e.m.) in both P4 and P5 fibroblasts compared to a healthy control, as determined by RNA-Seq. Bar graphs show the combined results from both patients relative to the control. Dot plots show the individual patient data calculated from three technical replicates. Red boxes indicate the genes where disease-causing mutations have been associated with thrombocytopenia with enlarged platelets; b , c Western blot analysis and densitometry of ABP candidates: (i) alpha-actinin 1, (ii) NM-2A, (iii) Diaph1, (iv) Filamin A and (v) Tpm4.1/4.2 in control (C), P4 and P5 fibroblast lysates. Significant upregulation is validated for all candidates except Diaph1. Data are represented relative to the control (mean +- s.d.; 6 replicates from 3 lysates; Kruskal-Wallis test); d Representative maximum intensity projections show alpha-actinin 1 (top row), NM-2A (second row), Filamin A (third row) and Tpm4.1/4.2 distribution within z-stack slices 1-2 of C, P4, P5 and BWCFF control fibroblasts. Cell boundaries are shown in red and cyan regions indicate the nuclear boundaries where basal sub-nuclear filaments localize. Scale bars are 20 um; e Quantification of the fluorescence intensity of each candidate ABP in the sub-nuclear region (mean +- s.d.; Kruskal-Wallis test). The number of cells analyzed from 3 experiments is indicated in
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
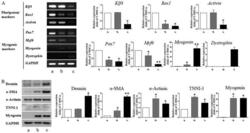
- Figure 3 Detection of myogenic markers in tonsil-derived mesenchymal stem cell (T-MSC)-derived myogenic cells. (A) Determination of the mRNA expression levels of pluripotent and myogenic markers. mRNA was isolated from (lane a) undifferentiated T-MSCs, (lane b) T-MSC-derived myoblasts cultured in replating medium as rosette-like spread spheres, and (lane c) terminally differentiated T-MSC-derived myocytes and the cells were examined by RT-PCR. (B) Protein expression levels of myogenic markers in T-MSCs during the process of myogenic induction (lane a, T-MSCs; lane b, T-MSC-derived myoblasts; lane c, T-MSC-derived myocytes). The levels of GAPDH were measured as a loading control. Band intensities were quantified using ImageJ software. Data are the means +- SEM of experiments performed in triplicate. * P
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
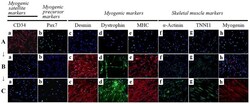
- Figure 4 Immunocytochemistry for the detection of myogenic markers. The expression of muscle-related proteins in the tonsil-derived mesenchymal stem cells (T-MSCs) during the process of myogenic induction (T-MSCs; T-MSC-derived myoblasts; T-MSC-derived myocytes) was evaluated by immunostaining using antibodies against myogenic satellite cells (panel a, CD34; red), precursors [panel b, paired box 7 (Pax7); green], differentiated myogenic cells [panel c, desmin (red); panel d, dystrophin (green); panel e, myosin heavy chain (MHC; red)], skeletal myogenic cells [panel f, alpha-actinin (green); panel g, troponin I type 1 (TNNI1; green); panel h, myogenin (red)]. The cells were counterstained with DAPI (blue). The samples were analyzed under a fluorescence microscope using appropriate filters. (A) Undifferentiated T-MSCs expressed (panel a) CD34 and (panel b) Pax7, but no other markers of myogenic cells. (B) Following differentiation into myoblasts, 80-90% of cells expressed (panel c) desmin, (panel d) dystrophin, and (panel e) MHC and 20-50% of cells expressed skeletal muscle (SKM) markers including (panel f) alpha-actinin, (panel g) TNNI1, and (panel h) myogenin. (Panel a) CD34 and (panel b) Pax7 were not expressed at any stage of the differentiation process from T-MSC-derived myoblasts into T-MSC-derived myocytes. (C) T-MSC-derived myocytes exhibited an increased expression of (panels c to h) myogenic and SKM cell markers compared with T-MSC-derived myoblasts and formed multinu
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
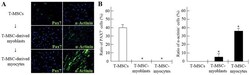
- Figure 6 Derivation of myogenic cells from human tonsil-derived mesenchymal stem cells (T-MSCs). (A) The expression of myogenic proteins in T-MSCs during the process of myogenic induction was evaluated by immunostaining using primary antibodies against paired box protein 7 (Pax7; green) or alpha-actinin (green). The cells were counterstained with DAPI (blue). The samples were analyzed under a fluorescence microscope using appropriate filters. (B) Quantification of immunofluorescence confirmed that during the process of myogenic differentiation, the expression of Pax7 and alpha-actinin was decreased or increased, respectively, indicating the differentiation potential of T-MSCs to form myocytes. Data are the means +- SEM. For each condition, 4 slides were used for quantification. Graphs represent the average of multiple tests from three independent experiments, * P
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry