Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [1]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Other assay [13]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- PA1-18416 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- Oxytocin Polyclonal Antibody
- Antibody type
- Polyclonal
- Antigen
- Synthetic peptide
- Description
- Reconstitute in 50 µL sterile water. Centrifuge to remove any insoluble material. It is recommended that a thawed sample is stored at 4 °C for no longer than 2 weeks. Allocation of appropriate anti-bacterial agent can increase shelf life by several weeks. Diluted serum should be prepared as required. Long term stability requires storage, preferably in small aliquots at -20 °C or lower. Glycerol (1:1) can be added to neat serum for additional stability if intended use does not prevent this.
- Reactivity
- Human
- Host
- Guinea Pig
- Isotype
- IgG
- Vial size
- 50 μL
- Concentration
- Conc. Not Determined
- Storage
- -20°C, Avoid Freeze/Thaw Cycles
Submitted references The distribution of oxytocin and the oxytocin receptor in rat brain: relation to regions active in migraine.
Warfvinge K, Krause D, Edvinsson L
The journal of headache and pain 2020 Feb 7;21(1):10
The journal of headache and pain 2020 Feb 7;21(1):10
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
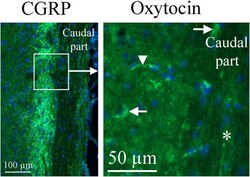
- Fig. 10 Oxytocin immunohistochemistry of the Spinal trigeminal nucleus. To the right, oxytocin immunohistochemistry is shown. A few cell bodies (arrows) express oxytocin in the Sp5. No immunoreactivity was found in fibers (asterisk). The arrowhead points at a stained capillary. On the left, CGRP expression in this region [ 25 ] is shown for comparison. The square in the left panel indicates the approximate location of the area presented in the right panel
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
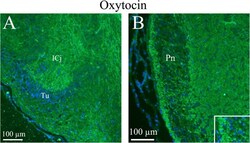
- Fig. 11 Oxytocin immunohistochemistry of the Islands of Calleja and the Pons. a . Thin slender processes in the Islands of Calleja (ICj) plus fibers structures in the surrounding area were oxytocin immunoreactive. b . In the pontine nucleus (Pn), the neurons were surrounded by thin oxytocin positive fibers (insert)
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
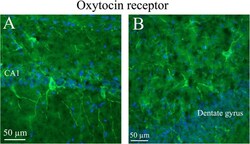
- Fig. 12 Oxytocin receptor immunohistochemistry of the hippocampus. Oxytocin receptor expression was found in the CA1 and CA2 regions of the hippocampus (CA1, CA2) and in the dentate gyrus. a . The left panel demonstrates positive pyramidal neurons in CA1. b . The right panel shows neurons of the dentate gyrus, with oxytocin receptor expression in both the cell soma and the processes
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
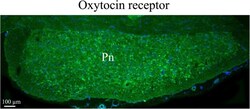
- Fig. 13 Oxytocin receptor immunohistochemistry in the pons. Neurons in the pons (Pn) expressed oxytocin receptor in the cell soma
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
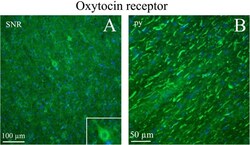
- Experimental details
- Fig. 14 Oxytocin receptor immunohistochemistry in the Substantia nigra and pyramidal tract. a . Neurons of the substantia nigra (SNR) expressed oxytocin receptor. Insert: Higher magnification of a positive neuron. b . The pyramidal tract (py) contained thick oxytocin receptor immunoreactive fibers
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
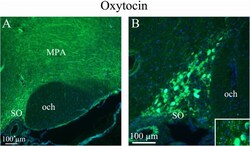
- Experimental details
- Fig. 2 Oxytocin immunohistochemistry of the supraoptic nucleus and optic chiasm. a. A and B . The image shows immunoreactive magnocellular neurons of the supraoptic nucleus (SO). The optic chiasm (och), close to the SO, shows no immunoreactivity. Immunoreactive fibers in the medial preoptic area (MPA) are seen. Insert in B: Higher magnification of stained magnocellular neurons and occasional thin fibers
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
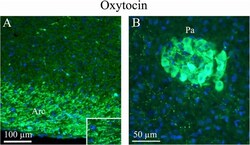
- Experimental details
- Fig. 3 Oxytocin immunohistochemistry of the paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus and the arcuate nucleus. a . The Arcuate nucleus (Arc), that project to the SO and paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus (Pa), show intense oxytocin expression. b . Pa, a nucleus of neurosecretory cells in the hypothalamus, exhibits intense oxytocin staining. As in the SO, pearl-like fibers expressing oxytocin also were found
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
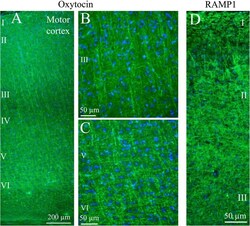
- Experimental details
- Fig. 4 Oxytocin immunohistochemistry of the cerebral cortex. a . Thin fibers of layers III-VI of the motor cortex displayed oxytocin immunoreactivity. b and c. These fibers spanned through the layers in a delicate and well-defined pattern. Layer III ( b ) and layers V-VI ( c ) are shown in a higher magnification. d . As a comparison, the calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor component (receptor activity-modifying protein 1) RAMP1 is shown in the right panel. These results have been published earlier [ 25 ]. We showed that RAMP1 positive fibers spanned through the cortical layers, but here layer II positivity was found. In addition to the transversal positive fibers, RAMP1 positive horizontal fibers were revealed
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
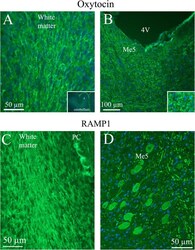
- Fig. 5 Oxytocin immunohistochemistry in the cerebellum and the Mesencephalic trigeminal nucleus. a . Oxytocin immunoreactivity was found in fibers in the cerebellar white matter and to some extend in the granular cell layer. No oxytocin positivity was observed in the Purkinje cell layer (PC) or the molecular layer. Insert: a low magnification image of cerebellar lobes. X indicates where the large magnification image is selected. b . In the Mesencephalic trigeminal nucleus (Me5), intense oxytocin immunoreactivity was found. In addition, surrounding the Me5 positive slender fibers were demonstrated. Insert: Higher magnification of Me5. c . The lower row shows in comparison RAMP1 immunoreactivity [ 25 ]. The staining of the white matter agrees with the one seen in the oxytocin staining. However, RAMP1 is also found in PC, which is not the case with oxytocin. d . RAMP1 staining showed distinct neuronal cytoplasmatic staining and, in addition, thick fiber immunoreactivity
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
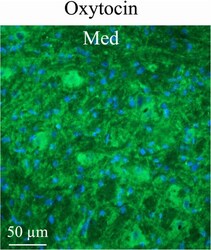
- Fig. 6 Oxytocin immunohistochemistry of the medial cerebellar nucleus (Med). Med contained large neurons intermixed with small neurons. Med exhibited intense oxytocin fiber staining, often so close to the cell nuclei that it appears like cell body staining
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
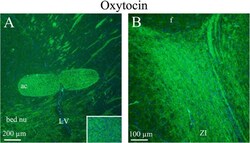
- Fig. 7 Oxytocin immunohistochemistry of the anterior commissure, bed nucleus and zona incerta. a . The white matter tract anterior commissure (ac) showed distinct fiber oxytocin immunoreactivity in fibers (Insert: higher magnification of ac). In addition, fibers in the bed nucleus also expressed oxytocin. b The zona incerta displayed intense oxytocin immunoreactivity in thin fibers
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
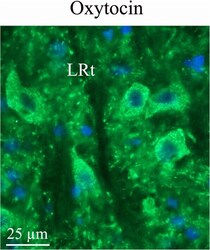
- Fig. 8 Oxytocin immunohistochemistry in the lateral reticular nucleus. In the reticular formation, a few bodies of the lateral reticular nucleus (LRt) were found to express oxytocin
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
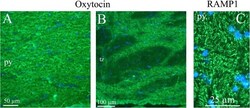
- Fig. 9 Oxytocin immunohistochemistry of the pyramidal tract and the trapetzoid body. a and b . Oxytocin immunoreactive thin fibers were observed in the pyramidal tract (py) and the trapetzoid body (tz). c . In comparison, we have previously found RAMP1 immunohistochemistry displayed a pattern with both positive thick and thin fibers [ 25 ] (left image)
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry Other assay
Other assay