Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [21]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunocytochemistry [3]
- Flow cytometry [3]
- Other assay [2]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- MA5-11961 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- NOTCH1 Monoclonal Antibody (A6)
- Antibody type
- Monoclonal
- Antigen
- Recombinant full-length protein
- Description
- MA5-11961 targets Notch-1 in WB, FACS and ICC/IF applications and shows reactivity with Human and mouse samples. The MA5-11961 immunogen is recombinant protein encoding the ligand binding region of human Notch-1.
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse
- Host
- Mouse
- Isotype
- IgG
- Antibody clone number
- A6
- Vial size
- 500 μL
- Concentration
- 0.2 mg/mL
- Storage
- 4°C
Submitted references Pannexin 3 regulates skin development via Epiprofin.
Ttyh1 regulates embryonic neural stem cell properties by enhancing the Notch signaling pathway.
Sphere-forming cells from peripheral cornea demonstrate the ability to repopulate the ocular surface.
Notch1 modulates mesenchymal stem cells mediated regulatory T-cell induction.
Distinct spatial and molecular features of notch pathway assembly in regulatory T cells.
Blockage of Notch1 signaling modulates the T-helper (Th)1/Th2 cell balance in chronic hepatitis B patients.
Candidate genes on chromosome 9q33-34 involved in the progression of childhood ependymomas.
Notch1 signaling and regulatory T cell function.
Changes in the expression of stem cell markers in oral lichen planus and hyperkeratotic lesions.
Changes in the expression of stem cell markers in oral lichen planus and hyperkeratotic lesions.
Antiparallel segregation of notch components in the immunological synapse directs reciprocal signaling in allogeneic Th:DC conjugates.
Sarcomatoid carcinomas of the lung--are these histogenetically heterogeneous tumors?
Evidence for a role for notch signaling in the cytokine-dependent survival of activated T cells.
Evidence for a role for notch signaling in the cytokine-dependent survival of activated T cells.
Pancreatic regeneration in chronic pancreatitis requires activation of the notch signaling pathway.
Expression of Notch-1 and its ligands, Delta-like-1 and Jagged-1, is critical for glioma cell survival and proliferation.
Distinct roles of EGF repeats for the Notch signaling system.
The Notch signaling pathway is related to neurovascular progression of pancreatic cancer.
The Notch signaling pathway is related to neurovascular progression of pancreatic cancer.
Isolation of precursor cells (PCs) from human dental follicle of wisdom teeth.
NB-3/Notch1 pathway via Deltex1 promotes neural progenitor cell differentiation into oligodendrocytes.
Zhang P, Ishikawa M, Doyle A, Nakamura T, He B, Yamada Y
Scientific reports 2021 Jan 19;11(1):1779
Scientific reports 2021 Jan 19;11(1):1779
Ttyh1 regulates embryonic neural stem cell properties by enhancing the Notch signaling pathway.
Kim J, Han D, Byun SH, Kwon M, Cho JY, Pleasure SJ, Yoon K
EMBO reports 2018 Nov;19(11)
EMBO reports 2018 Nov;19(11)
Sphere-forming cells from peripheral cornea demonstrate the ability to repopulate the ocular surface.
Mathan JJ, Ismail S, McGhee JJ, McGhee CN, Sherwin T
Stem cell research & therapy 2016 Jun 1;7(1):81
Stem cell research & therapy 2016 Jun 1;7(1):81
Notch1 modulates mesenchymal stem cells mediated regulatory T-cell induction.
Del Papa B, Sportoletti P, Cecchini D, Rosati E, Balucani C, Baldoni S, Fettucciari K, Marconi P, Martelli MF, Falzetti F, Di Ianni M
European journal of immunology 2013 Jan;43(1):182-7
European journal of immunology 2013 Jan;43(1):182-7
Distinct spatial and molecular features of notch pathway assembly in regulatory T cells.
Perumalsamy LR, Marcel N, Kulkarni S, Radtke F, Sarin A
Science signaling 2012 Jul 24;5(234):ra53
Science signaling 2012 Jul 24;5(234):ra53
Blockage of Notch1 signaling modulates the T-helper (Th)1/Th2 cell balance in chronic hepatitis B patients.
Pei J, Tang Z, Zang G, Yu Y
Hepatology research : the official journal of the Japan Society of Hepatology 2010 Aug;40(8):799-805
Hepatology research : the official journal of the Japan Society of Hepatology 2010 Aug;40(8):799-805
Candidate genes on chromosome 9q33-34 involved in the progression of childhood ependymomas.
Puget S, Grill J, Valent A, Bieche I, Dantas-Barbosa C, Kauffmann A, Dessen P, Lacroix L, Geoerger B, Job B, Dirven C, Varlet P, Peyre M, Dirks PB, Sainte-Rose C, Vassal G
Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 2009 Apr 10;27(11):1884-92
Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 2009 Apr 10;27(11):1884-92
Notch1 signaling and regulatory T cell function.
Asano N, Watanabe T, Kitani A, Fuss IJ, Strober W
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2008 Mar 1;180(5):2796-804
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2008 Mar 1;180(5):2796-804
Changes in the expression of stem cell markers in oral lichen planus and hyperkeratotic lesions.
Köse O, Lalli A, Kutulola AO, Odell EW, Waseem A
Journal of oral science 2007 Jun;49(2):133-9
Journal of oral science 2007 Jun;49(2):133-9
Changes in the expression of stem cell markers in oral lichen planus and hyperkeratotic lesions.
Köse O, Lalli A, Kutulola AO, Odell EW, Waseem A
Journal of oral science 2007 Jun;49(2):133-9
Journal of oral science 2007 Jun;49(2):133-9
Antiparallel segregation of notch components in the immunological synapse directs reciprocal signaling in allogeneic Th:DC conjugates.
Luty WH, Rodeberg D, Parness J, Vyas YM
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2007 Jul 15;179(2):819-29
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2007 Jul 15;179(2):819-29
Sarcomatoid carcinomas of the lung--are these histogenetically heterogeneous tumors?
Blaukovitsch M, Halbwedl I, Kothmaier H, Gogg-Kammerer M, Popper HH
Virchows Archiv : an international journal of pathology 2006 Oct;449(4):455-61
Virchows Archiv : an international journal of pathology 2006 Oct;449(4):455-61
Evidence for a role for notch signaling in the cytokine-dependent survival of activated T cells.
Bheeshmachar G, Purushotaman D, Sade H, Gunasekharan V, Rangarajan A, Sarin A
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2006 Oct 15;177(8):5041-50
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2006 Oct 15;177(8):5041-50
Evidence for a role for notch signaling in the cytokine-dependent survival of activated T cells.
Bheeshmachar G, Purushotaman D, Sade H, Gunasekharan V, Rangarajan A, Sarin A
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2006 Oct 15;177(8):5041-50
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2006 Oct 15;177(8):5041-50
Pancreatic regeneration in chronic pancreatitis requires activation of the notch signaling pathway.
Su Y, Büchler P, Gazdhar A, Giese N, Reber HA, Hines OJ, Giese T, Büchler MW, Friess H
Journal of gastrointestinal surgery : official journal of the Society for Surgery of the Alimentary Tract 2006 Nov;10(9):1230-41; discussion 1242
Journal of gastrointestinal surgery : official journal of the Society for Surgery of the Alimentary Tract 2006 Nov;10(9):1230-41; discussion 1242
Expression of Notch-1 and its ligands, Delta-like-1 and Jagged-1, is critical for glioma cell survival and proliferation.
Purow BW, Haque RM, Noel MW, Su Q, Burdick MJ, Lee J, Sundaresan T, Pastorino S, Park JK, Mikolaenko I, Maric D, Eberhart CG, Fine HA
Cancer research 2005 Mar 15;65(6):2353-63
Cancer research 2005 Mar 15;65(6):2353-63
Distinct roles of EGF repeats for the Notch signaling system.
Sakamoto K, Chao WS, Katsube K, Yamaguchi A
Experimental cell research 2005 Jan 15;302(2):281-91
Experimental cell research 2005 Jan 15;302(2):281-91
The Notch signaling pathway is related to neurovascular progression of pancreatic cancer.
Büchler P, Gazdhar A, Schubert M, Giese N, Reber HA, Hines OJ, Giese T, Ceyhan GO, Müller M, Büchler MW, Friess H
Annals of surgery 2005 Dec;242(6):791-800, discussion 800-1
Annals of surgery 2005 Dec;242(6):791-800, discussion 800-1
The Notch signaling pathway is related to neurovascular progression of pancreatic cancer.
Büchler P, Gazdhar A, Schubert M, Giese N, Reber HA, Hines OJ, Giese T, Ceyhan GO, Müller M, Büchler MW, Friess H
Annals of surgery 2005 Dec;242(6):791-800, discussion 800-1
Annals of surgery 2005 Dec;242(6):791-800, discussion 800-1
Isolation of precursor cells (PCs) from human dental follicle of wisdom teeth.
Morsczeck C, Götz W, Schierholz J, Zeilhofer F, Kühn U, Möhl C, Sippel C, Hoffmann KH
Matrix biology : journal of the International Society for Matrix Biology 2005 Apr;24(2):155-65
Matrix biology : journal of the International Society for Matrix Biology 2005 Apr;24(2):155-65
NB-3/Notch1 pathway via Deltex1 promotes neural progenitor cell differentiation into oligodendrocytes.
Cui XY, Hu QD, Tekaya M, Shimoda Y, Ang BT, Nie DY, Sun L, Hu WP, Karsak M, Duka T, Takeda Y, Ou LY, Dawe GS, Yu FG, Ahmed S, Jin LH, Schachner M, Watanabe K, Arsenijevic Y, Xiao ZC
The Journal of biological chemistry 2004 Jun 11;279(24):25858-65
The Journal of biological chemistry 2004 Jun 11;279(24):25858-65
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
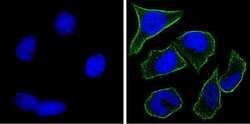
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of Notch-1 (green) showing staining in the membrane of HeLa cells. Formalin-fixed cells were permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 in TBS for 5-10 minutes and blocked with 3% BSA-PBS for 30 minutes at room temperature. Cells were probed with a Notch-1 monoclonal antibody (Product # MA5-11961) in 3% BSA-PBS at a dilution of 1:100 and incubated overnight at 4 ºC in a humidified chamber. Cells were washed with PBST and incubated with a DyLight-conjugated secondary antibody in PBS at room temperature in the dark. F-actin (red) was stained with a fluorescent red phalloidin and nuclei (blue) were stained with Hoechst or DAPI. Images were taken at a magnification of 100x.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
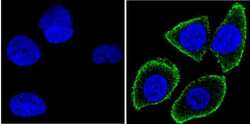
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of Notch-1 (green) showing staining in the membrane of MCF-7 cells. Formalin-fixed cells were permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 in TBS for 5-10 minutes and blocked with 3% BSA-PBS for 30 minutes at room temperature. Cells were probed with a Notch-1 monoclonal antibody (Product # MA5-11961) in 3% BSA-PBS at a dilution of 1:100 and incubated overnight at 4 ºC in a humidified chamber. Cells were washed with PBST and incubated with a DyLight-conjugated secondary antibody in PBS at room temperature in the dark. F-actin (red) was stained with a fluorescent red phalloidin and nuclei (blue) were stained with Hoechst or DAPI. Images were taken at a magnification of 100x.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
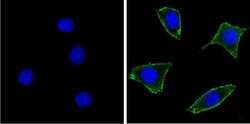
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of Notch-1 (green) showing staining in the membrane of NIH-3T3 cells. Formalin-fixed cells were permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 in TBS for 5-10 minutes and blocked with 3% BSA-PBS for 30 minutes at room temperature. Cells were probed with a Notch-1 monoclonal antibody (Product # MA5-11961) in 3% BSA-PBS at a dilution of 1:100 and incubated overnight at 4 ºC in a humidified chamber. Cells were washed with PBST and incubated with a DyLight-conjugated secondary antibody in PBS at room temperature in the dark. F-actin (red) was stained with a fluorescent red phalloidin and nuclei (blue) were stained with Hoechst or DAPI. Images were taken at a magnification of 100x.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
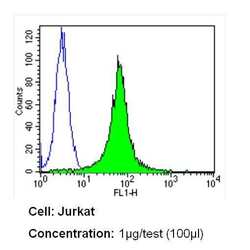
- Experimental details
- Flow cytometry analysis of Notch-1 in Jurkat cells (green) compared to an isotype control (blue). Cells were harvested, adjusted to a concentration of 1-5x10^6 cells/mL, fixed with 2% paraformaldehyde and washed with PBS. Cells were blocked with a 2% solution of BSA-PBS for 30 min at room temperature and incubated with a Notch-1 monoclonal antibody (Product # MA5-11961) at a dilution of 1 µg/test for 60 min at room temperature. Cells were then incubated for 40 min at room temperature in the dark using a Dylight 488-conjugated secondary antibody and re-suspended in PBS for FACS analysis.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
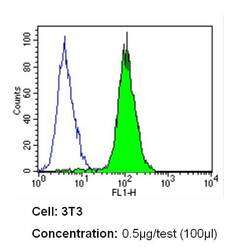
- Experimental details
- Flow cytometry analysis of Notch-1 in NIH-3T3 cells (green) compared to an isotype control (blue). Cells were harvested, adjusted to a concentration of 1-5x10^6 cells/mL, fixed with 2% paraformaldehyde and washed with PBS. Cells were blocked with a 2% solution of BSA-PBS for 30 min at room temperature and incubated with a Notch-1 monoclonal antibody (Product # MA5-11961) at a dilution of 0.5 µg/test for 60 min at room temperature. Cells were then incubated for 40 min at room temperature in the dark using a Dylight 488-conjugated secondary antibody and re-suspended in PBS for FACS analysis.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
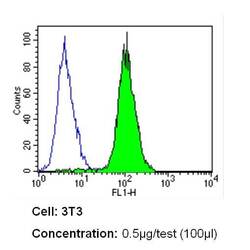
- Experimental details
- Flow cytometry analysis of Notch-1 in NIH-3T3 cells (green) compared to an isotype control (blue). Cells were harvested, adjusted to a concentration of 1-5x10^6 cells/mL, fixed with 2% paraformaldehyde and washed with PBS. Cells were blocked with a 2% solution of BSA-PBS for 30 min at room temperature and incubated with a Notch-1 monoclonal antibody (Product # MA5-11961) at a dilution of 0.5 µg/test for 60 min at room temperature. Cells were then incubated for 40 min at room temperature in the dark using a Dylight 488-conjugated secondary antibody and re-suspended in PBS for FACS analysis.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
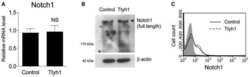
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
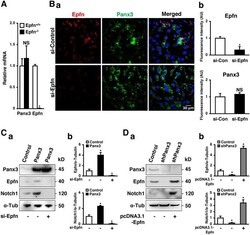
- Experimental details
- Figure 6 Epfn deficiency does not interfere with Panx3 expression. ( A ) qPCR for Panx3 and Epfn using total RNA prepared from skin of 6 weeks old Epfn +/+ and Epfn -/- mice. Results represent the mean +- SD; N = 3. * p < 0.01. NS, not significant. ( B ) Immunostaining of Panx3 (green) and Epfn (red) in si-Control or si-Epfn transfected HaCaT cells cultured in normal medium. The nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue in merged) ( a ). Relative fluorescence intensity comparison of images were analyzed ( b ). ( C ) Western blots of Epfn and Notch1 in Panx3 overexpressed HaCaT cells transfected with or without si-Epfn ( a ). Quantification of the ratios of Epfn/alpha-Tubulin (upper panel) and Notch1/alpha-Tubulin (lower panel). ( D ) Western blots of Epfn and Notch1 in shPanx3 transfected HaCaT cells with or without pcDNA3.1-Epfn ( a ). Quantification of the ratios of Epfn/alpha-Tubulin (upper panel) and Notch1/alpha-Tubulin (lower panel). * p < 0.01. NS, not significant.
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry